Atlanta Braves
| Atlanta Braves | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Established in 1871 | |||||
| Based in Atlanta since 1966 | |||||
| |||||
| Major league affiliations | |||||
| |||||
| Current uniform | |||||
 | |||||
| Retired numbers |
| ||||
| Colors | |||||
| |||||
| Name | |||||
| |||||
| Other nicknames | |||||
| |||||
| Ballpark | |||||
| |||||
| Major league titles | |||||
| World Series titles .mw-parser-output .noboldfont-weight:normal (3) |
| ||||
| NL Pennants (17) |
| ||||
| East Division titles (13) |
| ||||
West Division titles (5) |
| ||||
| Wild card berths (2) |
| ||||
| Front office | |||||
| Owner(s) | Liberty Media[2][3] | ||||
| Manager | Brian Snitker | ||||
| General Manager | Alex Anthopoulos[4] | ||||
The Atlanta Braves are an American professional baseball franchise based in the Atlanta metropolitan area. The franchise competes in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member of the National League (NL) East division. The Braves played home games at Atlanta–Fulton County Stadium from 1966 to 1996, and Turner Field from 1997 to 2016. Since 2017, their home stadium has been SunTrust Park, a new stadium 10 miles (16 km) northwest of downtown Atlanta in the Cumberland neighborhood of Cobb County.[5] The Braves play spring training games in Lake Buena Vista, Florida. The Braves have agreed to move their spring training home to North Port, Florida in 2019.[6][7]
The "Braves" name, which was first used in 1912, originates from a term for a Native American warrior. They are nicknamed "the Bravos", and often referred to as "America's Team" in reference to the team's games being broadcast on the nationally available TBS from the 1970s until 2007, giving the team a nationwide fan base.
From 1991 to 2005, the Braves were one of the most successful teams in baseball, winning division titles an unprecedented 14 consecutive times[8][9] (omitting the strike-shortened 1994 season in which there were no official division champions), and producing one of the greatest pitching rotations in the history of baseball. The Braves won the NL West 1991–93 and the NL East 1995–2005, and they returned to the playoffs as the National League Wild Card in 2010. The Braves advanced to the World Series five times in the 1990s, winning the title in 1995. Since their debut in the National League in 1876, the franchise has won 18 divisional titles, 17 National League pennants, and three World Series championships—in 1914 as the Boston Braves, in 1957 as the Milwaukee Braves, and in 1995 in Atlanta. The Braves are the only Major League Baseball franchise to have won the World Series in three different home cities.
The Braves and the Chicago Cubs are the National League's two remaining charter franchises. The Braves were founded in Boston, Massachusetts, in 1871, as the Boston Red Stockings (not to be confused with the American League's Boston Red Sox). The team states it is "the oldest continuously operating professional sports franchise in America."[10][b]
After various name changes, the team eventually began operating as the Boston Braves, which lasted for most of the first half of the 20th century. Then, in 1953, the team moved to Milwaukee, Wisconsin, and became the Milwaukee Braves, followed by the final move to Atlanta in 1966. The team's tenure in Atlanta is noted for Hank Aaron breaking Babe Ruth's career home run record in 1974.
Contents
1 History
1.1 Boston (1871–1952)
1.1.1 1871–1913
1.1.2 1914: Miracle
1.1.3 1915–1953
1.2 Milwaukee (1953–1965)
1.3 Atlanta (1966–present)
1.3.1 1966–1974
1.3.2 1976–1977: Ted Turner buys the team
1.3.3 1978–1990
1.3.4 1991–2005: Division dominance
1.3.4.1 1991–1994
1.3.4.2 1995–2005
1.3.4.3 Cy Young dominance
1.3.4.4 2005: A new generation
1.3.5 2006: Struggles
1.3.6 Sale to Liberty Media
1.3.7 2007: More struggles
1.3.8 2009: The return of solid pitching
1.3.9 2010: Cox's final season
1.3.10 2011: Fredi González takes over
1.3.10.1 September collapse
1.3.11 2012: Chipper's last season
1.3.12 2013: Braves win the East
1.3.13 2014: Losing season
1.3.14 2015–2016: Rebuilding
1.3.15 2017: SunTrust Park and front office changes
1.3.15.1 MLB investigation and penalties
2 World Series championships
3 Major rivalries
3.1 New York Mets
3.2 Philadelphia Phillies
4 Uniforms
5 Logos
6 Achievements
6.1 Awards
6.2 Team records
6.3 Team captains
6.4 Retired numbers
6.5 Braves Hall of Fame
6.6 Baseball Hall of Famers
6.7 Ford C. Frick Award recipients (broadcasters)
6.8 Georgia Sports Hall of Fame
7 Players
7.1 Current roster
8 Minor league affiliates
9 Home attendance
9.1 Turner Field
9.2 SunTrust Park
10 Radio and television
11 References
11.1 Footnotes
11.2 Citations
12 Further reading
13 External links
History
Boston (1871–1952)
1871–1913

1873 Boston Red Stockings team picture; it finished first with a record of 43–16
The Cincinnati Red Stockings, established in 1869 as the first openly all-professional baseball team, voted to dissolve after the 1870 season. Player-manager Harry Wright, with brother George and two other Cincinnati players, then went to Boston, Massachusetts at the invitation of Boston Red Stockings founder Ivers Whitney Adams to form the nucleus of the Boston Red Stockings, a charter member of the National Association of Professional Base Ball Players (NAPBBP). The original Boston Red Stockings team and its successors can lay claim to being the oldest continuously playing team in American professional sports.[10] (The only other team that has been organized as long, the Chicago Cubs, did not play for the two years following the Great Chicago Fire of 1871.) Two young players hired away from the Forest City club of Rockford, Illinois, turned out to be the biggest stars during the NAPBBP years: pitcher Al Spalding (founder of Spalding sporting goods) and second baseman Ross Barnes.
Led by the Wright brothers, Barnes, and Spalding, the Red Stockings dominated the National Association, winning four of that league's five championships. The team became one of the National League's charter franchises in 1876, sometimes called the "Red Caps" (as a new Cincinnati Red Stockings club was another charter member).
The Boston Red Caps played in the first game in the history of the National League, on Saturday, April 22, 1876, defeating the Athletics, 6–5.[11][12][13]

1888 Boston Beaneaters
Although somewhat stripped of talent in the National League's inaugural year, Boston bounced back to win the 1877 and 1878 pennants. The Red Caps/Beaneaters were one of the league's dominant teams during the 19th century, winning a total of eight pennants. For most of that time, their manager was Frank Selee. Boston came to be called the Beaneaters in 1883, while retaining red as the team color. The 1898 team finished 102–47, a club record for wins that would stand for almost a century. Stars of those 1890s Beaneater teams included the "Heavenly Twins", Hugh Duffy and Tommy McCarthy, as well as "Slidin'" Billy Hamilton.

Hugh Duffy played with the franchise from 1892 to 1900 and won the third Triple Crown in MLB history
The team was decimated when the American League's new Boston entry set up shop in 1901. Many of the Beaneaters' stars jumped to the new team, which offered contracts that the Beaneaters' owners did not even bother to match. They only managed one winning season from 1900 to 1913, and lost 100 games five times. In 1907, the Beaneaters (temporarily) eliminated the last bit of red from their stockings because their manager thought the red dye could cause wounds to become infected (as noted in The Sporting News Baseball Guide during the 1940s when each team's entry had a history of its nickname(s). The American League club's owner, Charles Taylor, wasted little time in adopting Red Sox as his team's first official nickname (up to that point they had been called by the generic "Americans"). Media-driven nickname changes to the Doves in 1907 and the Rustlers in 1911 did nothing to change the National League club's luck. The team became the Braves for the first time in 1912. Their owner, James Gaffney, was a member of New York City's political machine, Tammany Hall, which used an Indian chief as their symbol.[14]
1914: Miracle
Two years later, the Braves put together one of the most memorable seasons in baseball history. After a dismal 4–18 start, the Braves seemed to be on pace for a last place finish. On July 4, 1914, the Braves lost both games of a doubleheader to the Brooklyn Dodgers. The consecutive losses put their record at 26–40 and the Braves were in last place, 15 games behind the league-leading New York Giants, who had won the previous three league pennants. After a day off, the Braves started to put together a hot streak, and from July 6 through September 5, the Braves went 41–12.[15] On September 7 and 8, the Braves took two of three games from the New York Giants and moved into first place. The Braves tore through September and early October, closing with 25 wins against six losses, while the Giants went 16–16.[16] They were the only team, under the old eight-team league format, to win a pennant after being in last place on the Fourth of July. They were in last place as late as July 18, but were close to the pack, moving into fourth on July 21 and second place on August 12.[17]

