Portuguese language
| Portuguese | |
|---|---|
português, língua portuguesa | |
| Pronunciation | [puɾtuˈɣeʃ], [poʁtuˈɡes] |
| Native to | Primarily Portugal and Brazil; other Lusophone countries |
| Ethnicity | Lusophones
|
Native speakers | 220 million (2012–2016)[1] 20 million L2 speakers[1] |
Language family | Indo-European
|
Early form | Old Portuguese (Galician-Portuguese) |
Writing system | Latin (Portuguese alphabet) Portuguese Braille |
Signed forms | Manually coded Portuguese |
| Official status | |
Official language in | 9 countries
1 dependency
|
Recognised minority language in | Cultural language
Numerous international organisations |
| Regulated by | International Portuguese Language Institute Academia Brasileira de Letras (Brazil) Academia das Ciências de Lisboa, Classe de Letras (Portugal) Academia Galega da Língua Portuguesa (Galicia) CPLP |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | pt |
| ISO 639-2 | por |
| ISO 639-3 | por |
| Glottolog | port1283[6] |
| Linguasphere | 51-AAA-a |
 Native language Official and administrative language Cultural or secondary language Portuguese speaking minorities Portuguese-based creole languages | |
Portuguese (português or, in full, língua portuguesa) is a Western Romance language originating in the Iberian Peninsula. It is the sole official language of Portugal, Brazil, Cape Verde, Guinea-Bissau, Mozambique, Angola, and São Tomé and Príncipe.[7] It also has co-official language status in East Timor, Equatorial Guinea and Macau in China. As the result of expansion during colonial times, a cultural presence of Portuguese and Portuguese creole speakers are also found in Goa, Daman and Diu in India;[8] in Batticaloa on the east coast of Sri Lanka; in the Indonesian island of Flores; in the Malacca state of Malaysia; and the ABC islands in the Caribbean where Papiamento is spoken, while Cape Verdean Creole is the most widely spoken Portuguese-based Creole. A Portuguese-speaking person or nation may be referred to as "Lusophone" in both English and Portuguese.
Portuguese is part of the Ibero-Romance group that evolved from several dialects of Vulgar Latin in the medieval Kingdom of Galicia and the County of Portugal, and has kept some Celtic phonology and lexicon.[9][10] With approximately 215 to 220 million native speakers and 250 million total speakers, Portuguese is usually listed as the sixth most natively spoken language in the world, the third-most spoken European language in the world in terms of native speakers,[11] and the most spoken language in the Southern Hemisphere. It is also the most spoken language in South America and the second-most spoken in Latin America after Spanish, one of the 10 most spoken languages in Africa[12] and is an official language of the European Union, Mercosur, OAS, ECOWAS and the African Union.
Contents
1 History
2 Geographic distribution
2.1 Official status
2.2 Lusophone countries
2.3 Portuguese as a foreign language
2.4 Future
3 Dialects
3.1 Brazil
3.2 Portugal
3.3 Other countries and dependencies
3.4 Characterization and peculiarities
4 Vocabulary
5 Classification and related languages
5.1 Galician-Portuguese in Spain
5.2 Influence on other languages
5.3 Derived languages
6 Phonology
6.1 Vowels
6.2 Consonants
7 Grammar
8 Writing system
8.1 Spelling reforms
9 See also
10 References
10.1 Citations
10.2 Sources
11 External links
History
When the Romans arrived at the Iberian Peninsula in 216 B.C., they brought the Latin language with them, from which all Romance languages descend. The language was spread by Roman soldiers, settlers, and merchants, who built Roman cities mostly near the settlements of previous Celtic or Celtiberian civilizations established long before the Roman arrivals. For that reason, the language has kept a relevant substratum of much older, Atlantic European Megalithic Culture[13] and Celtic culture[14].
Between 409 A.D. and 711 A.D., as the Roman Empire collapsed in Western Europe, the Iberian Peninsula was conquered by Germanic peoples of the Migration Period. The occupiers, mainly Suebi[15][16], Visigoths and Buri[17] who originally spoke Germanic languages, quickly adopted late Roman culture and the Vulgar Latin dialects of the peninsula and over the next 300 years totally integrated into the local populations. After the Moorish invasion beginning in 711, Arabic became the administrative and common language in the conquered regions, but most of the remaining Christian population continued to speak a form of Romance commonly known as Mozarabic, which lasted three centuries longer in Spain.
Portuguese evolved from the medieval language, known today by linguists as Galician-Portuguese, Old Portuguese or Old Galician, of the northwestern medieval Kingdom of Galicia and County of Portugal. It is in Latin administrative documents of the 9th century that written Galician-Portuguese words and phrases are first recorded. This phase is known as Proto-Portuguese, which lasted from the 9th century until the 12th-century independence of the County of Portugal from the Kingdom of León, which had by then assumed reign over Galicia.
In the first part of the Galician-Portuguese period (from the 12th to the 14th century), the language was increasingly used for documents and other written forms. For some time, it was the language of preference for lyric poetry in Christian Hispania, much as Occitan was the language of the poetry of the troubadours in France. The Occitan digraphs lh and nh, used in its classical orthography, were adopted by the orthography of Portuguese, presumably by Gerald of Braga,[18] a monk from Moissac, who became bishop of Braga in Portugal in 1047, playing a major role in modernizing written Portuguese using classical Occitan norms.[19]. Portugal became an independent kingdom in 1139, under King Afonso I of Portugal. In 1290, King Denis of Portugal created the first Portuguese university in Lisbon (the Estudos Gerais, which later moved to Coimbra) and decreed for Portuguese, then simply called the "common language", to be known as the Portuguese language and used officially.
In the second period of Old Portuguese, in the 15th and 16th centuries, with the Portuguese discoveries, the language was taken to many regions of Africa, Asia, and the Americas. By the mid-16th century, Portuguese had become a lingua franca in Asia and Africa, used not only for colonial administration and trade but also for communication between local officials and Europeans of all nationalities.
Its spread was helped by mixed marriages between Portuguese and local people and by its association with Roman Catholic missionary efforts, which led to the formation of creole languages such as that called Kristang in many parts of Asia (from the word cristão, "Christian"). The language continued to be popular in parts of Asia until the 19th century. Some Portuguese-speaking Christian communities in India, Sri Lanka, Malaysia, and Indonesia preserved their language even after they were isolated from Portugal.
