Sea urchin
| Sea urchin Temporal range: Ordovician–Present PreЄ Є O S D C P T J K Pg N | |
|---|---|
 | |
Tripneustes ventricosus and Echinometra viridis | |
Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Echinodermata |
| Subphylum: | Echinozoa |
| Class: | Echinoidea Leske, 1778 |
| Subclasses | |
| |
Sea urchins or urchins (/ˈɜːrtʃɪnz/) are typically spiny, globular animals, echinoderms in the class Echinoidea. About 950 species live on the seabed, inhabiting all oceans and depth zones from the intertidal to 5,000 metres (16,000 ft; 2,700 fathoms).[1] Their tests (hard shells) are round and spiny, typically from 3 to 10 cm (1 to 4 in) across. Sea urchins move slowly, crawling with their tube feet, and sometimes pushing themselves with their spines. They feed primarily on algae but also eat slow-moving or sessile animals. Their predators include sea otters, starfish, wolf eels, and triggerfish.
Like other echinoderms, urchins have fivefold symmetry as adults, but their pluteus larvae have bilateral (mirror) symmetry, indicating that they belong to the Bilateria, the large group of animal phyla that includes chordates, arthropods, annelids and molluscs. They are widely distributed across all the oceans, all climates from tropical to polar, and inhabit marine benthic (sea bed) habitats from rocky shores to hadal zone depths. Echinoids have a rich fossil record dating back to the Ordovician, some 450 million years ago. Their closest relatives among the echinoderms are the sea cucumbers (Holothuroidea); both are deuterostomes, a clade which includes the chordates.
The animals have been studied since the 19th century as model organisms in developmental biology, as their embryos were easy to observe; this has continued with studies of their genomes because of their unusual fivefold symmetry and relationship to chordates. Species such as the slate pencil urchin are popular in aquariums, where they are useful for controlling algae. Fossil urchins have been used as protective amulets.
Contents
1 Diversity
2 Description
3 Systems
3.1 Musculoskeletal
3.2 Feeding and digestion
3.3 Circulation and respiration
3.4 Nervous system and senses
4 Life history
4.1 Reproduction
4.2 Development
4.3 Life cycle and development
5 Ecology
5.1 Trophic level
5.2 Predators, parasites, and diseases
5.3 Anti-predator defences
5.4 Range and habitat
6 Evolution
6.1 Fossil history
6.2 Phylogeny
6.2.1 External
6.2.2 Internal
7 Relation to humans
7.1 Injuries
7.2 Science
7.3 As food
7.4 As tools
7.5 Aquaria
7.6 Folklore
8 Notes
9 References
10 External links
Diversity
Sea urchins are members of the phylum Echinodermata, which also includes sea stars, sea cucumbers, brittle stars, and crinoids. Like other echinoderms, they have five-fold symmetry (called pentamerism) and move by means of hundreds of tiny, transparent, adhesive "tube feet". The symmetry is not obvious in the living animal, but is easily visible in the dried test.[2]
Specifically, the term "sea urchin" refers to the "regular echinoids", which are symmetrical and globular, and includes several different taxonomic groups, with two subclasses : Euechinoidea ("modern" sea urchins, including irregular ones) and Cidaroidea or "slate-pencil urchins", which have very thick, blunt spines, with algae and sponges growing on them. The "irregular" sea urchins are an infra-class inside the Euechinoidea, called Irregularia, and include Atelostomata and Neognathostomata. Irregular echinoids include: flattened sand dollars, sea biscuits, and heart urchins.[3]
Together with sea cucumbers (Holothuroidea), they make up the subphylum Echinozoa, which is characterized by a globoid shape without arms or projecting rays. Sea cucumbers and the irregular echinoids have secondarily evolved diverse shapes. Although many sea cucumbers have branched tentacles surrounding their oral openings, these have originated from modified tube feet and are not homologous to the arms of the crinoids, sea stars, and brittle stars.[2]
Paracentrotus lividus, a regular sea urchin (Euechinoidea, infraclass Carinacea).

A sand dollar, an irregular sea urchin (Irregularia).

Phyllacanthus imperialis, a cidaroid sea urchin (Cidaroidea).
Description

Sea urchin anatomy based on Arbacia sp.
Urchins typically range in size from 3 to 10 cm (1 to 4 in), although the largest species can reach up to 36 cm (14 in).[4] They have a rigid, usually spherical body bearing moveable spines, which gives the class the name Echinoidea (from the Greek ekhinos, spine).[5] The name "urchin" is an old word for hedgehog, which sea urchins resemble; they have archaically been called sea hedgehogs.[6][7] The name is derived from Old French herichun, from Latin ericius, hedgehog.[8]
Like other echinoderms, sea urchin early larvae have bilateral symmetry,[9] but they develop five-fold symmetry as they mature. This is most apparent in the "regular" sea urchins, which have roughly spherical bodies with five equally sized parts radiating out from their central axes. The mouth is at the base of the animal and the anus at the top; the lower surface is described as "oral" and the upper surface as "aboral".[a][2]
Several sea urchins, however, including the sand dollars, are oval in shape, with distinct front and rear ends, giving them a degree of bilateral symmetry. In these urchins, the upper surface of the body is slightly domed, but the underside is flat, while the sides are devoid of tube feet. This "irregular" body form has evolved to allow the animals to burrow through sand or other soft materials.[4]
Systems
Musculoskeletal

