Sedan (automobile)
@media all and (max-width:720px).mw-parser-output .tmulti>.thumbinnerwidth:100%!important;max-width:none!important.mw-parser-output .tmulti .tsinglefloat:none!important;max-width:none!important;width:100%!important;text-align:center



A sedan /sɪˈdæn/ — also saloon — is a passenger car in a three-box configuration with separate compartments for engine, passenger and cargo.[1]
Sedan's first recorded use as a name for an automobile body was in 1912.[2] The name comes from a 17th century development of a litter, the sedan chair, a one-person enclosed box with windows carried by porters.
Variations of the sedan style of body include: close-coupled sedan, club sedan, convertible sedan, fastback sedan, hardtop sedan, notchback sedan and sedanet/sedanette.
Contents
1 Definition
2 The name sedan
3 International terminology
4 Standard styles
4.1 Notchback sedans
4.2 Hatchback/liftback sedans
4.3 Fastback sedans
4.4 Hardtop sedans
5 Mid-20th century variations
5.1 Close-coupled sedans
5.2 Coach sedans
5.3 Close-coupled saloons
5.4 Club sedans
5.5 Sedanets
6 See also
7 References
Definition
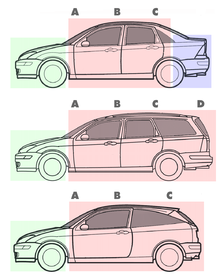
Typical profiles of a sedan, station wagon and hatchback
The current definition of a sedan is a car with a closed body (i.e. a fixed metal roof) with the engine, passengers and cargo in separate compartments.[3] This broad definition does not differentiate sedans from various other car body styles, but in practice the typical characteristics of sedans are:
- a B-pillar (between the front and rear windows) that supports the roof[4]
- two rows of seats[5](p134)
- a three-box design with the engine at the front and the cargo area at the rear[6][7]
- a less steeply sloping roofline than a coupé, which results in increased headroom for rear passenger and a less sporting appearance.[8]
- a rear interior volume of at least 33 cu ft (0.93 m3)[9][10]
It is sometimes suggested that sedans must have four doors (to provide a simple distinction between sedans and two-door coupés).[11] However, several sources state that a sedan can have two or four doors.[5](p134)[12][13] In addition, terms such as sedan and coupé have been more loosely interpreted by car manufacturers since 2010.[14]
When a manufacturer produces two-door sedan and four-door sedan versions of the same model, the shape and position of the greenhouse on both versions may be identical, with only the B-pillar positioned further back to accommodate the longer doors on the two-door versions.[15]
The name sedan

Turkish sedan chair from a historical exhibition
A sedan chair, a sophisticated litter, was an enclosed box with windows used to transport one person. It was carried by porters at the front and rear using horizontal poles.[16] Litters date back to long before ancient Egypt, India and China. Sedan chairs were developed in the 1630s. Their name came from the Latin sedere meaning to sit.[17]

Motor World November 14, 1912
Etymologists report the first recorded use of sedan for an automobile body occurred in 1912 when a new Studebaker model was described by its manufacturers as a sedan.[18] The same American dictionary provides this description: "Sedan (Chiefly North American) an enclosed automobile for four or more people, having two or four doors".[19]

1907 Cadillac with coupé body
There were fully enclosed automobile bodies before 1912. There is a claim that the body of a particular 1899 Renault Voiturette Type B is the first vehicle considered to be a sedan[20][21] although it was a two-door vehicle where the rear passengers sat outside the cabin. Other early cars which used a body style that would later be known as sedan are the 1905 Rational four-door limousine,[22](p573) 1907 Renault four-door limousine[22](p578) and 1910 Stella two-door saloon.[22](p649) On the other hand Georgano claims the earliest usage matching a modern definition of a sedan (i.e. a fixed roof car seating at least 4 people) was a 1911 Speedwell sedan manufactured in the United States.[23](p87)
International terminology
In American English and Latin American Spanish, the term sedan is used (accented as sedán in Spanish).[citation needed]
In British English, a car of this configuration is called a car or a saloon. Hatchback sedans are known simply as hatchbacks (not hatchback saloons); long-wheelbase luxury saloons with a division between the driver and passengers are limousines. Super saloon is often used to describe a high performance saloon car where sports saloon would have been used in the past. Saloon has been used by British car manufacturers in the United States, for example, the Rolls-Royce Park Ward.[citation needed]
In Australia and New Zealand sedan is now predominantly used, they were previously simply cars. In the 21st century saloon is still found in the long-established names of particular motor races.[citation needed]
In other languages, sedans are known as berline (French), berlina (European Spanish, European Portuguese, Romanian, and Italian) though they may include hatchbacks. These names, like sedan, all come from forms of passenger transport used before the advent of automobiles. In German sedans are berlines or limousines and limousines are stretch-limousines.[24]
Standard styles