The end of the Old Portuguese period was marked by the publication of the Cancioneiro Geral by Garcia de Resende, in 1516. The early times of Modern Portuguese, which spans the period from the 16th century to the present day, were characterized by an increase in the number of learned words borrowed from Classical Latin and Classical Greek because of the Renaissance (learned words borrowed from Latin also came from Renaissance Latin, the form of Latin during that time), which greatly enriched the lexicon. Most literate Portuguese speakers were also literate in Latin; and thus they easily adopted Latin words into their writing—and eventually speech—in Portuguese.[citation needed]
Spanish author Miguel de Cervantes once called Portuguese "the sweet and gracious language", while the Brazilian poet Olavo Bilac described it as a última flor do Lácio, inculta e bela ("the last flower of Latium, rustic and beautiful"). Portuguese is also termed "the language of Camões", after Luís Vaz de Camões, one of the greatest literary figures in the Portuguese language and author of the Portuguese epic poem Os Lusíadas.[20][21][22]
In March 2006, the Museum of the Portuguese Language, an interactive museum about the Portuguese language, was founded in São Paulo, Brazil, the city with the greatest number of Portuguese language speakers in the world.[23] The museum is the first of its kind in the world.[23] In 2015 the museum was destroyed in a fire, but there are plans to reconstruct it.[24]
Geographic distribution

Multilingual sign in Japanese, Portuguese, and English in Oizumi, Japan. Return immigration of Japanese Brazilians has led to a large Portuguese-speaking community in the town.[25]
Portuguese is the native language of the vast majority of people in Brazil[26] and Portugal,[27] and 99.8% of the population of São Tomé and Príncipe declared speaking Portuguese in the 1991 census.[citation needed] Perhaps 75% of the population of Angola speaks Portuguese natively,[28] and 85% are more or less fluent.[29] Just over 40% (and rapidly increasing) of the population of Mozambique are native speakers of Portuguese, and 60% are fluent, according to the 2007 census.[30] Portuguese is also spoken natively by 30% of the population in Guinea-Bissau, and a Portuguese-based creole is understood by all.[31] No data is available for Cape Verde, but almost all the population is bilingual, and the monolingual population speaks Cape Verdean Creole.
There are also significant Portuguese speaking immigrant communities in many countries including Andorra (15.4%),[32]Bermuda,[33]Canada (400,275 people in the 2006 census),[34]France (900,000 people),[35]Japan (400,000 people),[36]Jersey,[37]Namibia (about 4–5% of the population, mainly refugees from Angola in the north of the country),[38]Paraguay (10.7% or 636,000 people),[39]Macau (0.6% or 12,000 people),[40]Switzerland (196,000 nationals in 2008),[41]Venezuela (554,000).[42] and the United States (0.35% of the population or 1,228,126 speakers according to the 2007 American Community Survey).[43]
In some parts of former Portuguese India, namely Goa[44] and Daman and Diu,[45] the language is still spoken by about 10,000 people. In 2014, an estimated 1,500 students were learning Portuguese in Goa.[46]
Official status
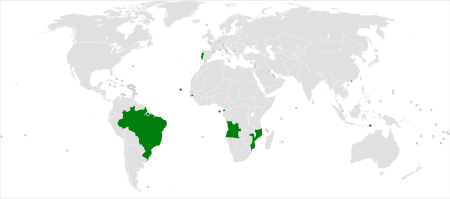
Countries and regions where Portuguese has official status.
The Community of Portuguese Language Countries[7]
(in Portuguese Comunidade dos Países de Língua Portuguesa, with the Portuguese acronym CPLP) consists of the eight independent countries that have Portuguese as an official language: Angola, Brazil, Cape Verde, East Timor, Equatorial Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Mozambique, Portugal and São Tomé and Príncipe.[7]
Equatorial Guinea made a formal application for full membership to the CPLP in June 2010, a status given only to states with Portuguese as an official language.[47] In 2011, Portuguese became its third official language (besides Spanish and French)[48] and, in July 2014, the country was accepted as a member of the CPLP.[49]
Portuguese is also one of the official languages of the Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China of Macau (alongside Chinese) and of several international organizations, including the Mercosur,[50] the Organization of Ibero-American States,[51] the Union of South American Nations,[52] the Organization of American States,[53] the African Union,[54] the Economic Community of West African States,[54] the Southern African Development Community[54] and the European Union.[55]
Lusophone countries
According to The World Factbook country population estimates for 2017, the population of each of the ten jurisdictions is as follows (by descending order):
| Country | Population (July 2017 est.)[56] | More information | Native language of the majority | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 207,353,391 | Portuguese in Brazil | Spoken by vast majority as a native language | ||
| 29,310,273 | Portuguese in Angola | Spoken by a majority (70%) as a native language; spoken by majority as a second language | ||
| 26,573,706 | Portuguese in Mozambique | Spoken by a significant minority as a native language; spoken by majority as a second language | ||
| 10,839,514 | Portuguese in Portugal1 | Spoken by vast majority as a native language | ||
| 1,792,338 | Portuguese in Guinea-Bissau | Spoken by a significant minority as a native language | ||
| 1,291,358 | Portuguese in East Timor | Spoken by a small minority as a second language | ||
| 778,358 | Portuguese in Equatorial Guinea | Spoken by a significant minority as a native language | ||
| 601,969 | Portuguese in Macau | Spoken by a small minority as a native language | ||
| 560,899 | Portuguese in Cape Verde | Spoken by majority as a second language | ||
| 201,025 | Portuguese in São Tomé and Príncipe | Spoken by vast majority as a native language | ||
| Total | c. 279 million | Community of Portuguese Language Countries |
Notes:
- Some linguists argue that Galician, spoken in Galicia, is merely a dialect of Portuguese rather than an independent language; this would make northwestern Spain a part of the Portuguese-speaking world.
Macau is not a sovereign nation. It is one of the two semi-autonomous Special Administrative Regions of the People's Republic of China (the other being Anglophone Hong Kong, a former British colony).- Equatorial Guinea adopted Portuguese as one of its official languages in 2007, being admitted to CPLP in 2014. The use of the Portuguese language in this country is limited. However, a Portuguese-based creole language, Annobonese Creole, is used, mainly on the islands of Annobon and Bioko.
The combined population of the entire Lusophone area was estimated at 279 million in July 2017. This number does not include the Lusophone diaspora, estimated at approximately 10 million people (including 4.5 million Portuguese, 3 million Brazilians, and half a million Cape Verdeans, among others), although it is hard to obtain official accurate numbers of diasporic Portuguese speakers because a significant portion of these citizens are naturalized citizens born outside of Lusophone territory or are children of immigrants, and may have only a basic command of the language. Additionally, a large part of the diaspora is a part of the already-counted population of the Portuguese-speaking countries and territories, such as the high number of Brazilian and PALOP emigrant citizens in Portugal or the high number of Portuguese emigrant citizens in the PALOP and Brazil.
