Polytope

A polygon is a 2-dimensional polytope. Some polygons of different kinds: open (excluding its boundary), bounding circuit only (ignoring its interior), closed (both), and self-intersecting with varying densities of different regions.
In elementary geometry, a polytope is a geometric object with "flat" sides. It is a generalization in any number of dimensions of the three-dimensional polyhedron. Polytopes may exist in any general number of dimensions n as an n-dimensional polytope or n-polytope. Flat sides mean that the sides of a (k+1)-polytope consist of k-polytopes that may have (k-1)-polytopes in common. For example, a two-dimensional polygon is a 2-polytope and a three-dimensional polyhedron is a 3-polytope.
Some theories further generalize the idea to include such objects as unbounded apeirotopes and tessellations, decompositions or tilings of curved manifolds including spherical polyhedra, and set-theoretic abstract polytopes.
Polytopes in more than three dimensions were first discovered by Ludwig Schläfli. The German term polytop was coined by the mathematician Reinhold Hoppe, and was introduced to English mathematicians as polytope by Alicia Boole Stott.
Contents
1 Approaches to definition
2 Elements
3 Important classes of polytope
3.1 Convex polytopes
3.2 Regular polytopes
3.3 Star polytopes
4 Generalisations of a polytope
4.1 Infinite polytopes
4.2 Abstract polytopes
4.3 Complex polytopes
5 Duality
5.1 Self-dual polytopes
6 History
7 Applications
8 See also
9 References
10 External links
Approaches to definition
The term polytope is nowadays a broad term that covers a wide class of objects, and different definitions are attested in mathematical literature. Many of these definitions are not equivalent, resulting in different sets of objects being called polytopes. They represent different approaches to generalizing the convex polytopes to include other objects with similar properties.
The original approach broadly followed by Ludwig Schläfli, Thorold Gosset and others begins with the extension by analogy into four or more dimensions, of the idea of a polygon and polyhedron respectively in two and three dimensions.[1]
Attempts to generalise the Euler characteristic of polyhedra to higher-dimensional polytopes led to the development of topology and the treatment of a decomposition or CW-complex as analogous to a polytope.[2] In this approach, a polytope may be regarded as a tessellation or decomposition of some given manifold. An example of this approach defines a polytope as a set of points that admits a simplicial decomposition. In this definition, a polytope is the union of finitely many simplices, with the additional property that, for any two simplices that have a nonempty intersection, their intersection is a vertex, edge, or higher dimensional face of the two.[3] However this definition does not allow star polytopes with interior structures, and so is restricted to certain areas of mathematics.
The discovery of star polyhedra and other unusual constructions led to the idea of a polyhedron as a bounding surface, ignoring its interior.[4] In this light convex polytopes in p-space are equivalent to tilings of the (p−1)-sphere, while others may be tilings of other elliptic, flat or toroidal (p−1)-surfaces – see elliptic tiling and toroidal polyhedron. A polyhedron is understood as a surface whose faces are polygons, a 4-polytope as a hypersurface whose facets (cells) are polyhedra, and so forth.
The idea of constructing a higher polytope from those of lower dimension is also sometimes extended downwards in dimension, with an (edge) seen as a 1-polytope bounded by a point pair, and a point or vertex as a 0-polytope. This approach is used for example in the theory of abstract polytopes.
In certain fields of mathematics, the terms "polytope" and "polyhedron" are used in a different sense: a polyhedron is the generic object in any dimension (referred to as polytope in this Wikipedia article) and polytope means a bounded polyhedron.[5] This terminology is typically confined to polytopes and polyhedra that are convex. With this terminology, a convex polyhedron is the intersection of a finite number of halfspaces and is defined by its sides while a convex polytope is the convex hull of a finite number of points and is defined by its vertices.