Tube feet of a purple sea urchin
Sea urchins may appear to be incapable of moving but this is a false impression. Sometimes the most visible sign of life is the spines, which are attached to ball-and-socket joints and can point in any direction; in most urchins, touch elicits a prompt reaction from the spines, which converge toward the touched point. Sea urchins have no visible eyes, legs, or means of propulsion, but can move freely but slowly over hard surfaces using adhesive tube feet, working in conjunction with the spines.[2]
The internal organs are enclosed in a hard shell or test composed of fused plates of calcium carbonate covered by a thin dermis and epidermis. The test is rigid, and divides into five ambulacral grooves separated by five interambulacral areas. Each of these areas consists of two rows of plates, so the sea urchin test includes 20 rows of plates in total. The plates are covered in rounded tubercles which contain the sockets to which the spines are attached by ball and socket joints. The inner surface of the test is lined by peritoneum.[4] Sea urchins convert aqueous carbon dioxide using a catalytic process involving nickel into the calcium carbonate portion of the test.[10]
Most species have two series of spines, primary (long) and secondary (short), distributed over the surface of the body, with the shortest at the poles and the longest at the equator. The spines are usually hollow and cylindrical. Contraction of the muscular sheath that covers the test causes the spines to lean in one direction or another, while an inner sheath of collagen fibres can reversibly change from soft to rigid which can lock the spine in one position. Located among the spines are several types of pedicellaria, moveable stalked structures with jaws.[2]
Sea urchins move by walking using their many flexible tube feet in a similar way to starfish; regular sea urchins do not have any favourite walking direction.[11] The tube feet protrude through pairs of pores in the test, and are operated by a water vascular system; this works through hydraulic pressure, allowing the sea urchin to pump water into and out of the tube feet. During locomotion, the tube feet are assisted by the spines which can be used for pushing the body along or to lift the test off the substrate. Movement is generally related to feeding, with the red sea urchin (Mesocentrotus franciscanus) managing about 7.5 cm (3 in) a day when there is ample food, and up to 50 cm (20 in) a day where there is not. An inverted sea urchin can right itself by progressively attaching and detaching its tube feet and manipulating its spines to roll its body upright.[2] Some species bury themselves in soft sediment using their spines, and Paracentrotus lividus uses its jaws to burrow into soft rocks.[12]

Test of an Echinus esculentus, a regular sea urchin

Test of an Echinodiscus tenuissimus, an irregular sea urchin ("sand dollar")
Test of a Phyllacanthus imperialis, a cidaroid sea urchin. These are characterised by their big tubercles, bearing large radiola

Close-up of the test showing an ambulacral groove with its two rows of pore-pairs, between two interambulacra areas (green). The tubercles are non-perforated.
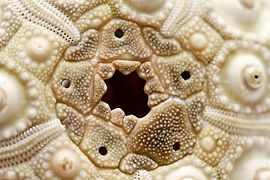
Close-up on a cidaroid sea urchin apical disc : the 5 holes are the gonopores, and the central one is the anus ("periproct"). The biggest genital plate is the madreporite.
Feeding and digestion
The mouth lies in the centre of the oral surface in regular urchins, or towards one end in irregular urchins. It is surrounded by lips of softer tissue, with numerous small, embedded bony pieces. This area, called the peristome, also includes five pairs of modified tube feet and, in many species, five pairs of gills.[4] The jaw apparatus consists of five strong arrow-shaped plates known as pyramids, the ventral surface of each of which has a toothband with a hard tooth pointing towards the centre of the mouth. Specialised muscles control the protrusion of the apparatus and the action of the teeth, and the animal can grasp, scrape, pull and tear.[2] The structure of the mouth and teeth have been found to be so efficient at grasping and grinding that similar structures have been tested for use in real-world applications.[13]
On the upper surface of the test at the aboral pole is a membrane, the periproct, which surrounds the anus. The periproct contains a variable number of hard plates, five of which, the genital plates, contain the gonopores, and one is modified to contain the madreporite, which is used to balance the water vascular system.[2]

Aristotle's lantern in a sea urchin, viewed in lateral section
The mouth of most sea urchins is made up of five calcium carbonate teeth or plates, with a fleshy, tongue-like structure within. The entire chewing organ is known as Aristotle's lantern from Aristotle's description in his History of Animals.
- ...the urchin has what we mainly call its head and mouth down below, and a place for the issue of the residuum up above. The urchin has, also, five hollow teeth inside, and in the middle of these teeth a fleshy substance serving the office of a tongue. Next to this comes the esophagus, and then the stomach, divided into five parts, and filled with excretion, all the five parts uniting at the anal vent, where the shell is perforated for an outlet... In reality the mouth-apparatus of the urchin is continuous from one end to the other, but to outward appearance it is not so, but looks like a horn lantern with the panes of horn left out. (Tr. D'Arcy Thompson)
However, this has recently been proven to be a mistranslation. Aristotle's lantern is actually referring to the whole shape of sea urchins, which look like the ancient lamps of Aristotle's time.[14][15]
Heart urchins are unusual in not having a lantern. Instead, the mouth is surrounded by cilia that pull strings of mucus containing food particles towards a series of grooves around the mouth.[4]

Digestive and circulatory systems of a regular sea urchin:
a = anus ; m = madreporite ; s = aquifer canal ; r = radial canal ; p = podial ampulla ; k = test wall ; i = intestine ; b = mouth
The lantern, where present, surrounds both the mouth cavity and the pharynx. At the top of the lantern, the pharynx opens into the esophagus, which runs back down the outside of the lantern, to join the small intestine and a single caecum. The small intestine runs in a full circle around the inside of the test, before joining the large intestine, which completes another circuit in the opposite direction. From the large intestine, a rectum ascends towards the anus. Despite the names, the small and large intestines of sea urchins are in no way homologous to the similarly named structures in vertebrates.[4]
Digestion occurs in the intestine, with the caecum producing further digestive enzymes. An additional tube, called the siphon, runs beside much of the intestine, opening into it at both ends. It may be involved in resorption of water from food.[4]
Circulation and respiration
The water vascular system leads downwards from the madreporite through the slender stone canal to the ring canal, which encircles the oesophagus. Radial canals lead from here through each ambulacral area to terminate in a small tentacle which passes through the ambulacral plate near the aboral pole. Lateral canals lead from these radial canals, ending in ampullae. From here, two tubes pass through a pair of pores on the plate to terminate in the tube feet.[2]
Sea urchins possess a hemal system with a complex network of vessels in the mesenteries around the gut, but little is known of the functioning of this system.[2] However, the main circulatory fluid fills the general body cavity, or coelom. This coelomic fluid contains phagocytic coelomocytes, which move through the vascular and hemal systems and are involved in internal transport and gas exchange. The coelomocytes are an essential part of blood clotting, but also collect waste products and actively remove them from the body through the gills and tube feet.[4]
Most sea urchins possess five pairs of external gills attached to the peristomial membrane around their mouths. These thin-walled projections of the body cavity are the main organs of respiration in those urchins that possess them. Fluid can be pumped through the gills' interiors by muscles associated with the lantern, but this does not provide a continuous flow, and occurs only when the animal is low in oxygen. Tube feet can also act as respiratory organs, and are the primary sites of gas exchange in heart urchins and sand dollars, both of which lack gills. The inside of each tube foot is divided by a septum which reduces diffusion between the incoming and outgoing streams of fluid.[2]