The Portuguese language therefore serves more than 250 million people daily, who have direct or indirect legal, juridical and social contact with it, varying from the only language used in any contact, to only education, contact with local or international administration, commerce and services or the simple sight of road signs, public information and advertising in Portuguese.
Portuguese as a foreign language
Portuguese is a mandatory subject in the school curriculum in Uruguay.[57] Other countries where Portuguese is commonly taught in schools or where it is being introduced as an option now include Venezuela,[58]Zambia,[59] the Republic of the Congo,[60]Senegal,[60]Namibia,[38]Swaziland,[60] and South Africa.[60] In all of the listed countries Portuguese is spoken either as native language by minorities due to the Portuguese colonial past or as a lingua franca in bordering and multilingual regions, such as on the border between Brazil and Uruguay and Angola and Namibia.
| Country | Population (July 2017 est.)[61] | More information | Mandatory taught | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3,444,006 | Portuguese in Uruguay | Spoken by a significant minority as a native language | ||
| 43,847,430 | Portuguese in Argentina | Spoken by a minority as a second language | ||
| 7,052,984 | Portuguese in Paraguay | Spoken by a significant minority as a native language | ||
| 31,568,179 | Portuguese in Venezuela | Spoken by a minority as a second language | ||
| 57,725,600 | Portuguese in South Africa | Spoken by a small minority as a native language | ||
| 2,606,971 | Portuguese in Namibia | Spoken by a small minority as a native language | ||
| 5,125,821 | Portuguese in Congo | Spoken by a small minority as a second language | ||
| 16,591,390 | Portuguese in Zambia | Spoken by a small minority as a second language | ||
| 15,411,614 | Portuguese in Senegal | Spoken by a small minority as a second language | ||
| 1,343,098 | Portuguese in Eswatini | Spoken by a small minority as a second language |
Future
According to estimates by UNESCO, Portuguese is the fastest-growing European language after English and the language has, according to the newspaper The Portugal News publishing data given from UNESCO, the highest potential for growth as an international language in southern Africa and South America.[62] Portuguese is a globalized language spoken officially on five continents, and as a second language by millions worldwide.
Since 1991, when Brazil signed into the economic community of Mercosul with other South American nations, namely Argentina, Uruguay and Paraguay, Portuguese is either mandatory, or taught, in the schools of those South American countries.
Although early in the 21st century, after Macau was ceded to China and Brazilian immigration to Japan slowed down, the use of Portuguese was in decline in Asia, it is once again becoming a language of opportunity there, mostly because of increased diplomatic and financial ties with economically powerful Portuguese-speaking countries (Brazil, Angola, Mozambique, etc.) in the world.[63]
Dialects
Ethnically diverse East Timor has Portuguese as one of its official languages
Você, a pronoun meaning "you", is used for educated, formal, and colloquial respectful speech in most Portuguese-speaking regions. In the Brazilian state of Rio Grande do Sul, você is virtually absent from the spoken language. In Portugal, it may be considered disrespectful to treat a stranger as você, so the pronoun is either replaced by the name of the person (or a title) or it is omitted, since the verbal conjugation allows the distinction between formal and informal treatment. Riograndense (or Gaúcho) Portuguese normally distinguishes formal from informal speech by verbal conjugation. Informal speech employs tu followed by third person verbs, formal language retains the traditional second person.
Conjugation of tu has three different forms in Brazil (verb "to see": tu viste?, in the traditional second person, tu viu?, in the third person, and tu visse?, in the innovative second person), the conjugation used in the Brazilian states of Pará, Santa Catarina and Maranhão being generally traditional second person, the kind that is used in other Portuguese-speaking countries and learned in Brazilian schools.
The predominance of Southeastern-based media products has established você as the pronoun of choice for the second person singular in both writing and multimedia communications. However, in the city of Rio de Janeiro, the country's main cultural centre, the usage of tu has been expanding ever since the end of the 20th century (see,[64] a linguistic research on the topic in Portuguese), being most frequent among youngsters and a number of studies have also shown an increase in its use in a number of other Brazilian dialects.[65][66]

The status of second person pronouns in Brazil. Red indicates near exclusive use of você. Mauve indicates decidedly predominant use of tu, but with near exclusive third person (você-like) verbal conjugation. Brown indicates 50-50 tu/você variation, being tu nearly always accompanied by third person (você-like) verbal conjugation. Light blue indicates decidedly predominant to near exclusive use of tu with reasonable frequency of second person (tu-like) verbal conjugation. Yellow indicates balanced você/tu distribution, being tu exclusively accompanied by third person (você-like) verbal conjugation. Green indicates balanced você/tu distribution, tu being predominantly accompanied by third person (você-like) verbal conjugation.
Modern Standard European Portuguese (português padrão or português continental) is based on the Portuguese spoken in the area including and surrounding the cities of Coimbra and Lisbon, in central Portugal. Standard European Portuguese is also the preferred standard by the Portuguese-speaking African countries. As such, and despite the fact that its speakers are dispersed around the world, Portuguese has only two dialects used for learning: the European and the Brazilian. Some aspects and sounds found in many dialects of Brazil are exclusive to South America, and cannot be found in Europe. However, the Santomean Portuguese in Africa may be confused with a Brazilian dialect by its phonology and prosody.
Audio samples of some dialects and accents of Portuguese are available below.[67] There are some differences between the areas but these are the best approximations possible. IPA transcriptions refer to the names in local pronunciation.