Starting pitcher Bill James was 2–0 in the 1914 World Series, and the Braves recorded the first sweep in World Series history
Despite their amazing comeback, the Braves entered the World Series as a heavy underdog to Connie Mack's Philadelphia A's. Nevertheless, the Braves swept the Athletics—the first unqualified sweep in the young history of the modern World Series (the 1907 Series had one tied game) to win the world championship. Meanwhile, Johnny Evers won the Chalmers Award.
The Braves played the World Series (as well as the last few games of the 1914 season) at Fenway Park, since their normal home, the South End Grounds, was too small. However, the Braves' success inspired owner Gaffney to build a modern park, Braves Field, which opened in August 1915. It was the largest park in the majors at the time, with 40,000 seats and a very spacious outfield. The park was novel for its time; public transportation brought fans right to the park.
1915–1953
After contending for most of 1915 and 1916, the Braves only twice posted winning records from 1917 to 1932. The lone highlight of those years came when Judge Emil Fuchs bought the team in 1923 to bring his longtime friend, pitching great Christy Mathewson, back into the game. However, Mathewson died in 1925, leaving Fuchs in control of the team.
Fuchs was committed to building a winner, but the damage from the years prior to his arrival took some time to overcome. The Braves finally managed to be competitive in 1933 and 1934 under manager Bill McKechnie, but Fuchs' revenue was severely depleted due to the Great Depression.
Looking for a way to get more fans and more money, Fuchs worked out a deal with the New York Yankees to acquire Babe Ruth, who had started his career with the Red Sox. Fuchs made Ruth team vice president, and promised him a share of the profits. He was also granted the title of assistant manager, and was to be consulted on all of the Braves' deals. Fuchs even suggested that Ruth, who had long had his heart set on managing, could take over as manager once McKechnie stepped down—perhaps as early as 1936.[18]
At first, it appeared that Ruth was the final piece the team needed in 1935. On opening day, he had a hand in all of the Braves' runs in a 4–2 win over the Giants. However, that proved to be the only time the Braves were over .500 all year. Events went downhill quickly. While Ruth could still hit, he could do little else. He could not run, and his fielding was so terrible that three of the Braves' pitchers threatened to go on strike if Ruth were in the lineup. It soon became obvious that he was vice president and assistant manager in name only and Fuchs' promise of a share of team profits was hot air. In fact, Ruth discovered that Fuchs expected him to invest some of his money in the team.[18]
Seeing a franchise in complete disarray, Ruth retired on June 1—only six days after he clouted what turned out to be the last three home runs of his career. He had wanted to quit as early as May 12, but Fuchs wanted him to hang on so he could play in every National League park.[18] The Braves finished 38–115, the worst season in franchise history. Their .248 winning percentage is the third-worst in baseball history, and the second-worst in National League history (behind only the 1899 Cleveland Spiders).
Fuchs lost control of the team in August 1935,[18] and the new owners tried to change the team's image by renaming it the Boston Bees. This did little to change the team's fortunes. After five uneven years, a new owner, construction magnate Lou Perini, changed the nickname back to the Braves. He immediately set about rebuilding the team. World War II slowed things down a little, but the team rode the pitching of Warren Spahn to impressive seasons in 1946 and 1947.

Spahn (right) with Johnny Sain
In 1948, the team won the pennant, behind the pitching of Spahn and Johnny Sain, who won 39 games between them. The remainder of the rotation was so thin that in September, Boston Post writer Gerald Hern wrote this poem about the pair:
- First we'll use Spahn
- then we'll use Sain
- Then an off day
- followed by rain
- Back will come Spahn
- followed by Sain
- And followed
- we hope
- by two days of rain.
The poem received such a wide audience that the sentiment, usually now paraphrased as "Spahn and Sain and pray for rain", entered the baseball vocabulary. However, in the 1948 season, the Braves actually had the same record in games that Spahn and Sain started that the team had overall, in terms of winning percentage.
The 1948 World Series, which the Braves lost in six games to the Indians, turned out to be the Braves' last hurrah in Boston. In 1950, Sam Jethroe became the team's first African American player, making his major league debut on April 18. Amid four mediocre seasons, attendance steadily dwindled until, on March 13, 1953, Perini, who had recently bought out his original partners, announced he was moving the team to Milwaukee, where the Braves had their top farm club, the Brewers. Milwaukee had long been a possible target for relocation. Bill Veeck had tried to return his St. Louis Browns there earlier the same year (Milwaukee was the original home of that franchise), but his proposal had been voted down by the other American League owners.
Milwaukee (1953–1965)
Milwaukee went wild over the Braves, drawing a then-NL record 1.8 million fans. The Braves finished 92–62 in their first season in Milwaukee. The success of the relocated team showed that baseball could succeed in new markets, and the Philadelphia Athletics, St. Louis Browns, Brooklyn Dodgers, and New York Giants would leave their hometowns within the next five years.

Milwaukee Braves cap logo
As the 1950s progressed, the reinvigorated Braves became increasingly competitive. Sluggers Eddie Mathews and Hank Aaron drove the offense (they would hit a combined 1,226 home runs as Braves, with 850 of those coming while the franchise was in Milwaukee), often aided by another power hitter, Joe Adcock, while Warren Spahn, Lew Burdette, and Bob Buhl anchored the rotation. The 1956 Braves finished second, only one game behind the Brooklyn Dodgers.
In 1957, the Braves celebrated their first pennant in nine years spearheaded by Aaron's MVP season, as he led the National League in home runs and RBI. Perhaps the most memorable of his 44 round-trippers that season came on September 23, a two-run walk-off home run that gave the Braves a 4–2 victory over the St. Louis Cardinals and clinched the League championship. The team then went on to its first World Series win in over 40 years, defeating the powerful New York Yankees of Berra, Mantle, and Ford in seven games. One-time Yankee Burdette, the Series MVP, threw three complete game victories against his former team, giving up only two earned runs.
In 1958, the Braves again won the National League pennant and jumped out to a three games to one lead in the World Series against the New York Yankees once more, thanks in part to the strength of Spahn's and Burdette's pitching. But the Yankees stormed back to take the last three games, in large part to World Series MVP Bob Turley's pitching.
The 1959 season saw the Braves finish the season in a tie with the Los Angeles Dodgers, both with 86–68 records. Many residents of Chicago and Milwaukee were hoping for a Sox-Braves Series, as the cities are only about 75 miles (121 km) apart, but it was not to be because Milwaukee fell in a best-of-3 playoff with two straight losses to the Dodgers. The Dodgers would go on to defeat the Chicago White Sox in the World Series.

Milwaukee Braves logo (1953–1956)
The next six years were up-and-down for the Braves. The 1960 season featured two no-hitters by Burdette and Spahn, and Milwaukee finished seven games behind the Pittsburgh Pirates, who ultimately were to win the World Series that year, in second place, one year after the Braves were on the winning end of the 13-inning near-perfect game of Pirates pitcher Harvey Haddix. The 1961 season saw a drop in the standings for the Braves down to fourth, despite Spahn recording his 300th victory and pitching another no-hitter that year.
Aaron hit 45 home runs in 1962, a Milwaukee career high for him, but this did not translate into wins for the Braves, as they finished fifth. The next season, Aaron again hit 44 home runs and notched 130 RBI, and Spahn was once again the ace of the staff, going 23–7. However, none of the other Braves produced at that level, and the team finished in the "second division", for the first time in its short history in Milwaukee.
The Braves were mediocre as the 1960s began, with an inflated win total fed by the expansion New York Mets and Houston Colt .45s. To this day, the Milwaukee Braves are the only major league team who played more than one season and never had a losing record.
Perini sold the Braves to a Chicago-based group led by William Bartholomay in 1962. Almost immediately Bartholomay started shopping the Braves to a larger television market. Keen to attract them, the fast-growing city of Atlanta, led by Mayor
Ivan Allen, Jr. constructed a new $18 million, 52,000-seat ballpark in less than one year, Atlanta Stadium, which was officially opened in 1965 in hopes of luring an existing major league baseball and/or NFL/AFL team. After the city failed to lure the Kansas City A's to Atlanta (the A's would move to Oakland in 1968), the Braves announced their intention to move to Atlanta for the 1965 season. However, an injunction filed in Wisconsin kept the Braves in Milwaukee for one final year. In 1966, the Braves completed the move to Atlanta.
Eddie Mathews is the only Braves player to have played for the organization in all three cities that they have been based in. Mathews played with the Braves for their last season in Boston, the team's entire tenure in Milwaukee, and their first season in Atlanta.
Atlanta (1966–present)
1966–1974
The Braves were a .500 team in their first few years in Atlanta; 85–77 in 1966, 77–85 in 1967, and 81–81 in 1968. The 1967 season was the Braves' first losing season since 1952, their last year in Boston. In 1969, with the onset of divisional play, the Braves won the first-ever National League West Division title, before being swept by the "Miracle Mets" in the National League Championship Series. They would not be a factor during the next decade, posting only two winning seasons between 1970 and 1981 – in some cases, fielding teams as bad as the worst Boston teams.

The fence over which Hank Aaron hit his 715th career home run still exists outside of Turner Field.
In the meantime, fans had to be satisfied with the achievements of Hank Aaron. In the relatively hitter-friendly confines and higher-than-average altitude of Atlanta Stadium ("The Launching Pad"), he actually increased his offensive production. Atlanta also produced batting champions in Rico Carty (in 1970) and Ralph Garr (in 1974). In the shadow of Aaron's historical home run pursuit, was the fact that three Atlanta sluggers hit 40 or more home runs in 1973 – Darrell Evans and Davey Johnson along with Aaron.
By the end of the 1973 season, Aaron had hit 713 home runs, one short of Ruth's record. Throughout the winter he received racially motivated death threats, but stood up well under the pressure. The next season, it was only a matter of time before he set a new record. On April 4, opening day, he hit No.714 in Cincinnati, and on April 8, in front of his home fans and a national television audience he finally beat Ruth's mark with a home run to left-center field off left-hander Al Downing of the Los Angeles Dodgers. Aaron spent most of his career as a Milwaukee and Atlanta Brave before asking to be traded to the Milwaukee Brewers, while Ruth finished his career as a Boston Brave. In fact, until Barry Bonds eclipsed the 714 home runs hit by Babe Ruth in 2006, the top two home run hitters in Major League history had at one time been Braves.
1976–1977: Ted Turner buys the team

Media magnate Ted Turner purchased the team in 1976, and played a large role in the team's operation.
In 1976, the team was purchased by media magnate Ted Turner, owner of superstation WTBS, as a means to keep the team (and one of his main programming staples) in Atlanta. The financially strapped Turner used money already paid to the team for their broadcast rights as a down-payment. It was then that Atlanta Stadium was renamed Atlanta–Fulton County Stadium. Turner quickly gained a reputation as a quirky, hands-on baseball owner. On May 11, 1977, Turner appointed himself manager, but because MLB passed a rule in the 1950s barring managers from holding a financial stake in their teams, Turner was ordered to relinquish that position after one game (the Braves lost 2–1 to the Pittsburgh Pirates to bring their losing streak to 17 games).
Turner used the Braves as a major programming draw for his fledgling cable network, making the Braves the first franchise to have a nationwide audience and fan base. WTBS marketed the team as "The Atlanta Braves: America's Team", a nickname that still sticks in some areas of the country, especially the South. Among other things, in 1976 Turner suggested the nickname "Channel" for pitcher Andy Messersmith and jersey number 17, in order to promote the television station that aired Braves games. Major League Baseball quickly nixed the idea.
1978–1990