Diadema setosum
Nervous system and senses
The nervous system of sea urchins has a relatively simple layout. With no true brain, the neural center is a large nerve ring encircling the mouth just inside the lantern. From the nerve ring, five nerves radiate underneath the radial canals of the water vascular system, and branch into numerous finer nerves to innervate the tube feet, spines, and pedicellariae.[4]
Sea urchins are sensitive to touch, light, and chemicals. There are numerous sensitive cells in the epithelium, especially in the spines, pedicellaria and tube feet, and around the mouth.[2] Although they do not have eyes or eye spots (except for diadematids, which can follow a threat with their spines), the entire body of most regular sea urchins might function as a compound eye.[16] In general, sea urchins are negatively attracted to light, and seek to hide themselves in crevices or under objects. Most species, apart from pencil urchins, have statocysts in globular organs called spheridia. These are stalked structures and are located within the ambulacral areas; their function is to help in gravitational orientation.[4]
Life history
Reproduction
 Play media
Play mediaMale flower urchin (Toxopneustes roseus) releasing milt, November 1, 2011, Lalo Cove, Sea of Cortez
Sea urchins are dioecious, having separate male and female sexes, although no distinguishing features are visible externally. Regular sea urchins have five gonads, lying underneath the interambulacral regions of the test, while the irregular forms mostly have four, with the hindmost gonad being absent; heart urchins have three or two. Each gonad has a single duct rising from the upper pole to open at a gonopore lying in one of the genital plates surrounding the anus. Some burrowing sand dollars have an elongated papilla that enables the liberation of gametes above the surface of the sediment.[2] The gonads are lined with muscles underneath the peritoneum, and these allow the animal to squeeze its gametes through the duct and into the surrounding sea water, where fertilization takes place.[4]
Development

Sea urchin blastula
During early development, the sea urchin embryo undergoes 10 cycles of cell division,[17] resulting in a single epithelial layer enveloping the blastocoel. The embryo then begins gastrulation, a multipart process which dramatically rearranges its structure by invagination to produce the three germ layers, involving an epithelial-mesenchymal transition; primary mesenchyme cells move into the blastocoel[18] and become mesoderm.[19]

The development of a regular sea urchin
An unusual feature of sea urchin development is the replacement of the larva's bilateral symmetry by the adult's broadly fivefold symmetry. During cleavage, mesoderm and small micromeres are specified. At the end of gastrulation, cells of these two types form coelomic pouches. In the larval stages, the adult rudiment grows from the left coelomic pouch; after metamorphosis, that rudiment grows to become the adult. The animal-vegetal axis is established before the egg is fertilized. The oral-aboral axis is specified early in cleavage, and the left-right axis appears at the late gastrula stage.[20]
Life cycle and development

Pluteus larva has bilateral symmetry.
In most cases, the female's eggs float freely in the sea, but some species hold onto them with their spines, affording them a greater degree of protection. The unfertilized egg meets with the free-floating sperm released by males, and develops into a free-swimming blastula embryo in as few as 12 hours. Initially a simple ball of cells, the blastula soon transforms into a cone-shaped echinopluteus larva. In most species, this larva has 12 elongated arms lined with bands of cilia that capture food particles and transport them to the mouth. In a few species, the blastula contains supplies of nutrient yolk and lacks arms, since it has no need to feed.[4]
Several months are needed for the larva to complete its development, the change into the adult form beginning with the formation of test plates in a juvenile rudiment which develops on the left side of the larva, its axis being perpendicular to that of the larva. Soon, the larva sinks to the bottom and metamorphoses into a juvenile urchin in as little as one hour.[2] In some species, adults reach their maximum size in about five years.[4] The purple urchin becomes sexually mature in two years and may live for twenty.[21]
Ecology
Trophic level
 Play media
Play mediaLiving sea urchin in natural habitat video
Sea urchins feed mainly on algae, so they are primarily herbivores, but can feed on sea cucumbers and a wide range of invertebrates, such as mussels, polychaetes, sponges, brittle stars, and crinoids, making them omnivores, consumers at a range of trophic levels.[22]
Predators, parasites, and diseases
Mass mortality of sea urchins was first reported in the 1970s, but diseases in sea urchins had been little studied before the advent of aquaculture. In 1981, bacterial "spotting disease" caused almost complete mortality in juvenile Pseudocentrotus depressus and Hemicentrotus pulcherrimus, both cultivated in Japan; the disease recurred in succeeding years. It was divided into a cool-water "spring" disease and a hot-water "summer" form.[23] Another condition, bald sea urchin disease, causes loss of spines and skin lesions and is believed to be bacterial in origin.[24]
Adult sea urchins are usually well protected against most predators by their strong and sharp spines, which can be venomous in some species.[25] The small urchin clingfish lives among the spines of urchins such as Diadema; juveniles feed on the pedicellariae and sphaeridia, adult males choose the tube feet and adult females move away to feed on shrimp eggs and molluscs.[26]
Sea urchins are one of the favourite foods of many lobsters, crabs, triggerfish, California sheephead, sea otter and wolf eels (which specialise in sea urchins). All these animals carry particular adaptations (teeth, pincers, claws) and a strength that allow them to overcome the excellent protective features of sea urchins. Left unchecked by predators, urchins devastate their environments, creating what biologists call an urchin barren, devoid of macroalgae and associated fauna.[27] Sea otters have re-entered British Columbia, dramatically improving coastal ecosystem health.[28]

Wolf eel, a highly specialized predator of sea urchins

A sea otter feeding on a purple sea urchin.