Brazil
Caipira — Spoken in the states of São Paulo (most markedly on the countryside and rural areas); southern Minas Gerais, northern Paraná and southeastern Mato Grosso do Sul. Depending on the vision of what constitutes caipira, Triângulo Mineiro, border areas of Goiás and the remaining parts of Mato Grosso do Sul are included, and the frontier of caipira in Minas Gerais is expanded further northerly, though not reaching metropolitan Belo Horizonte. It is often said that caipira appeared by decreolization of the língua brasílica and the related língua geral paulista, then spoken in almost all of what is now São Paulo, a former lingua franca in most of the contemporary Centro-Sul of Brazil before the 18th century, brought by the bandeirantes, interior pioneers of Colonial Brazil, closely related to its northern counterpart Nheengatu, and that is why the dialect shows many general differences from other variants of the language.[68] It has striking remarkable differences in comparison to other Brazilian dialects in phonology, prosody and grammar, often stigmatized as being strongly associated with a substandard variant, now mostly rural.[69][70][71][72][73]
Cearense or Costa norte — is a dialect spoken more sharply in the states of Ceará and Piauí. The variant of Ceará includes fairly distinctive traits it shares with the one spoken in Piauí, though, such as distinctive regional phonology and vocabulary (for example, a debuccalization process stronger than that of Portuguese, a different system of the vowel harmony that spans Brazil from fluminense and mineiro to amazofonia but is especially prevalent in nordestino, a very coherent coda sibilant palatalization as those of Portugal and Rio de Janeiro but allowed in fewer environments than in other accents of nordestino, a greater presence of dental stop palatalization to palato-alveolar in comparison to other accents of nordestino, among others, as well as a great number of archaic Portuguese words).[74][75][76][77][78][79]
Baiano — Found in Bahia, Sergipe, northern Minas Gerais and border regions with Goiás and Tocantins. Similar to nordestino, it has a very characteristic syllable-timed rhythm and the greatest tendency to pronounce unstressed vowels as open-mid [ɛ] and [ɔ].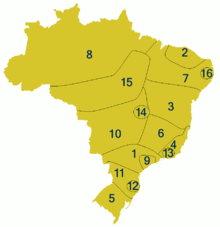
Variants and sociolects of Brazilian Portuguese. Fluminense — A broad dialect with many variants spoken in the states of Rio de Janeiro, Espírito Santo and neighbouring eastern regions of Minas Gerais. Fluminense formed in these previously caipira-speaking areas due to the gradual influence of European migrants, causing many people to distance their speech from their original dialect and incorporate new terms.[80]Fluminense is sometimes referred to as carioca, however carioca is a more specific term referring to the accent of the Greater Rio de Janeiro area by speakers with a fluminense dialect.
Fluminense — A broad dialect with many variants spoken in the states of Rio de Janeiro, Espírito Santo and neighbouring eastern regions of Minas Gerais. Fluminense formed in these previously caipira-speaking areas due to the gradual influence of European migrants, causing many people to distance their speech from their original dialect and incorporate new terms.[80]Fluminense is sometimes referred to as carioca, however carioca is a more specific term referring to the accent of the Greater Rio de Janeiro area by speakers with a fluminense dialect.
Gaúcho — in Rio Grande do Sul, similar to sulista. There are many distinct accents in Rio Grande do Sul, mainly due to the heavy influx of European immigrants of diverse origins who have settled in colonies throughout the state, and to the proximity to Spanish-speaking nations. The gaúcho word in itself is a Spanish loanword into Portuguese of obscure Indigenous Amerindian origins.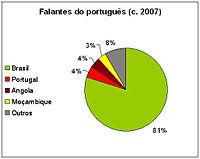
Percentage of worldwide Portuguese speakers per country.
Mineiro — Minas Gerais (not prevalent in the Triângulo Mineiro). As the fluminense area, its associated region was formerly a sparsely populated land where caipira was spoken, but the discovery of gold and gems made it the most prosperous Brazilian region, what attracted Portuguese colonists, commoners from other parts of Brazil and their African slaves. South-southwestern, southeastern and northern areas of the state have fairly distinctive speech, actually approximating to caipira, fluminense (popularly called, often pejoratively, carioca do brejo, "marsh carioca") and baiano respectively. Areas including and surrounding Belo Horizonte have a distinctive accent. Nordestino[81] — more marked in the Sertão (7), where, in the 19th and 20th centuries and especially in the area including and surrounding the sertão (the dry land after Agreste) of Pernambuco and southern Ceará, it could sound less comprehensible to speakers of other Portuguese dialects than Galician or Rioplatense Spanish, and nowadays less distinctive from other variants in the metropolitan cities along the coasts. It can be divided in two regional variants, one that includes the northern Maranhão and southern of Piauí, and other that goes from Ceará to Alagoas.
Nordestino[81] — more marked in the Sertão (7), where, in the 19th and 20th centuries and especially in the area including and surrounding the sertão (the dry land after Agreste) of Pernambuco and southern Ceará, it could sound less comprehensible to speakers of other Portuguese dialects than Galician or Rioplatense Spanish, and nowadays less distinctive from other variants in the metropolitan cities along the coasts. It can be divided in two regional variants, one that includes the northern Maranhão and southern of Piauí, and other that goes from Ceará to Alagoas.
Nortista or amazofonia — Most of Amazon Basin states i.e. Northern Brazil. Before the 20th century, most people from the nordestino area fleeing the droughts and their associated poverty settled here, so it has some similarities with the Portuguese dialect there spoken. The speech in and around the cities of Belém and Manaus has a more European flavor in phonology, prosody and grammar.
Paulistano — Variants spoken around Greater São Paulo in its maximum definition and more easterly areas of São Paulo state, as well perhaps "educated speech" from anywhere in the state of São Paulo (where it coexists with caipira). Caipira is the hinterland sociolect of much of the Central-Southern half of Brazil, nowadays conservative only in the rural areas and associated with them, that has a historically low prestige in cities as Rio de Janeiro, Curitiba, Belo Horizonte, and until some years ago, in São Paulo itself. Sociolinguistics, or what by times is described as 'linguistic prejudice', often correlated with classism,[82][83][84] is a polemic topic in the entirety of the country since the times of Adoniran Barbosa. Also, the "Paulistano" accent was heavily influenced by the presence of immigrants in the city of São Paulo, especially the Italians.
Sertanejo — Center-Western states, and also much of Tocantins and Rondônia. It is closer to mineiro, caipira, nordestino or nortista depending on the location.
Sulista — The variants spoken in the areas between the northern regions of Rio Grande do Sul and southern regions of São Paulo state, encompassing most of southern Brazil. The city of Curitiba does have a fairly distinct accent as well, and a relative majority of speakers around and in Florianópolis also speak this variant (many speak florianopolitano or manezinho da ilha instead, related to the European Portuguese dialects spoken in Azores and Madeira). Speech of northern Paraná is closer to that of inland São Paulo.
Florianopolitano — Variants heavily influenced by European Portuguese spoken in Florianópolis city (due to a heavy immigration movement from Portugal, mainly its insular regions) and much of its metropolitan area, Grande Florianópolis, said to be a continuum between those whose speech most resemble sulista dialects and those whose speech most resemble fluminense and European ones, called, often pejoratively, manezinho da ilha.
Carioca — Not a dialect, but sociolects of the fluminense variant spoken in an area roughly corresponding to Greater Rio de Janeiro. It appeared after locals came in contact with the Portuguese aristocracy amidst the Portuguese royal family fled in the early 19th century. There is actually a continuum between Vernacular countryside accents and the carioca sociolect, and the educated speech (in Portuguese norma culta, which most closely resembles other Brazilian Portuguese standards but with marked recent Portuguese influences, the nearest ones among the country's dialects along florianopolitano), so that not all people native to the state of Rio de Janeiro speak the said sociolect, but most carioca speakers will use the standard variant not influenced by it that is rather uniform around Brazil depending on context (emphasis or formality, for example).