Phil Niekro played with the Braves from 1964 to 1983 and in 1987; he holds the MLB record for most wins by a knuckleball pitcher
After three straight losing seasons, Bobby Cox was hired for his first stint as manager for the 1978 season. He promoted 22-year-old slugger Dale Murphy into the starting lineup. Murphy hit 77 home runs over the next three seasons, but he struggled on defense, unable to adeptly play either catcher or first base. In 1980, Murphy was moved to center field and demonstrated excellent range and throwing ability, while the Braves earned their first winning season since 1974. Cox was fired after the 1981 season and replaced with Joe Torre, under whose leadership the Braves attained their first divisional title since 1969. Strong performances from Bob Horner, Chris Chambliss, pitcher Phil Niekro, and short relief pitcher Gene Garber helped the Braves, but no Brave was more acclaimed than Murphy, who won both a Most Valuable Player and a Gold Glove award. Murphy also won an MVP award the following season, but the Braves began a period of decline that defined the team throughout the 1980s. Murphy, excelling in defense, hitting, and running, was consistently recognized as one of the league's best players, but the Braves averaged only 65 wins per season between 1985 and 1990. Their lowest point came in 1988, when they lost 106 games. The 1986 season saw the return of Bobby Cox as general manager. Also in 1986, the team stopped using their Indian-themed mascot, Chief Noc-A-Homa.
1991–2005: Division dominance
1991–1994
@media all and (max-width:720px).mw-parser-output .tmulti>.thumbinnerwidth:100%!important;max-width:none!important.mw-parser-output .tmulti .tsinglefloat:none!important;max-width:none!important;width:100%!important;text-align:center


Greg Maddux, Tom Glavine, and John Smoltz combined for six Cy Young Awards during their time in the Braves pitching rotation
Cox returned to the dugout as manager in the middle of the 1990 season, replacing Russ Nixon. The Braves finished the year with the worst record in baseball, at 65–97. They traded Dale Murphy to the Philadelphia Phillies after it was clear he was becoming a less dominant player. Pitching coach Leo Mazzone began developing young pitchers Tom Glavine, Steve Avery, and John Smoltz into future stars. That same year, the Braves used the number one overall pick in the 1990 MLB draft to select Chipper Jones, who became one of the best hitters in team history. Perhaps the Braves' most important move was not on the field, but in the front office. Immediately after the season, John Schuerholz was hired away from the Kansas City Royals as general manager.
The following season, Glavine, Avery, and Smoltz would be recognized as the best young pitchers in the league, winning 52 games among them. Meanwhile, behind position players David Justice, Ron Gant and unexpected league Most Valuable Player and batting champion Terry Pendleton, the Braves overcame a 39–40 start, winning 55 of their final 83 games over the last three months of the season and edging the Los Angeles Dodgers by one game in one of baseball's more memorable playoff races. The "Worst to First" Braves, who had not won a divisional title since 1982, captivated the city of Atlanta (and the entire southeast) during their improbable run to the flag. They defeated the Pittsburgh Pirates in a very tightly contested seven-game NLCS only to lose the World Series, also in seven games, to the Minnesota Twins. The series, considered by many to be one of the greatest ever, was the first time a team that had finished last in its division one year went to the World Series the next; both the Twins and Braves accomplished the feat.
Despite the 1991 World Series loss, the Braves' success would continue. In 1992, the Braves returned to the NLCS and once again defeated the Pirates in seven games, culminating in a dramatic game seven win. Francisco Cabrera's two-out single that scored David Justice and Sid Bream capped a three-run rally in the bottom of the ninth inning that gave the Braves a 3–2 victory. It was the first time in post season history that the tying and winning runs had scored on a single play in the ninth inning. The Braves lost the World Series to the Toronto Blue Jays, however. In 1993, the Braves signed Cy Young Award winning pitcher Greg Maddux from the Chicago Cubs, leading many baseball insiders to declare the team's pitching staff the best in baseball. The 1993 team posted a franchise-best 104 wins after a dramatic pennant race with the San Francisco Giants, who won 103 games. The Braves needed a stunning 55–19 finish to edge out the Giants, who led the Braves by nine games in the standings as late as August 11. However, the Braves fell in the NLCS to the Philadelphia Phillies in six games.
In 1994, in a realignment of the National League's divisions following the 1993 expansion, the Braves moved to the Eastern Division.[19] This realignment was the main cause of the team's heated rivalry with the New York Mets during the mid-to-late 1990s.[20][21][22]
The player's strike cut short the 1994 season, prior to the division championships, with the Braves six games behind the Montreal Expos with 48 games left to play.
1995–2005
The Braves returned strong the following strike-shortened (144 games instead of the customary 162) year and beat the Cleveland Indians in the 1995 World Series. This squelched claims by many Braves critics that they were the "Buffalo Bills of Baseball" (January 1996 issue of Beckett Baseball Card Monthly). With this World Series victory, the Braves became the first team in Major League Baseball to win world championships in three different cities. With their strong pitching as a constant, the Braves appeared in the 1996 and 1999 World Series (losing both to the New York Yankees, managed by Joe Torre, a former Braves manager),[21] and had a streak of division titles from 1991 to 2005 (three in the Western Division and eleven in the Eastern) interrupted only in 1994 when the strike ended the season early. Pitching was not the only constant in the Braves organization —Cox was the Braves' manager, while Schuerholz remained the team's GM until after the 2007 season when he was promoted to team president. Terry Pendleton finished his playing career elsewhere, but returned to the Braves system as the hitting coach.
In October 1996, Time Warner acquired Ted Turner's Turner Broadcasting System and all of its assets, including its cable channels and the Atlanta Braves. Over the next few years, Ted Turner's presence as owner of the team would diminish.

The 1995 World Series Commissioner's Trophy on display in the Ivan Allen Jr. Braves Museum and Hall of Fame at Turner Field
A 95–67 record in 2000 produced a ninth consecutive division title. However, a sweep by the St. Louis Cardinals in the National League Division Series prevented the Braves from reaching the NL Championship Series.[21]
In 2001, Atlanta won the National League East division yet again, swept the Houston Astros in the NLDS, then lost to the Arizona Diamondbacks in the National League Championship Series four games to one. One memorable game the Braves played that year came on September 21, when they played rival New York Mets in the first major professional sporting event held in New York City since 9/11.
In 2002, 2003 and 2004, the Braves won the Eastern division again, but lost in the NLDS in all three years in the same fashion: 3 games to 2 to the San Francisco Giants, Chicago Cubs, and Houston Astros.
Cy Young dominance
Six National League Cy Young Awards in the 1990s were awarded to three Braves pitchers:
- In 1991, left-handed pitcher Tom Glavine received his first award.
- Right-handed pitcher Greg Maddux won four in a row, three of them with the Braves from 1993 through 1995. His first award came in 1992 with the Cubs.
- In 1996, right-handed pitcher John Smoltz received his only Cy Young Award.
- In 1998, Glavine won his second.
2005: A new generation
In 2005, the Braves won the Division championship for the 14th consecutive time from 1991 to 2005. 14 consecutive division titles stands as the record for all major league baseball. The 2005 title marked the first time any MLB team made the postseason with more than 4 rookies who each had more than 100 ABs (Wilson Betemit, Brian McCann, Pete Orr, Ryan Langerhans, Jeff Francoeur).[citation needed] Catcher Brian McCann, right fielder Jeff Francoeur, and pitcher Kyle Davies all grew up in the suburbs of Atlanta. The large number of rookies to debut in 2005 were nicknamed the "Baby Braves" by fans and became an Atlanta-area sensation, helping to lead the club to a record of 90–72.
However, the season would end on a sour note as the Braves lost the National League Division Series to the Astros in four games. In Game 4, with the Braves leading by 5 in the eighth inning, the Astros battled back with a Lance Berkman grand slam and a two-out, ninth inning Brad Ausmus home run off of Braves closer Kyle Farnsworth. The game did not end until the 18th inning, becoming the longest game in playoff history at 5 hours 50 minutes. Chris Burke ended the marathon with a home run off of Joey Devine.
After the 2005 season, the Braves lost their long-time pitching coach Leo Mazzone, who left to go to the Baltimore Orioles. Roger McDowell took his place in the Atlanta dugout. Unable to re-sign shortstop Rafael Furcal, the Braves acquired shortstop Édgar Rentería from the Boston Red Sox.
2006: Struggles