A crab (Carpilius convexus) attacking a slate pencil sea urchin (Heterocentrotus mamillatus)

A wrasse finishing the remains of a damaged Tripneustes gratilla
Anti-predator defences

The flower urchin is a dangerous, potentially lethally venomous species.
The spines, long and sharp in some species, protect the urchin from predators. Some tropical sea urchins like Diadematidae, Echinothuriidae and Toxopneustidae have venomous spines. Other creatures also make use of these defences; crabs, shrimps and other organisms shelter among the spines, and often adopt the colouring of their host. Some crabs in the Dorippidae family carry sea urchins, starfish, sharp shells or other protective objects in their claws.[29]
Pedicellaria[30] are a good means of defense against ectoparasites, but not a panacea as some of them actually feed on it.[31] The hemal system defends against endoparasites.[32]
Range and habitat
Sea urchins are established in most seabed habitats from the intertidal downwards, at an extremely wide range of depths.[33] Some species, such as Cidaris abyssicola, can live at depths of several thousands metres. Many genera are only found in the abyssal zone, including many cidaroids, most of the genera in the Echinothuriidae family, and the "cactus urchins" Dermechinus. One of the deepest-living families is the Pourtalesiidae,[34] strange bottle-shaped irregular sea urchins that live only in the hadal zone and have been collected as deep as 6850 metres beneath the surface in the Sunda Trench.[35] Nevertheless, this makes sea urchin the class of echinoderms living the least deep, compared to brittle stars, starfish and crinoids that remain abundant below 8,000 m (26,250 ft) and sea cucumbers which have been recorded from 10,687 m (35,100 ft).[35]
Population densities vary by habitat, with more dense populations in barren areas as compared to kelp stands.[36][37] Even in these barren areas, greatest densities are found in shallow water. Populations are generally found in deeper water if wave action is present.[37] Densities decrease in winter when storms cause them to seek protection in cracks and around larger underwater structures.[37]
The shingle urchin (Colobocentrotus atratus), which lives on exposed shorelines, is particularly resistant to wave action. It is one of the few sea urchin that can survive many hours out of water.[38]
Sea urchins can be found in all climates, from warm seas to polar oceans.[33] The larvae of the polar sea urchin Sterechinus neumayeri have been found to use energy in metabolic processes twenty-five times more efficiently than do most other organisms.[39] Despite their presence in nearly all the marine ecosystems, most species are found on temperate and tropical coasts, between the surface and some tens of meters deep, close to photosynthetic food sources.[33]

Purple sea urchins at low tide in California. They dig a cavity in the rock to hide from predators during the day.

Dermechinus horridus, an abyssal species, at thousands of meters deep

Antarctic sea urchin (Sterechinus neumayeri) inhabits frozen seas.

The shape of the shingle urchin allows it to stay on wave-beaten cliffs.
Evolution
Fossil history

The thick spines (radiola) of Cidaridae were used for walking on the soft seabed.
The earliest echinoid fossils date to the upper part of the Ordovician period (circa 450 Mya).[40] There is a rich fossil record, their hard tests made of calcite plates surviving in rocks from every period since then.[41]
Spines are present in some well-preserved specimens, but usually only the test remains. Isolated spines are common as fossils. Some Jurassic and Cretaceous Cidaroida had very heavy, club-shaped spines.[42]
Most fossil echinoids from the Paleozoic era are incomplete, consisting of isolated spines and small clusters of scattered plates from crushed individuals, mostly in Devonian and Carboniferous rocks. The shallow-water limestones from the Ordovician and Silurian periods of Estonia are famous for echinoids.[43] Paleozoic echinoids probably inhabited relatively quiet waters. Because of their thin tests, they would certainly not have survived in the wave-battered coastal waters inhabited by many modern echinoids.[43] Echinoids declined to near extinction at the end of the Paleozoic era, with just six species known from the Permian period. Only two lineages survived this period's massive extinction and into the Triassic: the genus Miocidaris, which gave rise to modern cidaroida (pencil urchins), and the ancestor that gave rise to the euechinoids. By the upper Triassic, their numbers increased again. Cidaroids have changed very little since the Late Triassic, and are the only Paleozoic echinoid group to have survived.[43]
The euechinoids diversified into new lineages in the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods, and from them emerged the first irregular echinoids (the Atelostomata) during the early Jurassic.[44]
Some echinoids, such as Micraster in the chalk of the Cretaceous period, serve as zone or index fossils. Because they are abundant and evolved rapidly, they enable geologists to date the surrounding rocks.[45]
In the Paleogene and Neogene periods (circa 66 to 1.8 Mya), sand dollars (Clypeasteroida) arose. Their distinctive, flattened tests and tiny spines were adapted to life on or under loose sand in shallow water, and they are abundant as fossils in southern European limestones and sandstones.[43]

Archaeocidaris brownwoodensis, Cidaroida, Carboniferous, c. 300 mya

Miocidaris coaeva, Cidaroida, Middle Triassic, c. 240 mya
Clypeus plotti, Irregularia, Middle Jurassic, c. 162 mya

Echinocorys, Holasteroida, Upper Cretaceous, c. 80 mya
Echinolampas ovalis, Cassiduloida, Middle Eocene, c. 40 mya