Brasiliense — used in Brasília and its metropolitan area.[85] It is not considered a dialect, but more of a regional variant – often deemed to be closer to fluminense than the dialect commonly spoken in most of Goiás, sertanejo.
Arco do desflorestamento or serra amazônica — Known in its region as the "accent of the migrants", it has similarities with caipira, sertanejo and often sulista that make it differing from amazofonia (in the opposite group of Brazilian dialects, in which it is placed along nordestino, baiano, mineiro and fluminense). It is the most recent dialect, which appeared by the settlement of families from various other Brazilian regions attracted by the cheap land offer in recently deforested areas.[86][87]
Recifense — used in Recife and its metropolitan area.
Portugal
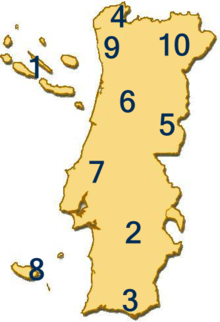
Dialects of Portuguese in Portugal
 Micaelense (Açores) (São Miguel)—Azores.
Micaelense (Açores) (São Miguel)—Azores. Alentejano—Alentejo (Alentejan Portuguese)
Alentejano—Alentejo (Alentejan Portuguese) Algarvio—Algarve (there is a particular dialect in a small part of western Algarve).
Algarvio—Algarve (there is a particular dialect in a small part of western Algarve). Minhoto—Districts of Braga and Viana do Castelo (hinterland).
Minhoto—Districts of Braga and Viana do Castelo (hinterland). Beirão; Alto-Alentejano—Central Portugal (hinterland).
Beirão; Alto-Alentejano—Central Portugal (hinterland). Beirão— Central Portugal.
Beirão— Central Portugal. Estremenho—Regions of Coimbra, Leiria and Lisbon (this is a disputed denomination, as Coimbra is not part of "Estremadura", and the Lisbon dialect has some peculiar features that are not only not shared with that of Coimbra, but also significantly distinct and recognizable to most native speakers from elsewhere in Portugal).
Estremenho—Regions of Coimbra, Leiria and Lisbon (this is a disputed denomination, as Coimbra is not part of "Estremadura", and the Lisbon dialect has some peculiar features that are not only not shared with that of Coimbra, but also significantly distinct and recognizable to most native speakers from elsewhere in Portugal). Madeirense (Madeiran)—Madeira.
Madeirense (Madeiran)—Madeira. Portuense—Regions of the district of Porto and parts of Aveiro.
Portuense—Regions of the district of Porto and parts of Aveiro. Transmontano—Trás-os-Montes e Alto Douro.
Transmontano—Trás-os-Montes e Alto Douro.
Other countries and dependencies
 Angola—
Angola— Angolano (Angolan Portuguese)
Angolano (Angolan Portuguese) Cape Verde—
Cape Verde— Cabo-verdiano (Cape Verdean Portuguese)
Cabo-verdiano (Cape Verdean Portuguese) East Timor—
East Timor— Timorense (East Timorese Portuguese)
Timorense (East Timorese Portuguese) India — Damaense (Damanese Portuguese) and Goês (Goan Portuguese)
India — Damaense (Damanese Portuguese) and Goês (Goan Portuguese) Guinea-Bissau—
Guinea-Bissau— Guineense (Guinean Portuguese)
Guineense (Guinean Portuguese) Macau—
Macau— Macaense (Macanese Portuguese)
Macaense (Macanese Portuguese) Mozambique—
Mozambique— Moçambicano (Mozambican Portuguese)
Moçambicano (Mozambican Portuguese) São Tomé and Príncipe—
São Tomé and Príncipe— Santomense (São Tomean Portuguese)
Santomense (São Tomean Portuguese) Spain—Oliventian Portuguese and other varieties sometimes controversially deemed as separate languages, such as Galician and Fala.
Spain—Oliventian Portuguese and other varieties sometimes controversially deemed as separate languages, such as Galician and Fala. Uruguay—Dialectos Portugueses del Uruguay (DPU)
Uruguay—Dialectos Portugueses del Uruguay (DPU)
Differences between dialects are mostly of accent and vocabulary, but between the Brazilian dialects and other dialects, especially in their most colloquial forms, there can also be some grammatical differences. The Portuguese-based creoles spoken in various parts of Africa, Asia, and the Americas are independent languages.
Characterization and peculiarities

Map highlighting the different accents within the Portuguese Republic
Portuguese, like Catalan, preserved the stressed vowels of Vulgar Latin, which became diphthongs in most other Romance languages; cf. Port., Cat., Sard. pedra ; Fr. pierre, Sp. piedra, It. pietra, Ro. piatră, from Lat. petra ("stone"); or Port. fogo, Cat. foc, Sard. fogu; Sp. fuego, It. fuoco, Fr. feu, Ro. foc, from Lat. focus ("fire"). Another characteristic of early Portuguese was the loss of intervocalic l and n, sometimes followed by the merger of the two surrounding vowels, or by the insertion of an epenthetic vowel between them: cf. Lat. salire ("to jump"), tenere ("to hold"), catena ("chain"), Sp. salir, tener, cadena, Port. sair, ter, cadeia.
When the elided consonant was n, it often nasalized the preceding vowel: cf. Lat. manum ("hand"), ranam ("frog"), bonum ("good"), Port. mão, rãa, bõo (now mão, rã, bom). This process was the source of most of the language's distinctive nasal diphthongs. In particular, the Latin endings -anem, -anum and -onem became -ão in most cases, cf. Lat. canis ("dog"), germanus ("brother"), ratio ("reason") with Modern Port. cão, irmão, razão, and their plurals -anes, -anos, -ones normally became -ães, -ãos, -ões, cf. cães, irmãos, razões.
The Portuguese language is the only Romance language that has preserved the clitic case mesoclisis: cf. dar-te-ei (I'll give thee), amar-te-ei (I'll love you), contactá-los-ei (I'll contact them). Like Galician, it also retains the Latin synthetic pluperfect tense: eu estivera (I had been), eu vivera (I had lived), vós vivêreis (you had lived).[88]Romanian also has this tense, but uses the -s- form.
Vocabulary

The National Library of Brazil, in Rio de Janeiro, the largest library in Latin America

The Central Post Office of Macau, Macau

Baroque Library of the Coimbra University, Portugal

Incidence of Germanic toponymy in Portugal-Galicia

A sign at Goa Central Library, in Panaji
Most of the lexicon of Portuguese is derived, directly or through other Romance languages, from Latin. Nevertheless, because of its original Lusitanian and Celtic Gallaecian heritage, and the later participation of Portugal in the Age of Discovery, it has some words from pre-Latin Paleohispanic languages and adopted loanwords from other languages around the world.