Andruw Jones at bat for the Braves in 2006
In 2006, the Braves did not perform at the level they had grown accustomed to. Due to an offensive slump, injuries to their starting rotation, and subpar bullpen performances, the Braves compiled a 6–21 record during June, the worst month ever in Atlanta with a winning percentage of .222; this was only better than the woeful Boston Braves in May 1935 (4–20) with a .166 winning percentage.
After the break, the Braves came out with their bats swinging, setting many franchise records. They won five straight, sweeping the Padres and taking two from the Cardinals, tallying a total of 65 runs in that span. The 65 runs in five games is the best by the franchise since 1897, when the Boston Beaneaters totaled 78, including 25 in one game and 21 in another, from May 31 – June 3; the 2006 Braves also became the first team since the 1930 New York Yankees to score ten runs or more in five straight games. The Braves had a total of 81 hits during their five-game run and 98 hits in their last six games, going back to an 8–3 victory over Cincinnati on July 9, the last game before the All-Star break. Additionally, Chipper Jones was able to maintain a 20-game hitting streak and tie Paul Waner's 69-year-old Major League record with a 14-game extra-base hit streak.[23]
However, on September 18, the New York Mets' win over the Florida Marlins mathematically eliminated the Braves from winning the NL East, ending the Atlanta Braves' 11-year reign over the NL East. On September 24, the Braves' loss to the Colorado Rockies mathematically eliminated the Braves from winning the NL Wild Card, making 2006 the first year that the Braves would not compete in the postseason since 1990, not counting the strike-shortened 1994 season. Also, a loss to the Mets on September 28 guaranteed the Braves their first losing season since 1990. Although the Braves won two of their last three games against the Astros, including rookie Chuck James besting Roger Clemens, Atlanta finished the season in third place, one game ahead of the Marlins, at 79–83.
Sale to Liberty Media
In December 2005, team owner Time Warner, who inherited the Braves after purchasing TBS in 1996, announced it was placing the team for sale.[24][25]Liberty Media began negotiations to purchase the team.
In February 2007, after more than a year of negotiations, Time Warner agreed to a deal that would sell the Braves to Liberty Media Group (a company which owned a large amount of stock in Time Warner, Inc.), pending approval by 75 percent of MLB owners and the Commissioner of Baseball, Bud Selig. The deal included the exchange of the Braves, valued in the deal at $450 million, a hobbyist magazine publishing company, and $980 million cash, for 68.5 million shares of Time Warner stock held by Liberty Media, then worth approximately $1.48 billion. Team President Terry McGuirk anticipated no change in the current front office structure, personnel, or day-to-day operations of the Braves. Liberty Media is not expected to take any type of "active" ownership in terms of day-to-day operations.[26]
On May 16, 2007, Major League Baseball's owners approved the sale of the Braves from Time Warner to Liberty Media.[2][27] The Braves are one of only two Major League Baseball teams under majority corporate ownership (and the only NL team with this distinction); the other team is the Toronto Blue Jays (owned by Canadian media conglomerate Rogers Communications).
2007: More struggles

Brian McCann bats for Atlanta in July 2007
On July 5, Chipper Jones surpassed Dale Murphy for the Atlanta club record of 372 home runs by belting two against the Los Angeles Dodgers.
After struggling during the second half of the 2007 season, Atlanta finished over .500 and missed the post season again. On October 12, 2007, John Schuerholz stepped down as General Manager to take over as team president.[28] Assistant GM Frank Wren took over as General Manager.
2009: The return of solid pitching

Kenshin Kawakami pitching for the Braves in 2009
On December 4, 2008, the Atlanta Braves received Javier Vázquez and Boone Logan, while the Chicago White Sox received prospects catcher Tyler Flowers, shortstop Brent Lillibridge, third baseman Jon Gilmore and pitcher Santos Rodriguez.[29] On January 13, 2009, the Braves signed Japanese pitcher Kenshin Kawakami to a three-year deal, and two days later signed free agent pitcher Derek Lowe to a four-year contract. During the course of the offseason, the Braves signed veteran pitcher and former Brave Tom Glavine, while losing long-time Brave John Smoltz to the Boston Red Sox.
On February 25, 2009, just before the start of spring training, Atlanta agreed to terms on a one-year contract with free-agent outfielder Garret Anderson. The additional outfield depth allowed the Braves to trade Josh Anderson to the Detroit Tigers for minor league pitcher Rudy Darrow on March 30, 2009.[30]
On June 3, 2009, the Braves acquired Nate McLouth from the Pittsburgh Pirates for prospects Jeff Locke, Charlie Morton and Gorkys Hernández. They also released veteran pitcher Tom Glavine. On July 10, 2009, the Braves traded outfielder Jeff Francoeur to the New York Mets for outfielder Ryan Church. On July 31, 2009, hours before the trade deadline, the Braves and Boston Red Sox swapped 1st basemen: Atlanta dealt Casey Kotchman to Boston and reacquired Adam LaRoche, whom the Braves had traded away during the 2006–07 off-season to Pittsburgh.
The Braves made a late-season surge, coming within 2 games of the wild card leading Colorado Rockies in late September. On October 1, 2009 with the Braves four games back, Colorado beat the Milwaukee Brewers 9–2 to clinch the wild card spot and end the Braves' 2009 postseason hopes.
2010: Cox's final season

Braves manager Bobby Cox retired in 2010 after 25 years of management
The 2010 Atlanta Braves Season features the Braves' attempt to reclaim a postseason berth for the first time since 2005. The Braves were once again skippered by Bobby Cox, now in his 25th and final season managing the team. The Braves started the 2010 season slowly and had a nine-game losing streak in April. Then they had a nine-game winning streak from May 26 through June 3, the Braves longest since 2000 when they won 16 in a row. On May 31, the Atlanta Braves defeated the then-first place Philadelphia Phillies at Turner Field to take sole possession of first place in the National League East standings, a position they had maintained through the middle of August.[31] The last time the Atlanta Braves led the NL East on August 1 was in 2005. On July 13, 2010 at the 2010 MLB All-Star Game in Anaheim, Braves catcher Brian McCann was awarded the All-Star Game MVP Award for his clutch two-out, three-run double in the seventh inning to give the National League its first win in the All-Star Game since 1996.[32] He became the first Brave to win the All-Star Game MVP Award since Fred McGriff did so in 1994. The Braves made two deals before the trade deadline to acquire Álex González, Rick Ankiel and Kyle Farnsworth from the Toronto Blue Jays and Kansas City Royals, giving up shortstop Yunel Escobar, pitchers Jo-Jo Reyes and Jesse Chavez, outfielder Gregor Blanco and three minor leaguers.[33][34] On August 18, 2010 they traded three pitching prospects for first baseman Derrek Lee from the Chicago Cubs.[35] On August 22, 2010 against the Chicago Cubs, Mike Minor struck out 12 batters across 6 innings; an Atlanta Braves single game rookie strikeout record.[36] The Braves dropped to second in the NL East in early September, but won the NL Wild Card. They lost to the San Francisco Giants in the National League Division Series in four games. Every game of the series was determined by one run. After the series-clinching victory for the Giants in Game 4, Bobby Cox was given a standing ovation by the fans, also by players and coaches of both the Braves and Giants.
2011: Fredi González takes over

Braves closer Craig Kimbrel pitching in 2011
On October 13, 2010, the Atlanta Braves announced that Fredi González would replace long-time Braves manager Bobby Cox as manager of the team in 2011.[37] The announcement came just two days after the 2010 Braves were eliminated from the postseason. It was also announced that pitching coach Roger McDowell, third-base coach Brian Snitker, and bullpen coach Eddie Pérez would retain their current positions, while former hitting coach Terry Pendleton would replace Glenn Hubbard as the first-base coach and newcomer Carlos Tosca would become the new bench coach. Hubbard and former bench coach Chino Cadahia were not offered positions on the new coaching staff. Larry Parrish was hired as hitting coach on October 29, 2010.
On November 16, 2010 in an offseason trade, the Braves acquired Dan Uggla from the Florida Marlins in exchange for left-handed reliever Mike Dunn and infielder Omar Infante. According to Elias Sports Bureau, the Braves had an all-time franchise win-loss record over .500 for the first time since 1923 after their win over the Houston Astros on June 11, 2011.[38] The Braves franchise became the third franchise in MLB history to reach 10,000 wins with their win over the Washington Nationals on July 15, 2011.[39] On July 31, 2011, just sixteen days after registering their 10,000th win, the Florida Marlins defeated the Braves by a score of 3–1, handing the team the 10,000th loss in franchise history. The Braves become only the second team in big league history with 10,000 losses after the Philadelphia Phillies reached the plateau in 2007.[40]
Players from the Braves' farm system, such as Freddie Freeman and Brandon Beachy, played regularly with the big league club, while Julio Teherán, Randall Delgado, and Mike Minor were called up for spot starts. With late season injuries to starters Jair Jurrjens and Tommy Hanson, these three young pitchers made their way into the starting rotation in their absence.[41] Eight players made their major league debuts for the team in 2011.
September collapse
The Braves led the National League Wild Card standings for much of the 2011 season, with the division-rival Philadelphia Phillies firmly in control of first place in the National League East. The Braves entered the final month of the regular season 25 games above .500 with a record of 80–55 and an 8 1⁄2-game lead in the Wild Card standings. The nearest team trailing them, the St. Louis Cardinals, who also trailed the National League Central-leading Milwaukee Brewers by 8 1⁄2 games at the time, were considered a long-shot to gain a spot in the postseason. Just days prior on August 26, the Cardinals found themselves 10 1⁄2 games behind and in third place.[42]
With 27 games to play, the Braves went 9–18 in September to finish the season with a record of 89–73. The Cardinals, meanwhile, went 18–8 to finish at 90–72. Braves closer Craig Kimbrel, who had not surrendered a single earned run in July or August, carried a 4.76 ERA in September with three blown saves. After being dominant in his role for much of the season, Braves setup man Jonny Venters posted a 5.11 September ERA. These sharp declines in both relievers led many critics to question the handling of the bullpen by Braves manager Fredi González.[43] Veteran starter Derek Lowe posted a win-loss record of 0–5 in September with an ERA of 8.75.[44] Shortly into the offseason, Lowe would be traded to the Cleveland Indians.[45] The Braves starters lasted six or more innings only three times over the last 23 games.[44] Over the last five games, all of which were losses for the Braves, the team managed to score only seven runs.[46] Braves catcher Brian McCann, often regarded as the best offensive catcher in the Majors, hit only .183 with two home runs in September.[44] The offense as a whole hit for only a .235 batting average and a .300 on-base percentage in September, both second-worst in the National League. The .195 RISP average by Braves hitters was second worst in the Majors.[44] Hitting coach Larry Parrish was fired two days following the last game of the season.[47]
2012: Chipper's last season