Clypeaster portentosus, Clypeasteroida, Miocene, c. 10 mya
Phylogeny
External
Echinoids are deuterostome animals, like the chordates. A 2014 analysis of 219 genes from all classes of echinoderms gives the following phylogenetic tree.[46] Approximate dates of branching of major clades are shown in millions of years ago (mya).
.mw-parser-output table.cladeborder-spacing:0;margin:0;font-size:100%;line-height:100%;border-collapse:separate;width:auto.mw-parser-output table.clade table.cladewidth:100%.mw-parser-output table.clade tdborder:0;padding:0;vertical-align:middle;text-align:center.mw-parser-output table.clade td.clade-labelwidth:0.8em;border:0;padding:0 0.2em;vertical-align:bottom;text-align:center.mw-parser-output table.clade td.clade-slabelborder:0;padding:0 0.2em;vertical-align:top;text-align:center.mw-parser-output table.clade td.clade-barvertical-align:middle;text-align:left;padding:0 0.5em.mw-parser-output table.clade td.clade-leafborder:0;padding:0;text-align:left;vertical-align:middle.mw-parser-output table.clade td.clade-leafRborder:0;padding:0;text-align:right
Bilateria |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |
Internal
The phylogeny of the sea urchins is as follows:[47][48]
Echinoidea |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 450 mya |
Relation to humans
Injuries

Sea urchin injury on the top side of the foot. This injury resulted in some skin staining from the natural purple-black dye of the urchin.
Sea urchin injuries are puncture wounds inflicted by the animal's brittle, fragile spines.[49]
These are a common source of injury to ocean swimmers, especially along coastal surfaces where coral with stationary sea urchins are present. Their stings vary in severity depending on the species. Their spines can be venomous or cause infection. Granuloma and staining of the skin from the natural dye inside the sea urchin can also occur. Breathing problems may indicate a serious reaction to toxins in the sea urchin.[50] They inflict a painful wound when they penetrate human skin, but are not themselves dangerous if fully removed promptly; if left in the skin, further problems may occur.[51]
Science
Sea urchins are traditional model organisms in developmental biology. This use originated in the 1800s, when their embryonic development became easily viewed by microscopy. The transparency of the urchin's eggs enabled them to be used to observe that sperm cells actually fertilize ova.[52] They continue to be used for embryonic studies, as prenatal development continues to seek testing for fatal diseases. Sea urchins are being used in longevity studies for comparison between the young and old of the species, particularly for their ability to regenerate tissue as needed.[53] Scientists at the University of St Andrews have discovered a genetic sequence, the '2A' region, in sea urchins previously thought to have belonged only to viruses that afflict humans like foot-and-mouth disease virus.[54]
More recently, Eric H. Davidson and Roy John Britten argued for the use of urchins as a model organism due to their easy availability, high fecundity, and long lifespan. Beyond embryology, urchins provide an opportunity to research cis-regulatory elements.[55]
Oceanography has taken in interest in monitoring the health of urchins and their populations as a way to assess overall ocean acidification,[56] temperatures, and ecological impacts.
The organism's evolutionary placement and unique embryology with five-fold symmetry were the major arguments in the proposal to seek the sequencing of its genome. Importantly, urchins act as the closest living relative to chordates and thus are of interest for the light they can shed on the evolution of vertebrates.[57] The genome of Strongylocentrotus purpuratus, was completed in 2006 and established homology between sea urchin and vertebrate immune system-related genes. Sea urchins code for at least 222 Toll-like receptor genes and over 200 genes related to the Nod-like-receptor family found in vertebrates.[58] This increases its usefulness as a valuable model organism for studying the evolution of innate immunity. The sequencing also revealed that while some genes were thought to be limited to vertebrates, there were also innovations that have previously never been seen outside the chordate classification, such as immune transcription factors PU.1 and SPIB.[57]
As food
The gonads of both male and female sea urchins, usually called sea urchin roe or corals,[59] are culinary delicacies in many parts of the world.[60][61][62]
In Mediterranean cuisines, Paracentrotus lividus is often eaten raw, or with lemon,[63] and known as ricci on Italian menus where it is sometimes used in pasta sauces. It can also flavour omelettes, scrambled eggs, fish soup,[64]mayonnaise, béchamel sauce for tartlets,[65] the boullie for a soufflé,[66] or Hollandaise sauce to make a fish sauce.[67] In Chilean cuisine, it is served raw with lemon, onions, and olive oil.
Though the edible Strongylocentrotus droebachiensis is found in the North Atlantic, it is not widely eaten. However, sea urchins (called uutuk in Alutiiq) are commonly eaten by the Alaska Native population around Kodiak Island. It is commonly exported, mostly to Japan.[68]
In the West Indies, slate pencil urchins are eaten.[60]
On the Pacific Coast of North America, Strongylocentrotus franciscanus was praised by Euell Gibbons; Strongylocentrotus purpuratus is also eaten.[60]
In New Zealand, Evechinus chloroticus, known as kina in Maori, is a delicacy, traditionally eaten raw. Though New Zealand fishermen would like to export them to Japan, their quality is too variable.[69]
In Japan, sea urchin is known as uni (うに), and its roe can retail for as much as ¥40000 ($360) per kg;[70] it is served raw as sashimi or in sushi, with soy sauce and wasabi. Japan imports large quantities from the United States, South Korea, and other producers. Japan consumes 50,000 tons annually amounting to over 80% of global production.[71] Japanese demand for sea urchins has raised concerns about overfishing.[72]Native Americans in California are also known to eat sea urchins.[73] The coast of Southern California is known as a source of high quality uni, with divers picking sea urchin from kelp beds in depths as deep as 24 m/80ft.[74] As of 2013, the state was limiting the practice to 300 sea urchin diver licenses.[74]

Sea urchin (uni) as sashimi with a dab of wasabi

Japanese uni-ikura don, sea urchin egg and salmon egg donburi

Open sea urchins in Sicily
As tools
In the Pacific, bunches of heavy spines from slate-pencil urchins (Heterocentrotus species) were used as abrasion tools for shipbuilding.[75]
Aquaria