Chrysler 300C notchback sedan
Notchback sedans
In the United States notchback sedan distinguishes models with a horizontal trunklid. The term is generally only referred to in the marketing when it is necessary to distinguish between two sedan body styles (e.g. notchback and fastback) of the same model range.
Hatchback/liftback sedans
Several sedans have a fastback profile, but instead of a trunk lid, the entire back of the vehicle lifts up (using a liftgate or hatch). Examples include the Chevrolet Malibu Maxx, Audi A5 Sportback and Tesla Model S.
The names "hatchback" and "sedan" are often used to differentiate between body styles of the same model. Therefore the term "hatchback sedan" is not often used, to avoid confusion.
Fastback sedans
There have been many sedans with a fastback style.
.mw-parser-output .mod-gallerydisplay:table.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery-defaultbackground:transparent;margin-top:0.5em.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery-centermargin-left:auto;margin-right:auto.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery-leftfloat:left.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery-rightfloat:right.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery-nonefloat:none.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery-collapsiblewidth:100%.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery .titledisplay:table-row.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery .title>divdisplay:table-cell;text-align:center;font-weight:bold.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery .maindisplay:table-row.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery .main>divdisplay:table-cell.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery .captiondisplay:table-row;vertical-align:top.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery .caption>divdisplay:table-cell;display:block;font-size:94%;padding:0.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery .footerdisplay:table-row.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery .footer>divdisplay:table-cell;text-align:right;font-size:80%;line-height:1em.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery .gallerybox .thumb imgbackground:none.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery .bordered-images imgborder:solid #eee 1px.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery .whitebg imgbackground:#fff!important.mw-parser-output .mod-gallery .gallerybox divbackground:#fff!important

VW
1939 Lincoln Zephyr

1948 Cadillac fastback

2013 Mercedes-Benz CLS
Hardtop sedans

1957 Cadillac four-door hardtop

1957 Sunbeam two-door hardtop
Hardtop sedans were a popular body style in the United States from the 1950s to the 1970s. Hardtops are manufactured without a B-pillar leaving uninterrupted open space or, when closed, glass along the side of the car.[25][26][27] The top was intended to look like a convertible's top but it was fixed and made of hard material that did not fold.[24]
All manufacturers in the United States from the early 1950s into the 1970s provided at least a 2-door hardtop model in their range and, if their engineers could manage it, a 4-door hardtop as well. The lack of side-bracing demanded a particularly strong and heavy chassis frame to combat unavoidable flexing. The fashion may have delayed the introduction of unibody construction.
In 1973 the US government passed Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard 216 creating a standard roof strength test to measure the integrity of roof structure in motor vehicles to come into effect some years later. Hardtop production stopped in 1976-1977. For a time roofs were covered with vinyl and B-pillars were minimised by using styling tricks like matt black finishes. Stylists and engineers soon developed more subtle solutions.[24]
Mid-20th century variations

1929 Packard Close Coupled Sedan
Close-coupled sedans
A close-coupled sedan is a body style produced in the United States during the 1920s and 1930s. Like other close-coupled body styles, the rear seats are located further forward than a regular sedan.[5](p43)[28] This reduced the length of the body, so close-coupled sedans (also known as town sedans) were the smallest of the sedan models offered.[29]
Models of close-coupled sedans include the Chrysler Imperial,[30][31]Duesenberg Model A[32] and Packard 745[33]
Coach sedans