Chipper Jones salutes the crowd at Turner Field prior to his final regular season game on September 30, 2012. Jones announced he would retire after 19 seasons with the Braves
In 2012, the Braves began their 138th season after an upsetting end to the 2011 season. On March 22, the Braves announced that third baseman Chipper Jones would retire following the 2012 season after 19 Major League seasons with the team. The Braves also lost many key players through trades or free agency, including pitcher Derek Lowe, shortstop Alex González, and outfielder Nate McLouth. To compensate for this, the team went on to receive many key players such as outfielder Michael Bourn, along with shortstops Tyler Pastornicky and Andrelton Simmons. To fill the void of a quality starting pitcher left by Lowe (as well as a mid-season injury to Brandon Beachy), manager Fredi González elected relief pitcher Kris Medlen to the starting pitching rotation. The Braves went on to win every game Medlen started, setting the MLB record for most consecutive wins when a single pitcher starts (total of 23). Atlanta stayed close to the Washington Nationals in the race to win the National League East title. They also stayed on top of the National League Wild Card race. Washington ended up winning their first division title in franchise history, but the Braves remained in first place of the NL wild card race. Keeping with a new MLB rule for the 2012 season, the top two wild card teams in each league must play each other in a playoff game before entering into the Division Series.
The Braves played the St. Louis Cardinals in the first ever Wild Card Game. The Braves were behind 6–3 in the bottom of the eighth inning when Andrelton Simmons hit a fly ball to left field that dropped in between the Cardinals shortstop and left fielder. Umpire Sam Holbrook called Simmons out, citing the infield fly rule. Had an infield fly not been called, Simmons would have been credited with a single and Atlanta would have had the bases loaded with one out. Fans at Turner Field began to litter the field with debris, prompting the game to be delayed for 19 minutes. The Braves lost the game 6–3, ending their season.
2013: Braves win the East

Evan Gattis catching for the Braves in 2013
During the offseason following a gut wrenching exit against the St. Louis Cardinals in the Wild Card Game, the Braves spent the 2012–2013 offseason revamping and retooling their offense. The Braves turned heads across baseball by acquiring B.J. Upton from the Tampa Bay Rays, signing him to a 5-year $75.25 million contract and making him their starting center fielder,[48] and uniting him with his younger brother Justin Upton from the Arizona Diamondbacks in a seven player trade that sent fan favorite utility man Martín Prado to the Diamondbacks,[49] they also filled a need for a new Third Baseman in Chris Johnson after the retirement of Chipper Jones the previous year. The Braves began the 2013 season with a hot start in April by going 17–9 for the month, which saw the emergence of rookie sensation Evan Gattis, while taking hold of first place in the National League East division, a lead they would never relinquish for the rest of the season. The Braves suffered many injuries to key players throughout the season, including injuries to Jason Heyward, Brian McCann, Freddie Freeman, Eric O'Flaherty, Jonny Venters, Ramiro Pena and others, but found a way to win despite these blows to the team. Leading up to the All Star break, First Baseman Freddie Freeman was voted in to play for the 2013 National League All-Star Team, in the 2013 All Star Game, which he did not play. The Braves also witnessed the emergence of rookie pitcher Julio Teherán after much hype during Spring training. From July 26 to August 10, the Braves won 14 games in a row.[50] The winning streak was the longest of its kind since April–May 2000.
On June 28, 2013 the Atlanta Braves retired former third baseman Chipper Jones' jersey, number 10, before the game against the Arizona Diamondbacks. He was honored before 51,300 fans at Turner Field in Atlanta.[51] He served as a staple of the Braves franchise for 19 years before announcing his retirement at the beginning of the 2012 season. Chipper Jones played his last regular season game for the Braves on September 30, 2012.
The Braves opened up a 15-game lead on the Washington Nationals in the National League East on September 3, 2013, riding that lead en route to its first division title since 2005, the last of 14 straight division titles. This was also Braves manager Fredi González's first division title since beginning his managerial career in 1990; including his first since becoming the manager of the Braves after the 2010 season. The Braves clinched the 18th division title in team history on September 22, 2013[52] after a Nationals loss to the Marlins in the first game of a double header; the Braves also won their game that day, beating the Chicago Cubs 5–2 at Wrigley Field.
After clinching the division title, they lost to the Dodgers 3–1 in the Division Series.
2014: Losing season

Jason Heyward runs the bases in 2014
On November 11, 2013, the Braves announced that they would vacate Turner Field for a new stadium in Cobb County, in the northwest suburbs outside of Atlanta in 2017. The move is to follow the expiration of the Braves' 20-year lease on Turner Field in 2016. The new stadium is to be constructed in a public/private partnership.[53][54][55][56][57][58][59] During the offseason the Braves signed few of their young talents to multi year contracts; Craig Kimbrel (4 years/$42M), Freddie Freeman (8 years/$135M), Kris Medlen (1 year/$5.8M), Jason Heyward (2 years/$13.3M), Julio Teherán (6 years/$32.4M) and Andrelton Simmons (7 years/$58M).
The Braves finished the season in a distant second place with a 79–83 record, which was their first losing season since 2008 and only their third since 1990.
2015–2016: Rebuilding
Prior to the 2015 season, the Braves fired their General Manager Frank Wren, and John Hart replaced him as interim general manager, choosing to only take the title of President of Baseball Operations. The Braves promptly traded Gold Glove Award winner Jason Heyward to the St. Louis Cardinals along with pitcher Jordan Walden for pitchers Shelby Miller and Tyrell Jenkins.[60] Hart would then trade All Star left fielder Justin Upton to the San Diego Padres for Max Fried, Jace Peterson, Dustin Peterson, and Mallex Smith.[61] Catcher Evan Gattis and minor league prospect James Hoyt were traded to the Houston Astros for minor leaguers Mike Foltynewicz, Rio Ruiz, and Andrew Thurman.[62] A day before the season began, the Braves made a final trade involving former All- Star Craig Kimbrel and outfielder Melvin Upton Jr.. They were traded to the San Diego Padres for outfielders Cameron Maybin and Carlos Quentin along with two minor league players.[63] By the beginning of the season, the Braves did 11 trades in all.
Prior to the start of the 2016 regular season, the Braves continued their offseason rebuilding by trading Andrelton Simmons to the Los Angeles Angels for Erick Aybar, and pitching prospects Sean Newcomb and Chris Ellis and $2.5 million. They agreed to 1 year contracts with Kelly Johnson, Chris Withrow, and Arodys Vizcaino, and agreed to terms on a minor league contract for Carlos Torres and Jeff Francoeur. The Braves would end up purchasing the Major League contract of Francoeur.
On April 13, 2016, Hector Olivera was arrested and charged with the assault of a woman at the team hotel when the Braves were in Washington D.C. facing the Nationals. He was placed on Administrative Leave by Major League Baseball and was placed on the Braves Restricted List until further disciplinary action is given.[64]
The Braves began the season on a nine-game losing streak, which is the worst opening by the franchise since 1988, when they dropped the first 10 games of that season.
After a 9–28 start in 2016, Fredi González was fired on May 17 and replaced by third base coach Brian Snitker as interim general manager. Snitker replaced González once before in the 2006–07 off-season as the Braves third base coach when González left the Braves to manage the Marlins. The Braves finished the season 68–93 and in last place in NL East.
During the 2016 off-season, the Braves signed pitchers R.A. Dickey[65] and Bartolo Colón[66] and promoted interim manager Brian Snitker to full-time manager.
2017: SunTrust Park and front office changes

