Dimethylglyoxime
 | |||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||
| Names | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
IUPAC name N,N′-Dihydroxy-2,3-butanediimine | |||||||||||||
Other names
| |||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||
CAS Number |
| ||||||||||||
3D model (JSmol) |
| ||||||||||||
ChEMBL |
| ||||||||||||
ChemSpider |
| ||||||||||||
ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.201 | ||||||||||||
EC Number | 202-420-1 | ||||||||||||
PubChem CID |
| ||||||||||||
RTECS number | EK2975000 | ||||||||||||
UNII |
| ||||||||||||
InChI
| |||||||||||||
SMILES
| |||||||||||||
| Properties | |||||||||||||
Chemical formula | C4H8N2O2 | ||||||||||||
Molar mass | 116.12 g·mol−1 | ||||||||||||
| Appearance | White/Off White Powder | ||||||||||||
Density | 1.37 g/cm3 | ||||||||||||
Melting point | 240 to 241 °C (464 to 466 °F; 513 to 514 K) | ||||||||||||
Boiling point | decomposes | ||||||||||||
Solubility in water | low | ||||||||||||
| Structure | |||||||||||||
Dipole moment | 0 | ||||||||||||
| Hazards | |||||||||||||
| Main hazards | Toxic, Skin/Eye Irritant | ||||||||||||
Safety data sheet | External MSDS | ||||||||||||
GHS pictograms |   | ||||||||||||
GHS signal word | Danger | ||||||||||||
GHS hazard statements | H228, H301 | ||||||||||||
GHS precautionary statements | P210, P240, P241, P264, P270, P280, P301+310, P321, P330, P370+378, P405, P501 | ||||||||||||
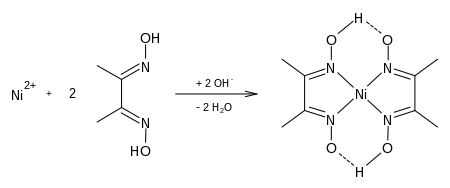
NFPA 704 | | Related compounds | Related compounds Hydroxylamine salicylaldoxime Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). Infobox references Dimethylglyoxime is a chemical compound described by the formula CH3C(NOH)C(NOH)CH3. Its abbreviation is dmgH2 for neutral form, and dmgH for anionic form, where H stands for hydrogen. This colourless solid is the dioxime derivative of the diketone butane-2,3-dione (also known as diacetyl). DmgH2 is used in the analysis of palladium or nickel. Its coordination complexes are of theoretical interest as models for enzymes and as catalysts. Many related ligands can be prepared from other diketones, e.g. benzil.
| |||||||||||