Polytopes in lower numbers of dimensions have standard names:
| Dimension of polytope | Description[6] |
|---|---|
| −1 | Nullitope |
| 0 | Monon |
| 1 | Dion |
| 2 | Polygon |
| 3 | Polyhedron |
| 4 | Polychoron |
Elements
A polytope comprises elements of different dimensionality such as vertices, edges, faces, cells and so on. Terminology for these is not fully consistent across different authors. For example, some authors use face to refer to an (n − 1)-dimensional element while others use face to denote a 2-face specifically. Authors may use j-face or j-facet to indicate an element of j dimensions. Some use edge to refer to a ridge, while H. S. M. Coxeter uses cell to denote an (n − 1)-dimensional element.[7][citation needed]
The terms adopted in this article are given in the table below:
| Dimension of element | Term (in an n-polytope) |
|---|---|
| −1 | Nullity (necessary in abstract theory)[8] |
| 0 | Vertex |
| 1 | Edge |
| 2 | Face |
| 3 | Cell |
⋮displaystyle vdots  | ⋮displaystyle vdots  |
j | j-face – element of rank j = −1, 0, 1, 2, 3, ..., n |
⋮displaystyle vdots  | ⋮displaystyle vdots  |
n − 3 | Peak – (n − 3)-face |
n − 2 | Ridge or subfacet – (n − 2)-face |
n − 1 | Facet – (n − 1)-face |
n | The polytope itself |
An n-dimensional polytope is bounded by a number of (n − 1)-dimensional facets. These facets are themselves polytopes, whose facets are (n − 2)-dimensional ridges of the original polytope. Every ridge arises as the intersection of two facets (but the intersection of two facets need not be a ridge). Ridges are once again polytopes whose facets give rise to (n − 3)-dimensional boundaries of the original polytope, and so on. These bounding sub-polytopes may be referred to as faces, or specifically j-dimensional faces or j-faces. A 0-dimensional face is called a vertex, and consists of a single point. A 1-dimensional face is called an edge, and consists of a line segment. A 2-dimensional face consists of a polygon, and a 3-dimensional face, sometimes called a cell, consists of a polyhedron.
Important classes of polytope
Convex polytopes
A polytope may be convex. The convex polytopes are the simplest kind of polytopes, and form the basis for several different generalizations of the concept of polytopes. A convex polytope is sometimes defined as the intersection of a set of half-spaces. This definition allows a polytope to be neither bounded nor finite. Polytopes are defined in this way, e.g., in linear programming. A polytope is bounded if there is a ball of finite radius that contains it. A polytope is said to be pointed if it contains at least one vertex. Every bounded nonempty polytope is pointed. An example of a non-pointed polytope is the set (x,y)∈R2∣x≥0displaystyle (x,y)in mathbb R ^2mid xgeq 0
A certain class of convex polytopes are reflexive polytopes. An integral ddisplaystyle d













Regular polytopes
A regular polytope is the most highly symmetrical kind, with the various groups of elements being transitive on the symmetries of the polytope, such that the polytope is said to be transitive on its flags. Thus, the dual of a regular polytope is also regular.
There are three main classes of regular polytope which occur in any number n of dimensions:
Simplices, including the equilateral triangle and the regular tetrahedron.
Hypercubes or measure polytopes, including the square and the cube.
Orthoplexes or cross polytopes, including the square and regular octahedron.
Dimensions two, three and four include regular figures which have fivefold symmetries and some of which are non-convex stars, and in two dimensions there are infinitely many regular polygons of n-fold symmetry, both convex and (for n ≥ 5) star. But in higher dimensions there are no other regular polytopes.[1]
In three dimensions the convex Platonic solids include the fivefold-symmetric dodecahedron and icosahedron, and there are also four star Kepler-Poinsot polyhedra with fivefold symmetry, bringing the total to nine regular polyhedra.
In four dimensions the regular 4-polytopes include one additional convex solid with fourfold symmetry and two with fivefold symmetry. There are ten star Schläfli-Hess 4-polytopes, all with fivefold symmetry, giving in all sixteen regular 4-polytopes.
Star polytopes
A non-convex polytope may be self-intersecting; this class of polytopes include the star polytopes. Some regular polytopes are stars.[1]
Generalisations of a polytope
Infinite polytopes
Not all manifolds are finite. Where a polytope is understood as a tiling or decomposition of a manifold, this idea may be extended to infinite manifolds. plane tilings, space-filling (honeycombs) and hyperbolic tilings are in this sense polytopes, and are sometimes called apeirotopes because they have infinitely many cells.
Among these, there are regular forms including the regular skew polyhedra and the infinite series of tilings represented by the regular apeirogon, square tiling, cubic honeycomb, and so on.
Abstract polytopes
The theory of abstract polytopes attempts to detach polytopes from the space containing them, considering their purely combinatorial properties. This allows the definition of the term to be extended to include objects for which it is difficult to define an intuitive underlying space, such as the 11-cell.
An abstract polytope is a partially ordered set of elements or members, which obeys certain rules. It is a purely algebraic structure, and the theory was developed in order to avoid some of the issues which make it difficult to reconcile the various geometric classes within a consistent mathematical framework. A geometric polytope is said to be a realization in some real space of the associated abstract polytope.[10]
Complex polytopes
Structures analogous to polytopes exist in complex Hilbert spaces Cndisplaystyle mathbb C ^n
Duality
Every n-polytope has a dual structure, obtained by interchanging its vertices for facets, edges for ridges, and so on generally interchanging its (j−1)-dimensional elements for (n−j)-dimensional elements (for j = 1 to n−1), while retaining the connectivity or incidence between elements.
For an abstract polytope, this simply reverses the ordering of the set. This reversal is seen in the Schläfli symbols for regular polytopes, where the symbol for the dual polytope is simply the reverse of the original. For example, 4, 3, 3 is dual to 3, 3, 4.