A number of Portuguese words can still be traced to the pre-Roman inhabitants of Portugal, which included the Gallaeci, Lusitanians, Celtici and Cynetes. Most of these words derived from the Hispano-Celtic Gallaecian language of northwestern Iberia, and are very often shared with Galician since both languages share a common origin in the medieval language of Galician-Portuguese. A few of these words existed in Latin as loanwords from other Celtic sources, often Gaulish. Altogether these are over 1,000 words, some verbs and toponymic names of towns, rivers, utensils and plants.
In the 5th century, the Iberian Peninsula (the Roman Hispania) was conquered by the Germanic Suebi and Visigoths. As they adopted the Roman civilization and language, however, these people contributed with some 500 Germanic words to the lexicon. Many of these words are related to warfare—such as espora "spur", estaca "stake", and guerra "war", from Gothic *spaúra, *stakka, and *wirro, respectively. The Germanic languages influence also exists in toponymic surnames and patronymic surnames borne by Visigoth sovereigns and their descendants, and it dwells on placenames such has Ermesinde, Esposende and Resende where sinde and sende are derived from the Germanic "sinths" (military expedition) and in the case of Resende, the prefix re comes from Germanic "reths" (council). Other examples of Portuguese names, surnames and town names of Germanic toponymic origin include Henrique, Henriques, Vermoim, Mandim, Calquim, Baguim, Gemunde, Guetim, Sermonde and many more, are quite common mainly in the old Suebi and later Visigothic dominated regions, covering today's Northern half of Portugal and Galicia.
Between the 9th and early 13th centuries, Portuguese acquired some 400 to 600 words from Arabic by influence of Moorish Iberia. They are often recognizable by the initial Arabic article a(l)-, and include common words such as aldeia "village" from الضيعة alḍai`a (or from Edictum Rothari: aldii, aldias),[89]alface "lettuce" from الخس alkhass, armazém "warehouse" from المخزن almakhzan, and azeite "olive oil" from الزيت azzait.
Starting in the 15th century, the Portuguese maritime explorations led to the introduction of many loanwords from Asian languages. For instance, catana "cutlass" from Japanese katana, chá "tea" from Chinese chá, and canja[90] "chicken-soup, piece of cake" from Malay.
From the 16th to the 19th centuries, because of the role of Portugal as intermediary in the Atlantic slave trade, and the establishment of large Portuguese colonies in Angola, Mozambique, and Brazil, Portuguese acquired several words of African and Amerind origin, especially names for most of the animals and plants found in those territories. While those terms are mostly used in the former colonies, many became current in European Portuguese as well. From Kimbundu, for example, came kifumate > cafuné "head caress" (Brazil), kusula > caçula "youngest child" (Brazil), marimbondo "tropical wasp" (Brazil), and kubungula > bungular "to dance like a wizard" (Angola). From South America came batata "potato", from Taino; ananás and abacaxi, from Tupi–Guarani naná and Tupi ibá cati, respectively (two species of pineapple), and pipoca "popcorn" from Tupi and tucano "toucan" from Guarani tucan.
Finally, it has received a steady influx of loanwords from other European languages, especially French and English. These are by far the most important languages when referring to loanwords. There are many examples such as: colchete/crochê "bracket"/"crochet", paletó "jacket", batom "lipstick", and filé/filete "steak"/"slice", rua "street" respectively, from French crochet, paletot, bâton, filet, rue; and bife "steak", futebol, revólver, stock/estoque, folclore, from English beef, football, revolver, stock, folklore.
Examples from other European languages: macarrão "pasta", piloto "pilot", carroça "carriage", and barraca "barrack", from Italian maccherone, pilota, carrozza, and baracca; melena "hair lock", fiambre "wet-cured ham" (in Portugal, in contrast with presunto "dry-cured ham" from Latin prae-exsuctus "dehydrated") or "canned ham" (in Brazil, in contrast with non-canned, wet-cured presunto cozido and dry-cured presunto cru), and castelhano "Castilian", from Spanish melena "mane", fiambre and castellano.
Before the last four decades, Brazilians adopted a greater number of loanwords from Japanese and other European languages (due to the historical immigration affecting their demographics), and they were and are also more willing to adopt foreign terms that come from globalization than the Portuguese, while the degree of African, Tupian and other Amerindian lexicon in Brazilian Portuguese is shown to be surprisingly lesser than that commonly expected of the said variant by the local Africanist and Indianist academia (that also has to some degree influenced the common sense of what gives a different cultural identity of Brazilians in relation to the Portuguese), so that its lexicon is almost identical (about 99%) to that of European Portuguese.[91][92][93]
Many Portuguese settlers to Colonial Brazil were from northern and insular Portugal,[94] apart from some historically important illegal immigrants from elsewhere in Europe, such as Galicia, France and the Netherlands.[95] Brazil received more European immigrants in its colonial history than the United States. Between 1500 and 1760, 700,000 Europeans (overwhelmingly Portuguese) settled in Brazil, while 530,000 Europeans settled in the United States for the same given time.[96]

Map showing the historical retreat and expansion of Portuguese (Galician-Portuguese) within the context of its linguistic neighbours between the year 1000 and 2000.
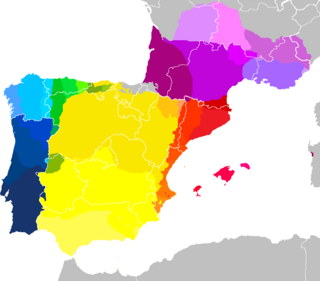
Map showing mostly contemporary West Iberian and Occitano-Romance languages, as well many of their mainland European dialects (take note that areas colored green, gold or pink/purple represent languages deemed endangered by UNESCO, so this may be outdated in less than a few decades). It shows European Portuguese, Galician, Eonavian, Mirandese and the Fala as not only closely related but as dialect continuum, though it excludes dialects spoken in insular Portugal (Azores and Madeira–Canaries is not shown either).
Portuguese belongs to the West Iberian branch of the Romance languages, and it has special ties with the following members of this group:
Galician, Fala and portunhol do pampa (the way riverense and its sibling dialects are referred to in Portuguese), its closest relatives.
Mirandese, Leonese, Asturian, Extremaduran and Cantabrian (Astur-Leonese languages). Mirandese is the only recognised regional language spoken in Portugal (beside Portuguese, the only official language in Portugal).