SunTrust Park prior to its first regular-season game
The Braves opened their new stadium, SunTrust Park, on April 14, 2017, with a four-game sweep of the San Diego Padres. The park received positive reviews. Woody Studenmund of the Hardball Times called the park a "gem" and he was impressed with "the compact beauty of the stadium and its exciting approach to combining baseball, business and social activities."[67] J.J. Cooper of Baseball America praised the "excellent sight lines for pretty much every seat."[68] Cooper also noted that "the Wi-Fi works and it's very fast, even with a park full of smartphone users."[68]
On October 2, 2017, John Coppolella resigned as general manager of the Braves amid a Major League Baseball investigation into Atlanta's international signings, having committed what the Braves termed "a breach of MLB rules regarding the international player market".[69] On November 13, 2017, the Braves announced Alex Anthopoulos as the new general manager and executive vice president.[70] John Hart was removed as team president and assumed a senior adviser role with the organization.[70] Braves chairman Terry McGuirk apologized to fans "on behalf of the entire Braves family" for the scandal.[70] McGuirk described Anthopoulos as "a man of integrity" and that "he will operate in a way that will make all of our Braves fans proud."[70] On November 17, 2017, the Braves announced that John Hart had stepped down as senior advisor for the organization.[71] Hart said in a statement that "with the hiring of Alex Anthopoulos as general manager, this organization is in great hands."[71]
MLB investigation and penalties
On November 21, 2017, Major League Baseball Commissioner Rob Manfred announced the findings of the MLB investigation into Atlanta's international signings.[72] Manfred ruled that the Braves must forfeit 13 international prospects, including highly touted Kevin Maitan, an infielder from Venezuela who signed for $4.25 million in 2016.[72] The team also forfeited a third-round draft pick in the 2018 draft. Former Braves general manager John Coppolella was placed on baseball's permanently ineligible list.[72]
Additionally, the Braves shall be prohibited from signing any international player for more than $10,000 during the 2019–20 signing period and their international signing bonus pool for the 2020–21 signing period will be reduced by 50%.[72]
World Series championships
Over its 138 seasons, the Braves franchise has won a total of three World Series Championships, one in each of the three cities they have played in.
| Season | Manager | Opponent | Series Score | Record |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1914 (Boston) | George Stallings | Philadelphia Athletics | 4–0 | 94–59 |
1957 (Milwaukee) | Fred Haney | New York Yankees | 4–3 | 95–59 |
1995 (Atlanta) | Bobby Cox | Cleveland Indians | 4–2 | 90–54 |
Total World Series championships: | 3 | |||
Major rivalries
New York Mets
The Braves–Mets rivalry is a rivalry between the two teams, featuring the Braves and the New York Mets as they both play in the National League East.[20]
Although their first major confrontation occurred when the Mets swept the Braves in the 1969 NLCS, en route to their first World Series championship, the first playoff series won by an expansion team (also the first playoff appearance by an expansion team), the rivalry did not become especially heated until the 1994 season when division realignment put both the Mets and the Braves in the NL East division.[19][73] During this time the Braves became one of the most dominant teams in professional baseball, earning 14 straight division titles through 2005, including five world series berths, and one world series championship during the 1995 season. The rivalry remained heated through the early 2000s.
Philadelphia Phillies
While their rivalry with the Philadelphia Phillies lacks the history and hatred of the Mets, it has been the more important one in the last decade. Between 1993 and 2013, the two teams reigned almost exclusively as NL East champions, the exceptions being in 2006, when the Mets won their first division title since 1988 (no division titles were awarded in 1994 due to the player's strike), and in 2012, when the Washington Nationals claimed their first division title since 1981 when playing as the Montreal Expos. The Phillies 1993 championship was also part of a four-year reign of exclusive division championships by the Phillies and the Pittsburgh Pirates, their in-state rivals.[74] While rivalries are generally characterized by mutual hatred, the Braves and Phillies deeply respect each other. Each game played (18 games in 2011) is vastly important between these two NL East giants, but at the end of the day, they are very similar organizations.[75] Overall, the Braves have one more National League East division title than the Phillies, having won 12 times each since 1969, with the Braves holding it for eleven consecutive years from 1995 through 2005.
Uniforms
This section may be too long and excessively detailed. |
 |  |  |  |  |
|---|
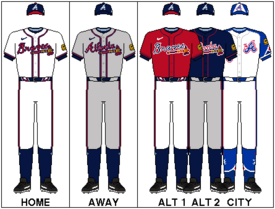
The Braves currently have five different game baseball uniform combinations. The home uniforms consist of a standard white uniform, a red, military appreciation jersey worn with the standard white pants, and a cream alternate uniform. The road uniforms consist of a standard gray uniform, and an alternate navy blue jersey worn with the standard gray pants.
The white home uniform, introduced in 1987, is the primary home uniform. The jersey has "Braves" written in script across the chest with the tomahawk logo underneath. The jersey also includes piping around the collar and down the front of the jersey and around the bottom of the sleeves. Player numbers appear on the back of the jersey with a nameplate above. The Braves script, player numbers, and piping are red with a navy blue border. The tomahawk is primarily red with blue and yellow detail and a navy blue border. The white pants have identical piping to the jersey about the belt loops and down the outside seam of the pants. The player names consist of navy blue lettering sewn to a white nameplate. The player names originally used vertically arched lettering but, since 2006, the team has used radially arched lettering. The white uniform is paired with the standard home cap. It is a red brimmed, navy blue cap with a white embroidered "script A" logo. The home batting helmet is identical to the primary home cap.[76]
The gray road uniforms are the primary road uniform. The uniforms are identical to the white home uniforms with the exception of the "Braves" script, which is replaced by the "Atlanta" script. Player names are sewn to a gray nameplate. The primary uniforms are very similar to the uniforms that the Braves wore from 1946 to 1965—during their latter years in Boston and throughout their tenure in Milwaukee.
The red, military appreciation jersey was introduced on February 5, 2014. The jerseys feature navy blue piping with a white border, the Braves script in blue with white stars, and the American Flag on the left sleeve. The updated red jerseys will not include the tomahawk logo. The jerseys will be worn for five home games in 2014: April 26 vs. the Cincinnati Reds (military family night), June 13 vs. the LA Angels of Anaheim (celebrating the Army), July 26 vs. the San Diego Padres (celebrating the Marines), Aug. 30 vs. the Miami Marlins (celebrating the Navy), and September 19 vs. NY Mets (celebrating the Air Force).[77] The jerseys will be paired with camouflage caps.[78] The military appreciation jerseys replace the red jerseys introduced in 2005.[79] Worn with the white pants, these jerseys included the same elements as the white jerseys, with the Braves script, player numbers, and piping in navy blue with a white border. The tomahawk was primarily blue, with red and yellow detail and a white border. The player names consisted of white lettering sewn to a red nameplate. These jerseys were paired with an alternate home cap, which was a red brimmed, navy blue cap with a red, embroidered "script A" logo with a tomahawk, outlined in white. The alternate cap did not have a matching batting helmet. The red alternate jerseys were worn for Sunday home games from 2005 to 2011. The only exceptions to this were the opening game of the 2005 NLDS, which was played on a Wednesday, and on Memorial Day in 2006. The 2006 Memorial Day game is also the only time the red jerseys were paired with the primary home cap. With the introduction of the cream uniform in 2012, the red jerseys were worn for Friday night home games from 2012 to 2013. However, the Braves chose to wear the traditional white jerseys for their 2012 home opener, which took place on Friday, April 13.
The cream alternate uniforms were introduced in February 2012 as a tribute to the Braves' first season in Atlanta in 1966. The jersey includes the "Braves" script across the breastplate, but the player number replaces the tomahawk underneath the "Braves" script on the left placket. Player numbers and the "Braves" script are in red with a navy blue border. The player names consist of navy blue lettering sewn to a cream nameplate. The jersey has a thin, navy piping about the collar and down the front of the jersey. There is no piping around the sleeves. The cream pants include piping identical to the jersey down the outside seam. The left sleeve of the jersey has a "crossed tomahawk" logo that replaces the "screaming Indian" logo that appeared on the 1966 jerseys. The new logo has two, primarily red, crossed tomahawks. Underneath the tomahawks is a blue circle outlined in red, with "1876" in red above (commemorating the year the franchise was founded), and "Atlanta Braves" in white below. The cream uniforms are paired with the standard home cap and are worn for Saturday and Sunday home games.[80]
The alternate navy blue road jerseys were introduced on opening night of the 2008 season against the Washington Nationals. Worn with the gray road pants, the jerseys feature the "Atlanta" script on the breastplate in navy blue with a white outline. The tomahawk is primarily navy blue with red and yellow detail and a white border. The player numbers are blue with white borders and the player names are white letters sewn to a navy blue nameplate. The navy blue jerseys have no piping either on the sleeves or around the collar.
From 1987 to 2008, the red brimmed, primary home cap was also worn on the road. However, when the navy blue jerseys were introduced in 2008, they were paired with a navy blue cap, similar to the team's road cap worn from 1966 to 1971. While the red brimmed cap was still primarily worn with the gray road uniforms, the team sometimes wore the navy blue cap with the gray jerseys, and the red brimmed cap was occasionally worn with the navy blue jerseys. The red brimmed home batting helmets were also worn on the road from 1987 through 2008. Beginning in 2009, the navy blue cap became the official road cap and was paired with a navy blue road batting helmet.