1947 Bugatti Coach

1932 Chevrolet Coach
A two-door sedan for four or five passengers but with less room for passengers than a standard sedan. A Coach body has no external trunk for luggage. Haajanen notes it can be difficult to tell the difference between a Club and a Brougham and a Coach body as if manufacturers were more concerned with marketing their product than adhering to strict body style definitions.[24]

1967 Rover 3-litre coupé
Close-coupled saloons
Close-coupled saloons originated as four-door thoroughbred sporting horse-drawn carriages with little room for the feet of rear passengers.
In automotive use, manufacturers in the United Kingdom used the term for a development of the chummy body where passengers were forced to be friendly because they were tightly packed. They provided weather protection for extra passengers in what would otherwise be a two-seater car. Two-door versions would be described in the US and France as coach bodies.[34] A postwar example is the Rover 3 Litre Coupé.
Club sedans

1932 Buick series 90 Club Sedan

1954 Kaiser Manhattan Club Sedan
Produced in the United States from the mid-1920s to the mid-1950s, the name club sedan was used for highly appointed models using the sedan chassis.[5](p44) Some people describe a club sedan as a two-door vehicle with a body style otherwise identical to the sedan models in the range.[35] Others describe a club sedan as having either two or four doors and a shorter roof (and therefore less interior space) than the other sedan models in the range.[5](p44)
The term "club sedan" originates from the club carriage (e.g. the lounge or parlour carriage) in a railroad train.[5](p44)