Spanish and calão (the way caló, language of the Iberian Romani, is referred to in Portuguese).
Portuguese and other Romance languages (namely French and Italian) are moderately mutually intelligible, and share considerable similarities in both vocabulary and grammar. Portuguese speakers will usually need some formal study before attaining strong comprehension in those Romance languages, and vice versa. However, Portuguese and Galician are mutually intelligible, and Spanish is highly asymmetrically comprehensible to Portuguese speakers. Given that Portuguese has a larger phonemic inventory than Spanish, Portuguese is still considerably intelligible (if spoken slowly and without jargon) to most Spanish speakers, owing to their genealogical proximity and shared genealogical history as West Iberian (Ibero-Romance languages), historical contact between speakers and mutual influence, shared areal features as well as modern lexical, structural, and grammatical similarity (89%) between them.[97][98][99][100]
Portunhol, a form of code-switching, has a more lively use and is more readily mentioned in popular culture in South America. Said code-switching is not to be confused with the portunhol spoken on the borders of Brazil with Uruguay (dialeto do pampa) and Paraguay (dialeto dos brasiguaios), and of Portugal with Spain (barranquenho), that are Portuguese dialects spoken natively by thousands of people, which have been heavily influenced by Spanish.[101]
Portuguese and Spanish are the only Ibero-Romance languages, and perhaps the only Romance languages with such thriving inter-language forms, in which visible and lively bilingual contact dialects and code-switching have formed, in which functional bilingual communication is achieved through attempting an approximation to the target foreign language (known as 'Portunhol') without a learned acquisition process, but nevertheless facilitates communication. There is an emerging literature focused on such phenomena (including informal attempts of standardization of the linguistic continua and their usage).[101]
Galician-Portuguese in Spain
The closest relative of Portuguese is Galician, which is spoken in the autonomous community (region) and historical nationality of Galicia (northwestern Spain). The two were at one time a single language, known today as Galician-Portuguese, but they have diverged especially in pronunciation and vocabulary due to the political separation of Portugal from Galicia. There is, however, still a linguistic continuity consisting of the variant of Galician referred to as galego-português baixo-limiao, which is spoken in several Galician villages between the municipalities of Entrimo and Lobios and the transborder region of the natural park of Peneda-Gerês/Xurês. It is "considered a rarity, a living vestige of the medieval language that ranged from Cantabria to Mondego [...]".[102]
As reported by UNESCO, due to the pressure of the Spanish language on the standard official version of the Galician language, the Galician language was on the verge of disappearing.[102] According to the Unesco philologist Tapani Salminen, the proximity to Portuguese protects Galician.[103]
Nevertheless, the core vocabulary and grammar of Galician are still noticeably closer to Portuguese than to those of Spanish. In particular, like Portuguese, it uses the future subjunctive, the personal infinitive, and the synthetic pluperfect. Mutual intelligibility (estimated at 90% by R. A. Hall, Jr., 1989)[104] is excellent between Galicians and northern Portuguese. Many linguists consider Galician to be a co-dialect of the Portuguese language.
Another member of the Galician-Portuguese group, most commonly thought of as a Galician dialect, is spoken in the Eonavian region in a western strip in Asturias and the westernmost parts of the provinces of León and Zamora, along the frontier with Galicia, between the Eo and Navia rivers (or more exactly Eo and Frexulfe rivers). It is called eonaviego or gallego-asturiano by its speakers.
The Fala language, known by its speakers as xalimés, mañegu, a fala de Xálima and chapurráu and in Portuguese as a fala de Xálima, a fala da Estremadura, o galego da Estremadura, valego ou galaico-estremenho, is another descendant of Galician-Portuguese, spoken by a small number of people in the Spanish towns of Valverde del Fresno (Valverdi du Fresnu), Eljas (As Ellas) and San Martín de Trevejo (Sa Martín de Trevellu) in the autonomous community of Extremadura, near the border with Portugal.
There are a number of other places in Spain in which the native language of the common people is a descendant of the Galician-Portuguese group, such as La Alamedilla, Cedillo (Cedilho), Herrera de Alcántara (Ferreira d'Alcântara) and Olivenza (Olivença), but in these municipalities, what is spoken is actually Portuguese, not disputed as such in the mainstream.
It should be noticed that the diversity of dialects of the Portuguese language is known since the time of medieval Portuguese-Galician language when it coexisted with the Lusitanian-Mozarabic dialect, spoken in the south of Portugal. The dialectal diversity becomes more evident in the work of Fernão d'Oliveira, in the Grammatica da Lingoagem Portuguesa, (1536), where he remarks that the people of Portuguese regions of Beira, Alentejo, Estremadura, and Entre Douro e Minho, all speak differently from each other. Also Contador d'Argote (1725) distinguishes three main varieties of dialects: the local dialects, the dialects of time, and of profession (work jargon). Of local dialects he highlights five main dialects: the dialect of Estremadura, of Entre-Douro e Minho, of Beira, of Algarve and of Trás-os-Montes. He also makes reference to the overseas dialects, the rustic dialects, the poetic dialect and that of prose.[105]
In the kingdom of Portugal, Ladinho (or Lingoagem Ladinha) was the name given to the pure Portuguese language romance, without any mixture of Aravia or Gerigonça Judenga.[106] While the term língua vulgar was used to name the language before D. Dinis decided to call it "Portuguese language",[107] the erudite version used and known as Galician-Portuguese (the language of the Portuguese court) and all other Portuguese dialects were spoken at the same time. In a historical perspective the Portuguese language was never just one dialect. Just like today there is a standard Portuguese (actually two) among the several dialects of Portuguese, in the past there was Galician-Portuguese as the "standard", coexisting with other dialects.
Influence on other languages
Portuguese has provided loanwords to many languages, such as Indonesian, Manado Malay, Malayalam, Sri Lankan Tamil and Sinhalese, Malay, Bengali, English, Hindi, Swahili, Afrikaans, Konkani, Marathi, Tetum, Xitsonga, Japanese, Lanc-Patuá (spoken in northern Brazil), Esan and Sranan Tongo (spoken in Suriname). It left a strong influence on the língua brasílica, a Tupi–Guarani language, which was the most widely spoken in Brazil until the 18th century, and on the language spoken around Sikka in Flores Island, Indonesia. In nearby Larantuka, Portuguese is used for prayers in Holy Week rituals.