A fossil sea urchin found on a Middle Saxon site in Lincolnshire, thought to have been used as an amulet[76]
Some species of sea urchins, such as the slate pencil urchin (Eucidaris tribuloides), are commonly sold in aquarium stores. Some species are effective at controlling filamentous algae, and they make good additions to an invertebrate tank.[77]
Folklore
A folk tradition in Denmark and southern England imagined sea urchin fossils to be thunderbolts, able to ward off harm by lightning or by witchcraft, as an apotropaic symbol.[78] Another version supposed they were petrified eggs of snakes, able to protect against heart and liver disease, poisons, and injury in battle, and accordingly they were carried as amulets. These were, according to the legend, created by magic from foam made by the snakes at midsummer.[79]
Notes
^ The tube feet are present in all parts of the animal except around the anus, so technically, the whole surface of the body should be considered to be the oral surface, with the aboral (non-mouth) surface limited to the immediate vicinity of the anus.[2]
References
^ "Animal Diversity Web – Echinoidea". University of Michigan Museum of Zoology. Retrieved 26 August 2012..mw-parser-output cite.citationfont-style:inherit.mw-parser-output .citation qquotes:"""""""'""'".mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registrationcolor:#555.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration spanborder-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output code.cs1-codecolor:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-errordisplay:none;font-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-errorfont-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-maintdisplay:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-formatfont-size:95%.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-leftpadding-left:0.2em.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-rightpadding-right:0.2em
^ abcdefghijklmno Ruppert, Edward E.; Fox, Richard, S.; Barnes, Robert D. (2004). Invertebrate Zoology, 7th edition. Cengage Learning. pp. 896–906. ISBN 978-81-315-0104-7.
^ Kroh, A.; Hansson, H. (2013). "Echinoidea (Leske, 1778)". World Register of Marine Species. Retrieved 2014-01-04.CS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list (link)
^ abcdefghijklm Barnes, Robert D. (1982). Invertebrate Zoology. Philadelphia, PA: Holt-Saunders International. pp. 961–981. ISBN 0-03-056747-5.
^ Guill, Michael. "Taxonomic Etymologies EEOB 111". Retrieved 13 March 2018.
^ Wright, Anne. 1851. The Observing Eye, Or, Letters to Children on the Three Lowest Divisions of Animal Life. London: Jarrold and Sons, p. 107.
^ Soyer, Alexis. 1853. The Pantropheon Or History of Food, And Its Preparation: From The Earliest Ages Of The World. Boston: Ticknor, Reed, and Fields,, p. 245.
^ "urchin (n.)". Online Etymology Dictionary. Retrieved 13 March 2018.
^ Stachan and Read, Human Molecular Genetics, p. 381: "What Makes Us Human"
^ "Sea urchins reveal promising carbon capture alternative". Gizmag. 4 February 2013. Retrieved 2013-02-05.
^ Kazuya Yoshimura, Tomoaki Iketani et Tatsuo Motokawa, "Do regular sea urchins show preference in which part of the body they orient forward in their walk ?", Marine Biology, vol. 159, no 5, 2012, p. 959–965.
^ Boudouresque, Charles F.; Verlaque, Marc (2006). "13: Ecology of Paracentrotus lividus". In Lawrence, John, M. Edible Sea Urchins: Biology and Ecology. Elsevier. p. 243. ISBN 978-0-08-046558-6.
^ Claw inspired by sea urchins' mouth can scoop up Martian soil
^ Voultsiadou, Eleni; Chintiroglou, Chariton (2008). "Aristotle's lantern in echinoderms: an ancient riddle". Cahiers de Biologie Marine. Station Biologique de Roscoff. 49 (3): 299–302.
^ Choi, Charles Q. (29 December 2010). "Rock-Chewing Sea Urchins Have Self-Sharpening Teeth". National Geographic News. Retrieved 2017-11-12.
^ Knight, K. (2009). "Sea Urchins Use Whole Body As Eye". Journal of Experimental Biology. 213 (2): i. doi:10.1242/jeb.041715. Lay summary – LiveScience (December 28, 2009).
^ A. Gaion, A. Scuderi; D. Pellegrini; D. Sartori (2013). "Arsenic Exposure Affects Embryo Development of Sea Urchin, Paracentrotus lividus (Lamarck, 1816)". Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology: 1–5. doi:10.3109/01480545.2015.1041602.
^ Kominami, Tetsuya; Takata, Hiromi (2004). "Gastrulation in the sea urchin embryo: a model system for analyzing the morphogenesis of a monolayered epithelium". Development, Growth & Differentiation. 46 (4): 309–26. doi:10.1111/j.1440-169x.2004.00755.x.