1947 Buick Sedanet
Sedanets
From the 1910s to the 1950s, several United States manufacturers have named models either Sedanet or Sedanette. The term originated as a smaller version of the sedan,[36] however it has also been used for convertibles and fastback coupes.
Models which have been called Sedanet or Sedanette include: 1917 Dort Sedanet,[37]King,[36] 1919 Lexington,[36] 1930s Cadillac Fleetwood Sedanette,[38] 1949 Cadillac Series 62 Sedanette,[39] 1942-1951 Buick Super Sedanet[40][41] and 1956 Studebaker.
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Sedans. |
- Car classification
- Limousine
- Sports sedan
References
^ "Car Design Glossary - Part 2: One-Box (Monospace or Monovolume)". Car Design News. Archived from the original on 3 December 2013. Retrieved 9 September 2015.The principal volumes of the traditional sedan can be split into separate compartments or boxes: the hood/bonnet is the first box; the passenger compartment the second, and the trunk/boot the third - i.e. it's a 'three-box' car.
.mw-parser-output cite.citationfont-style:inherit.mw-parser-output qquotes:"""""""'""'".mw-parser-output code.cs1-codecolor:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registrationcolor:#555.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration spanborder-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-errordisplay:none;font-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-errorfont-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-formatfont-size:95%.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-leftpadding-left:0.2em.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-rightpadding-right:0.2em
^ "Where Does the Word "Sedan" Come From?". www.thenewswheel.com. 10 January 2017. Retrieved 25 November 2018.
^ "Definition of sedan in English by Oxford Dictionaries". www.oxforddictionaries.com. Retrieved 25 November 2018.
^ Duffy, James (2008). Auto Body Repair Technology (Fifth ed.). Cengage Learning. pp. 27–28. ISBN 9781418073541. Retrieved 9 September 2015.
^ abcdef Haajanen, Lennart W. (2007). Illustrated Dictionary of Automobile Body Styles. McFarland. ISBN 9780786437375. Retrieved 9 September 2015.
^ Morello, Lorenzo (2011). The automotive body - Volume I, Components design. Springer. p. 184. ISBN 9789400705128. Retrieved 9 September 2015.
^ "Starting Out: Car Design Glossary - Part 2". www.cardesignnews.com. Archived from the original on 3 December 2013.
^ "What is the difference between coupe and sedan?". www.chicagotribune.com. Retrieved 25 November 2018.
^ "Club Coupes". www.hemmings.com. Retrieved 7 December 2018.
^ "Coupe vs. Sedan: What's the Difference and Definitions of the Body Styles?". www.automoblog.net. 12 February 2009. Retrieved 7 December 2018.
^ "A Sedan or a Coupe? What's the difference?". www.middletownhonda.com. 31 July 2013. Retrieved 25 November 2018.
^ Morello, L.; Rossini, Lorenzo Rosti; Pia, Giuseppe; Tonoli, Andrea (2011). The Automotive Body: Volume I: Components Design. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 184. ISBN 9789400705135.
^ "Coupe vs. Sedan: What's the Difference and Definitions of the Body Styles?". www.automoblog.net. Retrieved 25 November 2018.
^ "Range Rover's $295K Coupe SUV Proves No Niche Is Too Small". www.wired.com. Retrieved 25 November 2018.
^ "1962 Rambler Brochure". oldcarbrochures.com. pp. 6–7. Retrieved 9 September 2015.
^ "Definition of sedan". www.oxforddictionaries.com.
^ "sedan (n.)". www.etymonline.com. Retrieved 17 November 2018.
^ The Motor World, November 14, 1912 page 18. Motor World Publishing Company, New York
^ Stevenson, Lindberg, ed. New Oxford American Dictionary, Oxford University Press, 2011 eISBN: 9780199891535
^ "Renault Voiturette Type B (1899)". www.speeddoctor.net. Retrieved 18 November 2018.
^ "Renault's first ever car attends Paris Motor Show". www.autoclassics.com. Retrieved 18 November 2018.
^ abc Georgano, G.N. (1973). The Complete Encyclopedia of Motorcars: 1885 to the Present. New York: Dutton. ISBN 0-525-08351-0.
^ Georgano, G.N (1985). Cars: Early and Vintage, 1886-1930. London: Grange-Universal.
^ abcd Haajanen, Lennart W. (2007). Illustrated Dictionary of Automobile Body Styles. McFarland. ISBN 9780786437375.
^ "Hardtop meaning". Engineering Dictionary. Retrieved 6 March 2018.
^ Thomas, Alfred; Jund, Michael (2009). Collision repair and refinishing: a foundation course for technicians. Cengage Learning. p. 164. ISBN 978-1-4018-8994-4. Retrieved 28 February 2013.
^ "Rambler has everything new - even a hardtop wagon". Popular Mechanics. 105 (1): 116–117. January 1956. Retrieved 28 February 2013.
^ Severson, Aaron (15 August 2009). "From Pillar to Post: More Automotive Definitions". www.ateupwithmotor.com. Retrieved 11 December 2018.
^ Cummings, Christopher (2014). Cadillac V-16s Lost and Found: Tracing the Histories of the 1930s Classics. McFarland. p. 50.
^ "1931 Chrysler Imperial Close Coupled Sedan". www.imperialclub.org. Retrieved 24 November 2018.
^ "1931 Chrysler Imperial Close-Coupled Sedan". www.rmsothebys.com. 22 July 2017. Retrieved 24 November 2018.
^ "1925 Duesenberg Model A Close Coupled Sedan - Amazing Original Car!". www.car-from-uk.com. Retrieved 24 November 2018.
^ "1930 Packard". www.sealcoveautomuseum.org. Retrieved 24 November 2018.
^ Haajanen, Lennart W. (2007). Illustrated Dictionary of Automobile Body Styles. McFarland. ISBN 9780786437375. Retrieved 24 December 2018.
^ "Club Coupes". www.hemmings.com. Retrieved 18 November 2018.
^ abc Haajanen, Lennart W. (2017). Illustrated Dictionary of Automobile Body Styles, 2d ed. McFarland. p. 136. ISBN 9780786499182. Retrieved 25 November 2018.
^ Dort Motor Car Co, Wisconsin Motorist November 1916, H A Apple, publisher, Milwaukee
^ GM Heritage Centre
^ Willson, Quentin (1997). Classic American Cars. DK Publishing. ISBN 9780789420831. Retrieved 25 November 2018.
^ "1948 Buick Series 40 Special Sedanet – Just A Few Inches Short Of A GM's Greatest Hit". www.curbsideclassic.com. Retrieved 25 November 2018.
^ "Fastback Fascination – 1949 Buick Model 56-S Super Sedanet". www.hemmings.com. Retrieved 25 November 2018.