In the case of a geometric polytope, some geometric rule for dualising is necessary, see for example the rules described for dual polyhedra. Depending on circumstance, the dual figure may or may not be another geometric polytope.[12]
If the dual is reversed, then the original polytope is recovered. Thus, polytopes exist in dual pairs.
Self-dual polytopes
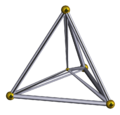
The 5-cell (4-simplex) is self-dual with 5 vertices and 5 tetrahedral cells.
If a polytope has the same number of vertices as facets, of edges as ridges, and so forth, and the same connectivities, then the dual figure will be similar to the original and the polytope is self-dual.
Some common self-dual polytopes include:
- Every regular n-simplex, in any number of dimensions, with Schlafli symbol 3n. These include the equilateral triangle 3, regular tetrahedron 3,3, and 5-cell 3,3,3.
- Every hypercubic honeycomb, in any number of dimensions. These include the apeirogon ∞, square tiling 4,4 and cubic honeycomb 4,3,4.
- Numerous compact, paracompact and noncompact hyperbolic tilings, such as the icosahedral honeycomb 3,5,3, and order-5 pentagonal tiling 5,5.
- In 2 dimensions, all regular polygons (regular 2-polytopes)
- In 3 dimensions, the canonical polygonal pyramids and elongated pyramids, and tetrahedrally diminished dodecahedron.
- In 4 dimensions, the 24-cell, with Schlafli symbol 3,4,3. Also the great 120-cell 5,5/2,5 and grand stellated 120-cell 5/2,5,5/2.
History
Polygons and polyhedra have been known since ancient times.
An early hint of higher dimensions came in 1827 when August Ferdinand Möbius discovered that two mirror-image solids can be superimposed by rotating one of them through a fourth mathematical dimension. By the 1850s, a handful of other mathematicians such as Arthur Cayley and Hermann Grassmann had also considered higher dimensions.
Ludwig Schläfli was the first to consider analogues of polygons and polyhedra in these higher spaces. He described the six convex regular 4-polytopes in 1852 but his work was not published until 1901, six years after his death. By 1854, Bernhard Riemann's Habilitationsschrift had firmly established the geometry of higher dimensions, and thus the concept of n-dimensional polytopes was made acceptable. Schläfli's polytopes were rediscovered many times in the following decades, even during his lifetime.
In 1882 Reinhold Hoppe, writing in German, coined the word polytop to refer to this more general concept of polygons and polyhedra. In due course Alicia Boole Stott, daughter of logician George Boole, introduced the anglicised polytope into the English language.[1]:vi
In 1895, Thorold Gosset not only rediscovered Schläfli's regular polytopes but also investigated the ideas of semiregular polytopes and space-filling tessellations in higher dimensions. Polytopes also began to be studied in non-Euclidean spaces such as hyperbolic space.
An important milestone was reached in 1948 with H. S. M. Coxeter's book Regular Polytopes, summarizing work to date and adding new findings of his own.
Meanwhile, the French mathematician Henri Poincaré had developed the topological idea of a polytope as the piecewise decomposition (e.g. CW-complex) of a manifold. Branko Grünbaum published his influential work on Convex Polytopes in 1967.
In 1952 Geoffrey Colin Shephard generalised the idea as complex polytopes in complex space, where each real dimension has an imaginary one associated with it. Coxeter developed the theory further.
The conceptual issues raised by complex polytopes, non-convexity, duality and other phenomena led Grünbaum and others to the more general study of abstract combinatorial properties relating vertices, edges, faces and so on. A related idea was that of incidence complexes, which studied the incidence or connection of the various elements with one another. These developments led eventually to the theory of abstract polytopes as partially ordered sets, or posets, of such elements. Peter McMullen and Egon Schulte published their book Abstract Regular Polytopes in 2002.
Enumerating the uniform polytopes, convex and nonconvex, in four or more dimensions remains an outstanding problem.
In modern times, polytopes and related concepts have found many important applications in fields as diverse as computer graphics, optimization, search engines, cosmology, quantum mechanics and numerous other fields. In 2013 the amplituhedron was discovered as a simplifying construct in certain calculations of theoretical physics.
Applications
In the field of optimization, linear programming studies the maxima and minima of linear functions; these maxima and minima occur on the boundary of an n-dimensional polytope. In linear programming, polytopes occur in the use of generalized barycentric coordinates and slack variables.
In twistor theory, a branch of theoretical physics, a polytope called the amplituhedron is used in to calculate the scattering amplitudes of subatomic particles when they collide. The construct is purely theoretical with no known physical manifestation, but is said to greatly simplify certain calculations.[13]
See also
- List of regular polytopes
Bounding volume-Discrete oriented polytope- Intersection of a polyhedron with a line
- Extension of a polyhedron
- Polytope de Montréal
- Honeycomb (geometry)
- Opetope
References
Notes
^ abcd Coxeter (1973)
^ Richeson, S.; Euler's Gem: The Polyhedron Formula and the Birth of Topology, Princeton University, 2008.