Unlike the home uniforms, which are worn based on a schedule, the road uniforms are chosen on game day by the starting pitcher. However, they are also subject to Major League Baseball rules requiring the road team to wear uniforms that contrast with the uniforms worn by the home team. Due to this rule, the gray uniforms are worn when the home team chooses to wear navy blue, and sometimes when the home team chooses to wear black.
Logos
From 1945 to 1955 the Braves primary logo consisted of the head of an Indian warrior.[81] From 1956 to 1965 it was a laughing Indian with a mohawk and one feather in his hair.[82] When the Braves moved to Atlanta in 1966, the "Braves" script was added underneath the laughing Indian.[83] In 1985, the Braves made a small script change to the logo.[83] The Braves modern logo debuted in 1987.[83] The modern logo is the word "Braves" in cursive with a tomahawk below it.[83] In 2018, the Braves made a subtle color change to the primary logo.[83]
Achievements
Awards
Team records
Team captains
Johnny Evers 1914–1917
Eddie Mathews 1965–1966
Hank Aaron 1969–1974
Bob Horner 1982–1986
Dale Murphy 1987-1990
Retired numbers
The Braves have retired eleven numbers in the history of the franchise, including most recently Chipper Jones' number 10 in 2013, John Smoltz's number 29 in 2012, Bobby Cox's number 6 in 2011, Tom Glavine's number 47 in 2010, and Greg Maddux's number 31 in 2009. Additionally, Hank Aaron's 44, Dale Murphy's 3, Phil Niekro's 35, Eddie Mathews' 41, Warren Spahn's 21 and Jackie Robinson's 42, which is retired for all of baseball with the exception of Jackie Robinson Day, have also been retired.[84] The color and design of the retired numbers reflect the uniform design at the time the person was on the team, excluding Robinson.[85]
|
Of the ten Braves whose numbers have been retired, all who are eligible for the National Baseball Hall of Fame have been elected with the exception of Murphy, whose eligibility has expired.
Braves Hall of Fame
Baseball Hall of Famers
| Atlanta Braves Hall of Famers | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Affiliation according to the National Baseball Hall of Fame and Museum | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Ford C. Frick Award recipients (broadcasters)
| Atlanta Braves Ford C. Frick Award recipients | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Affiliation according to the National Baseball Hall of Fame and Museum | |||||||||
|
Georgia Sports Hall of Fame
Braves in the Georgia Sports Hall of Fame | ||||
| No. | Player | Position | Tenure | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| — | Paul Richards | GM | 1967–1972 | |
| — | John Schuerholz | GM President | 1990–2007 2007–present | |
| — | Skip Caray | Broadcaster | 1976–2008 | |
| — | George Stallings | Manager | 1913–1920 | Born in Augusta |
| 3 | Dale Murphy | OF | 1976–1990 | |
| 4 | Jo-Jo White | Coach | 1963–1966 | Born in Red Oak |
| 5, 31 | Whit Wyatt | Coach | 1958–1967 | Born in Kensington, attended Georgia Tech |
| 6 | Bobby Cox | Manager | 1978–1981 1990–2010 | |
| 10 | Chipper Jones | 3B/LF | 1993–2012 | |
| 13 | Blue Moon Odom | P | 1975 | Elected mainly on his performance with Oakland A's, grew up in Macon |
| 29 | John Smoltz | P | 1988–1999 2001–2008 | |
| 32 | Ernie Johnson | P Broadcaster | 1950, 1952–1958 1962–1999 | |
| 35 | Phil Niekro | P | 1964–1983, 1987 | |
| 36 | Bob Hendley | P | 1961–1963 | Born in Macon |
| 44 | Hank Aaron | RF | 1954–1974 | |
Players
Current roster
Atlanta Braves 2019 spring training roster | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40-man roster | Non-roster invitees | Coaches/Other | ||||
Pitchers
| Catchers
Infielders
Outfielders
| Manager
Coaches
39 active, 0 inactive, 0 non-roster invitees
| ||||
Minor league affiliates
| Level | Team | League | Location |
|---|---|---|---|
AAA | Gwinnett Stripers | International League | Lawrenceville, Georgia |
AA | Mississippi Braves | Southern League | Pearl, Mississippi |
Advanced A | Florida Fire Frogs | Florida State League | Kissimmee, Florida |
A | Rome Braves | South Atlantic League | Rome, Georgia |
Rookie | Danville Braves | Appalachian League | Danville, Virginia |
GCL Braves | Gulf Coast League | Lake Buena Vista, Florida | |
DSL Braves | Dominican Summer League | Dominican Republic |
Home attendance
Turner Field
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
SunTrust Park
| |||||||||||||||||||
Radio and television
After years of stability, the Braves have faced a period of transition in their radio and television coverage.
The 2007 season was the last for Braves baseball on the TBS Superstation. TBS showed 70 games throughout the country, then cleared the decks to make way for a new national broadcast package that began in earnest with the 2007 postseason, and expanded to Sunday afternoon games in 2008. Until his dismissal in 2009, Chip Caray, one of the Braves' current broadcasters, called play-by-play for the national package, which includes the Division Series every season and alternating coverage of the ALCS and NLCS. Caray is joined by Joe Simpson, who has provided color commentary for the Braves since 1992.
Braves baseball had been on TBS since it was WTCG in 1972 and had been a cornerstone of the national superstation since it began in 1976. WPCH-TV/Peachtree TV, formerly WTBS Atlanta, still carried Braves games after 2007, but only in parts of the Southern United States. After the transfer of the channel's operations from Time Warner to Meredith Corporation, all Peachtree TV games were simulcast on Fox Sports South outside of the Peachtree TV coverage area in 2011 and 2012.[87] On February 27, 2013, it was announced that Fox Sports South and SportSouth (now called Fox Sports Southeast) would carry every regionally televised Braves game exclusively, ending the team's partnership with WPCH-TV after 40 years.[88]
After the 2004 season, longtime radio flagship station 750 WSB was replaced by WGST 640AM. Due to WGST's weak signal at night, which fails to cover the entire Atlanta metropolitan area, all games began to be simulcast on FM radio when the rights were transferred. The games first appeared on 96.1 WKLS (formerly "96 Rock") in 2005, but moved to country music station 94.9 WUBL ("94.9 The Bull") in 2007 after WKLS underwent a change in format from classic rock to active rock and became Project 9–6–1. As of the 2009 season, the Braves returned to WKLS on the FM frequency but remained on WGST on AM. It was announced that for the 2010 season, the Braves will be flagshipped on WCNN 680 The Fan and in Atlanta on the AM dial and WNNX 100.5 FM.[89]
The Atlanta Braves radio network currently serves 134 radio stations across the Southern United States, including 20 in Alabama, 4 in Florida, 68 in Georgia, 1 in Mississippi, 13 in North Carolina, 14 in South Carolina, and 14 in Tennessee.[90]
Since 2009, the radio announcers have been former Brewers announcer Jim Powell and Don Sutton. Sutton was released after the 2006 season and called Washington Nationals games on television from 2007 to 2008, but he has since returned for the 2009 season.[91] Longtime Braves voices Skip Caray and Pete Van Wieren were the primary play-by-play voices of Braves baseball until Skip's sudden death on August 3, 2008,[92] and Van Wieren's retirement after the 2008 season.[93]
References
Footnotes
^ The team's official colors are navy blue and scarlet red, according to the team's mascot (BLOOPER)'s official website.[1]
^ The Braves were founded in 1871. The Cubs are a full season older (originally formed as the Chicago White Stockings in 1870), Chicago did not sponsor a White Stockings team for two seasons due to the Great Chicago Fire. The Braves have played more consecutive seasons.
Citations
^ "Meet BLOOPER". Braves.com. MLB Advanced Media. Retrieved August 21, 2018..mw-parser-output cite.citationfont-style:inherit.mw-parser-output qquotes:"""""""'""'".mw-parser-output code.cs1-codecolor:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registrationcolor:#555.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration spanborder-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-errordisplay:none;font-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-errorfont-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-formatfont-size:95%.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-leftpadding-left:0.2em.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-rightpadding-right:0.2em
^ ab Bloom, Barry M. (May 16, 2007). "Braves sale is approved". Major League Baseball Advanced Media. Retrieved October 1, 2015.
^ "Executive Offices". Major League Baseball Advanced Media. Atlanta Braves. October 1, 2015. Retrieved October 1, 2015.
^ Nightengale, Bob (November 13, 2017). "Atlanta Braves hire Alex Anthopoulos as next general manager". USA Today. Retrieved November 13, 2017.
^ Bowman, Mark (November 11, 2013). "Braves leaving Turner Field for Cobb County". Braves.com. MLB Advanced Media. Retrieved October 1, 2015.
^ Bowman, Mark (January 17, 2017). "Braves eye new Spring Training complex in North Port". MLB.com. MLB Advanced Media. Retrieved August 23, 2017.
^ Murdock, Zack (January 17, 2017). "Atlanta Braves pick Sarasota County for spring training". Sarasota Herald-Tribune. Retrieved February 27, 2017.
^ "Yanks celebrate ninth straight East title". Retrieved July 11, 2008.
^ Bowman, Mark (September 13, 2006). "Braves have set lofty benchmark". Braves.com. MLB Advanced Media. Archived from the original on February 19, 2007. Retrieved August 21, 2018.
^ ab "Story of the Braves". Atlanta Braves. November 1, 2015. Archived from the original on October 30, 2015. Retrieved November 1, 2015.
^ Events of Saturday, April 22, 1876. Retrosheet. Retrieved 2011-09-30.
^ Noble, Marty (September 23, 2011). "MLB carries on strong, 200,000 games later: Look what they started on a ballfield in Philadelphia in 1876". MLB.com. Retrieved 2011-09-30.[B]aseball is about to celebrate its 200,000th game — [in the division series on] Saturday [October 1, 2011] ....
^ Thorn, John (May 4, 2015). "Why Is the National Association Not a Major League … and Other Records Issues". OurGame.MLBlogs.com. Major League Baseball Advanced Media. Retrieved November 1, 2015.The National Association, 1871–1875, shall not be considered as a 'major league' due to its erratic schedule and procedures, but it will continue to be recognized as the first professional baseball league.