^ Shook, D; Keller, R (2003). "Mechanisms, mechanics and function of epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in early development". Mechanisms of Development. 120 (11): 1351–83. doi:10.1016/j.mod.2003.06.005. PMID 14623443.; Katow, Hideki; Solursh, Michael (1980). "Ultrastructure of primary mesenchyme cell ingression in the sea urchinLytechinus pictus". Journal of Experimental Zoology. 213 (2): 231–246. doi:10.1002/jez.1402130211.; Balinsky, BI (1959). "An electro microscopic investigation of the mechanisms of adhesion of the cells in a sea urchin blastula and gastrula". Experimental Cell Research. 16 (2): 429–33. doi:10.1016/0014-4827(59)90275-7. PMID 13653007.; Hertzler, PL; McClay, DR (1999). "alphaSU2, an epithelial integrin that binds laminin in the sea urchin embryo". Developmental Biology. 207 (1): 1–13. doi:10.1006/dbio.1998.9165. PMID 10049560.; Fink, RD; McClay, DR (1985). "Three cell recognition changes accompany the ingression of sea urchin primary mesenchyme cells". Developmental Biology. 107 (1): 66–74. doi:10.1016/0012-1606(85)90376-8. PMID 2578117.; Burdsal, CA; Alliegro, MC; McClay, DR (1991). "Tissue-specific, temporal changes in cell adhesion to echinonectin in the sea urchin embryo". Developmental Biology. 144 (2): 327–34. doi:10.1016/0012-1606(91)90425-3. PMID 1707016.; Miller, JR; McClay, DR (1997). "Characterization of the Role of Cadherin in Regulating Cell Adhesion during Sea Urchin Development". Developmental Biology. 192 (2): 323–39. doi:10.1006/dbio.1997.8740. PMID 9441671.; Miller, JR; McClay, DR (1997). "Changes in the pattern of adherens junction-associated beta-catenin accompany morphogenesis in the sea urchin embryo". Developmental Biology. 192 (2): 310–22. doi:10.1006/dbio.1997.8739. PMID 9441670.; Anstrom, JA (1989). "Sea urchin primary mesenchyme cells: ingression occurs independent of microtubules". Developmental Biology. 131 (1): 269–75. doi:10.1016/S0012-1606(89)80058-2. PMID 2562830.; Anstrom, JA (1992). "Microfilaments, cell shape changes, and the formation of primary mesenchyme in sea urchin embryos". The Journal of Experimental Zoology. 264 (3): 312–22. doi:10.1002/jez.1402640310. PMID 1358997.
^ Warner, Jacob F.; Lyons, Deirdre C.; McClay, David R. (2012). "Left-Right Asymmetry in the Sea Urchin Embryo: BMP and the Asymmetrical Origins of the Adult". PLoS Biology. 10 (10): e1001404. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1001404. PMC 3467244.
^ Worley, Alisa (2001). "Strongylocentrotus purpuratus". Animal Diversity Web. Retrieved 2016-12-05.
^ Baumiller, Tomasz K. (2008). "Crinoid Ecological Morphology". Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences. 36: 221–49. Bibcode:2008AREPS..36..221B. doi:10.1146/annurev.earth.36.031207.124116.
^ Lawrence, John M. (2006). Edible Sea Urchins: Biology and Ecology. Elsevier. pp. 167–168. ISBN 978-0-08-046558-6.
^ Jangoux, Michel (1987). "Diseases of Echinodermata. I. Agents microorganisms and protistans" (PDF). Diseases of Aquatic Organisms. 2: 147–162. doi:10.3354/dao002147.
^ "Defence – spines". Echinoid Directory. Natural History Museum.
^ Sakashita, Hiroko (1992). "Sexual dimorphism and food habits of the clingfish, Diademichthys lineatus, and its dependence on host sea urchin". Environmental Biology of Fishes. 34 (1): 95–101. doi:10.1007/BF00004787.
^ Terborgh, John; Estes, James A (2013). Trophic Cascades: Predators, Prey, and the Changing Dynamics of Nature. Island Press. pp. 38–38. ISBN 978-1-59726-819-6.
^ "Aquatic Species at Risk – Species Profile – Sea Otter". Fisheries and Oceans Canada. Archived from the original on 2008-01-23. Retrieved 2007-11-29.
^ Thiel, Martin; Watling, Les (2015). Lifestyles and Feeding Biology. Oxford University Press. pp. 200–202. ISBN 978-0-19-979702-8.
^ "Defence – pedicellariae". Echinoid Directory. Natural History Museum.
^ Hiroko Sakashita, " Sexual dimorphism and food habits of the clingfish, Diademichthys lineatus, and its dependence on host sea urchin ", Environmental Biology of Fishes, vol. 34, no 1, 1994, p. 95–101
^ Jangoux, M. (1984). "Diseases of echinoderms" (PDF). Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ abc Kroh, Andreas (2010). "The phylogeny and classification of post-Palaeozoic echinoids". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 8 (2): 147–212. doi:10.1080/14772011003603556..
^ Mah, Christopher (April 12, 2011). "Sizes and Species in the Strangest of the Strange : Deep-Sea Pourtalesiid Urchins". The Echinoblog..
^ ab Mah, Christopher (8 April 2014). "What are the Deepest known echinoderms?". The Echinoblog. Retrieved 22 March 2018..
^ Mattison, J.E.; Trent, J.D.; Shanks, AL; Akin, T.B.; Pearse, J.S. (1977). "Movement and feeding activity of red sea urchins (Strongylocentrotus franciscanus) adjacent to a kelp forest". Marine Biology. 39 (1): 25–30. doi:10.1007/BF00395589.
^ abc Konar, Brenda (2000). "Habitat influences on sea urchin populations". In: Hallock and French (eds). Diving for Science...2000. Proceedings of the 20th Annual Scientific Diving Symposium. American Academy of Underwater Sciences. Retrieved 7 January 2011.
^ ChrisM. "The Echinoblog". echinoblog.blogspot.com.
^ Antarctic Sea Urchin Shows Amazing Energy-Efficiency in Nature's Deep Freeze 15 March 2001 University of Delaware. Retrieved 22 March 2018
^ "Echinoids". British Geological Survey. 2017. Retrieved 14 March 2018.
^ "The Echinoid Directory | Introduction". Natural History Museum. Retrieved 16 March 2018.
^ "The Echinoid Directory | Spines". Natural History Museum. Retrieved 16 March 2018.
^ abcd Kirkaldy, J. F. (1967). Fossils in Colour. London: Blandford Press. pp. 161–163.
^ Schultz, Heinke A.G. (2015). Echinoidea: with pentameral symmetry. Walter de Gruyter. pp. 36 ff, section 2.4. ISBN 978-3-11-038601-1.
^ Wells, H. G.; Huxley, Julian; Wells, G. P. (1931). The Science of life. pp. 346–348.
^ Telford, M. J.; Lowe, C. J.; Cameron, C. B.; Ortega-Martinez, O.; Aronowicz, J.; Oliveri, P.; Copley, R. R. (2014). "Phylogenomic analysis of echinoderm class relationships supports Asterozoa". Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 281 (1786): 20140479–20140479. doi:10.1098/rspb.2014.0479. PMC 4046411.