^ Grünbaum (2003)
^ Cromwell, P.; Polyhedra, CUP (ppbk 1999) pp 205 ff.
^ Nemhauser and Wolsey, "Integer and Combinatorial Optimization," 1999, .mw-parser-output cite.citationfont-style:inherit.mw-parser-output .citation qquotes:"""""""'""'".mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registrationcolor:#555.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration spanborder-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output code.cs1-codecolor:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-errordisplay:none;font-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-errorfont-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-maintdisplay:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-formatfont-size:95%.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-leftpadding-left:0.2em.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-rightpadding-right:0.2em
ISBN 978-0471359432, Definition 2.2.
^ Johnson, Norman W.; Geometries and Transformations, Cambridge University Press, 2018, p.224.
^ Regular polytopes, p. 127 The part of the polytope that lies in one of the hyperplanes is called a cell
^ Johnson, Norman W.; Geometries and Transformations, Cambridge University Press, 2018, p.224.
^ Beck, Matthias; Robins, Sinai (2007), Computing the Continuous Discretely, Integer-point enumeration in polyhedra, Undergraduate Texts in Mathematics, New York: Springer-Verlag,
ISBN 978-0-387-29139-0, MR 2271992
^ McMullen, Peter; Schulte, Egon (December 2002), Abstract Regular Polytopes (1st ed.), Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0-521-81496-0
^ Coxeter, H.S.M.; Regular Complex Polytopes, 1974
^ Wenninger, M.; Dual Models, CUP (1983).
^ Arkani-Hamed, Nima; Trnka, Jaroslav (2013). "The Amplituhedron". Journal of High Energy Physics. 2014. arXiv:1312.2007. Bibcode:2014JHEP...10..030A. doi:10.1007/JHEP10(2014)030.
Sources
.mw-parser-output .refbeginfont-size:90%;margin-bottom:0.5em.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>ullist-style-type:none;margin-left:0.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>ul>li,.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>dl>ddmargin-left:0;padding-left:3.2em;text-indent:-3.2em;list-style:none.mw-parser-output .refbegin-100font-size:100%
Coxeter, Harold Scott MacDonald (1973), Regular Polytopes, New York: Dover Publications, ISBN 978-0-486-61480-9.
Grünbaum, Branko (2003), Kaibel, Volker; Klee, Victor; Ziegler, Günter M., eds., Convex polytopes (2nd ed.), New York & London: Springer-Verlag, ISBN 0-387-00424-6.
Ziegler, Günter M. (1995), Lectures on Polytopes, Graduate Texts in Mathematics, 152, Berlin, New York: Springer-Verlag.
External links
| Look up polytope in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
- Weisstein, Eric W. "Polytope". MathWorld.
"Math will rock your world" – application of polytopes to a database of articles used to support custom news feeds via the Internet – (Business Week Online)- Regular and semi-regular convex polytopes a short historical overview:
Fundamental convex regular and uniform polytopes in dimensions 2–10 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Family | An | Bn | I2(p) / Dn | E6 / E7 / E8 / F4 / G2 | Hn | |||||||
Regular polygon | Triangle | Square | p-gon | Hexagon | Pentagon | |||||||
Uniform polyhedron | Tetrahedron | Octahedron • Cube | Demicube | Dodecahedron • Icosahedron | ||||||||
Uniform 4-polytope | 5-cell | 16-cell • Tesseract | Demitesseract | 24-cell | 120-cell • 600-cell | |||||||
Uniform 5-polytope | 5-simplex | 5-orthoplex • 5-cube | 5-demicube | |||||||||
Uniform 6-polytope | 6-simplex | 6-orthoplex • 6-cube | 6-demicube | 122 • 221 | ||||||||
Uniform 7-polytope | 7-simplex | 7-orthoplex • 7-cube | 7-demicube | 132 • 231 • 321 | ||||||||
Uniform 8-polytope | 8-simplex | 8-orthoplex • 8-cube | 8-demicube | 142 • 241 • 421 | ||||||||
Uniform 9-polytope | 9-simplex | 9-orthoplex • 9-cube | 9-demicube | |||||||||
Uniform 10-polytope | 10-simplex | 10-orthoplex • 10-cube | 10-demicube | |||||||||
| Uniform n-polytope | n-simplex | n-orthoplex • n-cube | n-demicube | 1k2 • 2k1 • k21 | n-pentagonal polytope | |||||||
| Topics: Polytope families • Regular polytope • List of regular polytopes and compounds | ||||||||||||