^ Kaese, Harold The Boston Braves, Northeaster University Press, 1948.
^ "1914 Boston Braves Schedule by Baseball Almanac". Baseball-almanac.com. Retrieved July 25, 2011.
^ "1914 New York Giants Schedule by Baseball Almanac". Baseball-almanac.com. Retrieved July 25, 2011.
^ Cohen, Neft, Johnson and Deutsch, The World Series, The Dial Press, 1976.
^ abcd Neyer, Rob (2006). Rob Neyer's Big Book of Baseball Blunders. New York: Fireside. ISBN 978-0-7432-8491-2.
^ ab Bodley, Hal (September 16, 1993). "Pirates OK new realignment". USA Today. p. 1C.The Pirates will switch from the East next season. They opposed the move last week when realignment was approved, but agreed to allow Atlanta to move to the East.
^ ab Olson, Lisa (July 8, 2003). "Crazy scene at Shea takes luster off Mets-Braves rivalry". New York Daily News.
^ abc The subway series: the Yankees, the Mets and a season to remember. St. Louis, Mo.: The Sporting News. 2000. ISBN 978-0-89204-659-1.
^ Chass, Murray (October 17, 2000). "From Wild Card to World Series". New York Times.
^ The Sporting News Baseball Record Book, 2007, p. 29.
^ Pelline, Jeff (September 23, 1995). "Time Warner Closes Deal for Turner". San Francisco Chronicle.
^ Isidore, Chris (December 14, 2005). "Time Warner considers Braves sale". CNNMoney.com. Retrieved April 27, 2011.
^ Burke, Monte (May 5, 2008). "Braves' New World – Forbes Magazine". Forbes. Retrieved July 25, 2011.
^ Bowman, Mark (May 16, 2007). "Braves excited by news of team sale". Major League Baseball Advanced Media. Atlanta Braves. Retrieved October 1, 2015.
^ Bodley, Hal (October 12, 2007). "GM Schuerholz was Braves' guiding force". USA Today. Retrieved April 25, 2010.
^ Bowman. Mark."Atlanta adds Vazquez to new-look staff, Braves complete deal for durable veteran starter, reliever Logan". mlb.com, December 4, 2008.
^ "Tigers acquire Josh Anderson from Atlanta Braves" MLB.com, March 30, 2009.
^ "MLB.mlb.com". MLB.mlb.com. May 31, 2010. Retrieved July 25, 2011.
^ Barry M. Bloom. "MLB.mlb.com". MLB.mlb.com. Retrieved July 25, 2011.
^ "Sports.espn.go.com". ESPN. July 15, 2010. Retrieved July 25, 2011.
^ "Sports.espn.go.com". ESPN. August 1, 2010. Retrieved July 25, 2011.
^ Mark Bowman. "MLB.mlb.com". MLB.mlb.com. Retrieved July 25, 2011.
^ "Scores.espn.go.com". ESPN. August 22, 2010. Retrieved July 25, 2011.
^ "Braves act quickly, name Gonzalez skipper". Atlanta.braves.mlb.com. October 13, 2010. Archived from the original on June 16, 2011. Retrieved July 25, 2011.
^ "ESPN – Elias Says: Sports Statistics – Stats from the Elias Sports Bureau – ESPN". ESPN. Retrieved July 25, 2011.
^ "MLB Game Recap – Nationals v Braves | ajc.com". Ajc.stats.com. Retrieved July 25, 2011.
^ "Florida vs. Atlanta Recap: Marlins beat Atlanta 3–1, Braves' 10,000th loss". Sports Illustrated. July 31, 2011. Retrieved August 13, 2012.
^ Atlanta team statistics for 2010, 2011. baseball-reference.com. Accessed May 20, 2011.
^ "Braves collapsed before playoffs". ESPN. 29 September 2011.
^ "Anatomy of a Collapse (Or Three)". MLB Blog Buzz. September 29, 2011. Archived from the original on October 16, 2011.
^ abcd O'Brien, David (October 1, 2011). "Chronology of Braves' collapse". The Atlanta Journal-Constitution. Archived from the original on October 3, 2011. Retrieved April 19, 2018.
^ "Lowe dealt to Tribe for Minor League reliever". atlantabraves.com. 31 October 2011.
^ "Braves complete colossal collapse, lose to Phils". CBS Sports. 29 September 2011.
^ "Parrish let go as Braves hitting coach". atlantabraves.com. 30 September 2011.
^ "B.J. Upton introduced in Atlanta after signing deal".
^ "Justin Upton introduced, takes his place with Braves".
^ "Atlanta Braves beat Miami Marlins for 14th straight win". USA Today.
^ "Braves retire Chipper's No. 10 before game".
^ "Braves overcome injuries to capture National League East title".
^ "The Braves are leaving Turner Field after the 2016 season". NBCSports.com. November 11, 2013. Retrieved November 11, 2013.
^ "Braves plan to build new stadium in Cobb".
^ Brown, Maury (November 11, 2013). "Atlanta Braves Plan On Moving Into New $672 Million Ballpark In Cobb Co. – Forbes". Forbes.
^ "Atlanta Braves announce plans to move to new stadium". USA Today.
^ The Marietta Daily Journal – Braves headed to Cobb in 2017
^ "Stunning news: Atlanta Braves moving to Cobb".
^ Braves leaving Turner Field, building new stadium in Cobb Co. – Atlanta News, Weather, Traffic, and Sports | FOX 5 Archived November 11, 2013, at the Wayback Machine.
^ "Braves ship Heyward to Cards in 4-player deal".
^ [1]
^ "Braves trade Gattis to Astros for 3 prospects".
^ "Padres acquire Kimbrel, M. Upton from Braves".
^ "Braves' Hector Olivera arrested for assault".
^ Waldstein, David (2016-11-10). "R. A. Dickey Isn't Done; Signs One-Year Deal With Atlanta Braves". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 2016-11-18.
^ "BASEBALL: Atlanta Braves officially sign pitcher Bartolo Colon". savannahnow.com. Retrieved 2016-11-18.
^ Studenmund, Woody (May 3, 2017). "Atlanta's SunTrust Park: The First of a New Generation?". Hardball Times. Retrieved November 18, 2017.
^ ab Cooper, J.J. (May 2, 2017). "Braves' New Ballpark Has All Modern Touches, But It's What Surrounds SunTrust Park That Makes It Stand Out". Baseball America. Retrieved November 18, 2017.
^ "Braves GM John Coppolella Resigns Amid MLB Investigation Over International Signings". Sports Illustrated. October 2, 2017. Retrieved November 13, 2017.
^ abcd "Braves hire former Dodgers, Blue Jays exec Alex Anthopoulos as GM". ESPN. November 13, 2017. Retrieved November 13, 2017.
^ ab "John Hart steps down as senior advisor for Braves". ESPN. November 17, 2017. Retrieved November 18, 2017.
^ abcd "Ex-Braves GM John Coppolella permanently banned; team loses prospects". ESPN. November 21, 2017. Retrieved November 21, 2017.
^ Chass, Murray (September 16, 1993). "Pirates Relent on New Alignment". New York Times. p. B14.
^ Collier, Gene (September 27, 1993). "Pirates, Phillies Have Owned the Outgoing NL East Division". Pittsburgh Post-Gazette. p. D1.
^ Schultz, Jeff. "If Braves send message to Phillies, it will be done nicely". The Atlanta Journal Constitution. Archived from the original on April 11, 2011. Retrieved May 26, 2011.
^ "Braves Uniforms". Major League Baseball Advanced Media. Retrieved January 26, 2018.
^ Walton, Carroll Rogers (February 11, 2014). "Braves to honor military with alternative jerseys". The Atlanta Journal-Constitution. Retrieved April 19, 2018.
^ "Braves introduce alternate jersey".
^ O'Brien, David (February 5, 2014). "Braves' home-red jerseys dropped from lineup". The Atlanta Journal-Constitution. Retrieved April 19, 2018.
^ "Atlanta Braves unveil a new alternate home uniform". MLB Advanced Media. February 6, 2012. Retrieved April 19, 2018.
^ "Boston Braves Logos". SportsLogos.net. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
^ "Milwaukee Braves Logos". SportsLogos.net. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
^ abcde "Atlanta Braves Logos". SportsLogos.net. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
^ Araton, Harvey (April 14, 2010). "Yankees' Mariano Rivera Is the Last No. 42". The New York Times. Retrieved July 30, 2012.
^ Pahigian, Josh; Kevin O'Connell (2004). The Ultimate Baseball Road-trip: A Fan's Guide to Major League Stadiums. Globe Pequot. ISBN 1-59228-159-1.
^ ab "Atlanta Braves Attendance". baseball-reference.com. Retrieved 24 July 2012.
^ "MLB NOTEBOOK: FSN reaches agreement with Peachtree TV to broadcast 45 Braves games in 2011; Ex-Braves Jones signs with Yanks". Albanyherald.com. Retrieved July 25, 2011.
[dead link]
^ Tucker, Tim (March 1, 2013). "Braves' TV deal changes; games move off Peachtree TV". The Atlanta Journal-Constitution. Retrieved April 19, 2018.
^ Press Release- "Atlanta Braves and Clear Channel Announce Move to Project 9–6–1 for 2009 Games." March 2, 2009. Retrieved July 8, 2010.
^ "Affiliate Radio Stations | braves.com: Schedule". Atlanta.braves.mlb.com. Archived from the original on July 14, 2011. Retrieved July 25, 2011.
^ Rogers, Carroll (January 27, 2009). "Sutton rejoins Braves' broadcast team". Ajc.com. Archived from the original on June 29, 2011. Retrieved July 25, 2011.
^ "Sportingnews.com". Sportingnews.com. Archived from the original on August 9, 2008. Retrieved July 25, 2011.
^ Mark Bowman (October 21, 2008). "Atlanta.braves.mlb.com". Atlanta.braves.mlb.com. Archived from the original on June 16, 2011. Retrieved July 25, 2011.
Further reading
Wilkinson, Jack (2007). Game of my Life: Atlanta Braves. Champaign, Illinois: Sports Publishing LLC. ISBN 978-1-59670-099-4.
Green, Jr., Ron (2008). 101 Reasons to Love the Braves. Stewart, Tabori & Chang. ISBN 978-1-58479-670-1.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Atlanta Braves. |
- Atlanta Braves official website
Team index page at Baseball Reference- Milwaukee Braves informational website
- Sports Illustrated Atlanta Braves Page
- ESPN Atlanta Braves Page
- History of the Boston Braves on MassHistory.com
| Achievements | ||
|---|---|---|
| Preceded by Philadelphia Athletics 1913 | World Series champions Boston Braves 1914 | Succeeded by Boston Red Sox 1915 |
| Preceded by New York Yankees 1956 | World Series champions Milwaukee Braves 1957 | Succeeded by New York Yankees 1958 |
| Preceded by Toronto Blue Jays 1993 | World Series champions Atlanta Braves 1995 | Succeeded by New York Yankees 1996 |
| Achievements | ||
|---|---|---|
| Preceded by Chicago White Stockings 1876 | National League champions Boston Red Caps 1877 and 1878 | Succeeded by Providence Grays 1879 |
| Preceded by Chicago White Stockings 1882 | National League champions Boston Beaneaters 1883 | Succeeded by Providence Grays 1884 |
| Preceded by Brooklyn Bridegrooms 1890 | National League champions Boston Beaneaters 1891–1893 | Succeeded by Baltimore Orioles 1894 |
| Preceded by Baltimore Orioles 1896 | National League champions Boston Beaneaters 1897 and 1898 | Succeeded by Brooklyn Superbas 1899 |
| Preceded by New York Giants 1913 | National League champions Boston Braves 1914 | Succeeded by Philadelphia Phillies 1915 |
| Preceded by Brooklyn Dodgers 1947 | National League champions Boston Braves 1948 | Succeeded by Brooklyn Dodgers 1949 |
| Preceded by Brooklyn Dodgers 1956 | National League champions Milwaukee Braves 1957 and 1958 | Succeeded by Los Angeles Dodgers 1959 |
| Preceded by Cincinnati Reds 1990 | National League champions Atlanta Braves 1991 and 1992 | Succeeded by Philadelphia Phillies 1993 |
| Preceded by Philadelphia Phillies 1993 | National League champions Atlanta Braves 1995 and 1996 | Succeeded by Florida Marlins 1997 |
| Preceded by San Diego Padres 1998 | National League champions Atlanta Braves 1999 | Succeeded by New York Mets 2000 |