^ Planet, Paul J.; Ziegler, Alexander; Schröder, Leif; Ogurreck, Malte; Faber, Cornelius; Stach, Thomas (2012). "Evolution of a Novel Muscle Design in Sea Urchins (Echinodermata: Echinoidea)". PLoS ONE. 7 (5): e37520. Bibcode:2012PLoSO...737520Z. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0037520.
^ Kroh, Andreas; Smith, Andrew B. (2010). "The phylogeny and classification of post-Palaeozoic echinoids". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 8 (2): 147–212. doi:10.1080/14772011003603556.
^ James, William D.; Berger, Timothy G.; et al. (2006). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: clinical Dermatology. Saunders Elsevier. p. 431. ISBN 0-7216-2921-0.
^ Gallagher, Scott A. "Echinoderm Envenomation". eMedicine. Retrieved 12 October 2010.
^ Matthew D. Gargus; David K. Morohashi (2012). "A sea-urchin spine chilling remedy" (letter to the Editor). New England Journal of Medicine. 30 (19): 1867–1868. doi:10.1056/NEJMc1209382.
^ "Insight from the Sea Urchin". Microscope Imaging Station. Exploratorium. Archived from the original on 2013-12-01. Retrieved 2018-03-07.
^ Bodnar, Andrea G.; Coffman, James A. (2016-08-01). "Maintenance of somatic tissue regeneration with age in short- and long-lived species of sea urchins". Aging Cell. 15 (4): 778–787. doi:10.1111/acel.12487. ISSN 1474-9726. PMC 4933669. PMID 27095483.
^ Roulston, C.; Luke, G.A.; de Felipe, P.; Ruan, L.; Cope, J.; Nicholson, J.; Sukhodub, A.; Tilsner, J.; Ryan, M.D. (2016). "'2A‐Like' Signal Sequences Mediating Translational Recoding: A Novel Form of Dual Protein Targeting" (PDF). Traffic. 17: 923–39. doi:10.1111/tra.12411. PMC 4981915. PMID 27161495.
^ "Sea Urchin Genome Project". sugp.caltech.edu. Retrieved 2016-12-05.
^ "Stanford seeks sea urchin's secret to surviving ocean acidification | Stanford News Release". news.stanford.edu. Retrieved 2016-12-05.
^ ab Sodergren, E; Weinstock, GM; Davidson, EH; et al. (2006-11-10). "The Genome of the Sea Urchin Strongylocentrotus purpuratus". Science. 314 (5801): 941–952. Bibcode:2006Sci...314..941S. doi:10.1126/science.1133609. PMC 3159423. PMID 17095691.
^ Rast, JP; Smith, LC; Loza-Coll, M; Hibino, T; Litman, GW (2006). "Genomic Insights into the Immune System of the Sea Urchin". Science. 314 (5801): 952–6. Bibcode:2006Sci...314..952R. doi:10.1126/science.1134301. PMC 3707132. PMID 17095692.
^ Laura Rogers-Bennett, "The Ecology of Strongylocentrotus franciscanus and Strongylocentrotus purpuratus" in John M. Lawrence, Edible sea urchins: biology and ecology, p. 410
^ abc Davidson, Alan (2014) Oxford Companion to Food. Oxford University Press, 3rd edition. pp. 730–731.
^ John M. Lawrence, "Sea Urchin Roe Cuisine" in John M. Lawrence, Edible sea urchins: biology and ecology
^ "The Rise of the Sea Urchin", Franz Lidz July 2014 – Smithsonian
^ for Puglia, Italy: Touring Club Italiano, Guida all'Italia gastronomica, 1984, p. 314; for Alexandria, Egypt: Claudia Roden, A Book of Middle Eastern Food, p. 183
^ Alan Davidson, Mediterranean Seafood, p. 270
^ Larousse Gastronomique[page needed]
^ Curnonsky, Cuisine et vins de France, nouvelle édition, 1974, p. 248
^ Davidson, Alan (2014) Oxford Companion to Food. Oxford University Press, 3rd edition. p. 280
^ Kleiman, Dena (October 3, 1990). "Scorned at Home, Maine Sea Urchin Is a Star in Japan". New York Times. p. C1.
^ Wassilieff, Maggy (March 2, 2009). "sea urchins". Te Ara: The Encyclopedia of New Zealand.
^ Macey, Richard (November 9, 2004). "The little urchins that can command a princely price". The Sydney Morning Herald.
^ Zatylny, Jane (6 September 2018). "Searchin' for Urchin: A Culinary Quest". Hakai magazine. Retrieved 10 September 2018.
^ "Sea Urchin Fishery and Overfishing", TED Case Studies 296, American University full text
^ Martin, R.E.; Carter, E.P.; Flick, G.J.; Davis, L.M. (2000). Marine and Freshwater Products Handbook. Taylor & Francis. p. 268. ISBN 978-1-56676-889-4. Retrieved 2014-12-03.
^ ab Lam, Francis (2014-03-14). "California Sea Urchin Divers, Interviewed by Francis Lam". Bon Appetit. Retrieved 2017-03-26.
^ Crowe, Andrew (2018). Pathway of the Birds: The Voyaging Achievements of Māori and their Polynesian Ancestors. Auckland, New Zealand: Bateman. ISBN 9781869539610.
^ "Amulet | LIN-B37563". Portable Antiquities Scheme. Retrieved 14 March 2018.
^ Tullock, John H. (2008). Your First Marine Aquarium: Everything about Setting Up a Marine Aquarium, Including Conditioning, Maintenance, Selecting Fish and Invertebrates, and More. Barron's Educational Series. p. 63. ISBN 978-0-7641-3675-7.
^ McNamara, Ken (2012). "Prehistoric fossil collectors". The Geological Society. Retrieved 14 March 2018.
^ Marren, Peter; Mabey, Richard (2010). Bugs Britannica. Chatto & Windus. pp. 469–470. ISBN 978-0-7011-8180-2.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Echinoidea. |
World Register of Marine Species link: Echinoidea Leske, 1778 (+species list)- The sea urchin genome project
Sea Urchin Harvesters Association – California Also, (604) 524-0322.
The Echinoid Directory from the Natural History Museum.
Virtual Urchin at Stanford- California Sea Urchin commission
Introduction to the Echinoidea at UCMP Berkeley


