The Japanese–Portuguese dictionary Nippo Jisho (1603) was the first dictionary of Japanese in a European language, a product of Jesuit missionary activity in Japan. Building on the work of earlier Portuguese missionaries, the Dictionarium Anamiticum, Lusitanum et Latinum (Annamite–Portuguese–Latin dictionary) of Alexandre de Rhodes (1651) introduced the modern orthography of Vietnamese, which is based on the orthography of 17th-century Portuguese. The Romanization of Chinese was also influenced by the Portuguese language (among others), particularly regarding Chinese surnames; one example is Mei. During 1583–88 Italian Jesuits Michele Ruggieri and Matteo Ricci created a Portuguese–Chinese dictionary—the first ever European–Chinese dictionary.[108][109]
For instance, as Portuguese merchants were presumably the first to introduce the sweet orange in Europe, in several modern Indo-European languages the fruit has been named after them. Some examples are Albanian portokall, Bosnian (archaic) portokal, prtokal, Bulgarian портокал (portokal), Greek πορτοκάλι (portokáli), Macedonian portokal, Persian پرتقال (porteghal), and Romanian portocală.[110][111] Related names can be found in other languages, such as Arabic البرتقال (burtuqāl), Georgian ფორთოხალი (p'ort'oxali), Turkish portakal and Amharic birtukan.[110] Also, in southern Italian dialects (e.g. Neapolitan), an orange is portogallo or purtuallo, literally "(the) Portuguese (one)", in contrast to standard Italian arancia.
Derived languages

Participating countries of the Lusophony Games
Beginning in the 16th century, the extensive contacts between Portuguese travelers and settlers, African and Asian slaves, and local populations led to the appearance of many pidgins with varying amounts of Portuguese influence. As each of these pidgins became the mother tongue of succeeding generations, they evolved into fully fledged creole languages, which remained in use in many parts of Asia, Africa and South America until the 18th century. Some Portuguese-based or Portuguese-influenced creoles are still spoken today, by over 3 million people worldwide, especially people of partial Portuguese ancestry.
Phonology
Spoken Brazilian Portuguese
Portuguese phonology is similar to those of languages such as French (especially that of Quebec), the Gallo-Italic languages, Occitan, Catalan and Franco-Provençal, unlike that of Spanish, which is similar to those of Sardinian and the Southern Italian dialects. Some would describe the phonology of Portuguese as a blend of Spanish, Gallo-Romance (e.g. French) and the languages of northern Italy (especially Genoese), but with a deeper Celtic influence.[112]
There is a maximum of 9 oral vowels, 2 semivowels and 21 consonants; though some varieties of the language have fewer phonemes. There are also five nasal vowels, which some linguists regard as allophones of the oral vowels.
Vowels

Chart of monophthongs of the Portuguese of Lisbon, with its /ɐ, ɐ̃/ in central schwa position.
Like Catalan and German, Portuguese uses vowel quality to contrast stressed syllables with unstressed syllables. Unstressed isolated vowels tend to be raised and sometimes centralized.
Consonants
Labial | Dental/ Alveolar | Dorsal | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
plain | labialized | ||||
Nasal | m | n | ɲ | ||
Plosive | voiceless | p | t | k | kʷ |
voiced | b | d | ɡ | ɡʷ | |
Fricative | voiceless | f | s | ʃ | |
voiced | v | z | ʒ | ||
Approximant | semivowel | j | w | ||
lateral | l | ʎ | |||
Rhotic | trill/fricative | ʁ | |||
flap | ɾ | ||||
Phonetic notes
- Semivowels contrast with unstressed high vowels in verbal conjugation, as in (eu) rio /ˈʁi.u/ and (ele) riu /ˈʁiw/.[117] Phonologists discuss whether their nature is vowel or consonant.[118]
- In most of Brazil and Angola, the consonant hereafter denoted as /ɲ/ is realized as a nasal palatal approximant [j̃], which nasalizes the vowel that precedes it: [ˈnĩj̃u].[119][120]
Bisol (2005:122) proposes that Portuguese possesses labio-velar stops /kʷ/ and /ɡʷ/ as additional phonemes rather than sequences of a velar stop and /w/.[116]- The consonant hereafter denoted as /ʁ/ has a variety of realizations depending on dialect. In Europe, it is typically a uvular trill [ʀ]; however, a pronunciation as a voiced uvular fricative [ʁ] may be becoming dominant in urban areas. There is also a realization as a voiceless uvular fricative [χ], and the original pronunciation as an alveolar trill [r] also remains very common in various dialects.[121] A common realization of the word-initial /r/ in the Lisbon accent is a voiced uvular trill fricative [ʀ̝].[122] In Brazil, /ʁ/ can be velar, uvular, or glottal and may be voiceless unless between voiced sounds.[123] It is usually pronounced as a voiceless velar fricative [x], a voiceless glottal fricative [h] or voiceless uvular fricative [χ]. See also Guttural R in Portuguese.
/s/ and /z/ are normally lamino-alveolar, as in English. However, a number of dialects in northern Portugal pronounce /s/ and /z/ as apico-alveolar sibilants (sounding somewhat like a soft [ʃ] or [ʒ]), as in the Romance languages of northern Iberia. A very few northeastern Portugal dialects still maintain the medieval distinction between apical and laminal sibilants (written s/ss and c/ç/z, respectively).- As a phoneme, /tʃ/ occurs only in loanwords, with a tendency for speakers to substitute in /ʃ/. However, [tʃ] is an allophone of /t/ before /i/ in a number of Brazilian dialects. Similarly, [dʒ] is an allophone of /d/ in the same contexts.
- In northern and central Portugal, the voiced stops (/b/, /d/, and /ɡ/) are usually lenited to fricatives [β], [ð], and [ɣ], respectively, except at the beginning of words or after nasal vowels.[124][125] A similar process occurs in Spanish.
Grammar
A notable aspect of the grammar of Portuguese is the verb. Morphologically, more verbal inflections from classical Latin have been preserved by Portuguese than by any other major Romance language. Portuguese and Spanish share very similar grammar. Portuguese also has some grammatical innovations not found in other Romance languages (except Galician and Fala):
- The present perfect has an iterative sense unique to the Galician-Portuguese language group. It denotes an action or a series of actions that began in the past but expected to occur again in the future. For instance, the sentence Tenho tentado falar com ela would be translated to "I have been trying to talk to her", not "I have tried to talk to her." On the other hand, the correct translation of "Have you heard the latest news?" is not *Tem ouvido a última notícia? but Ouviu a última notícia? since no repetition is implied.[126]
Vernacular Portuguese makes use of the future subjunctive mood, which developed from medieval West Iberian Romance. In modern Spanish and Galician, it has almost entirely fallen into disuse. The future subjunctive appears in dependent clauses that denote a condition that must be fulfilled in the future so that the independent clause will occur. English normally employs the present tense under the same circumstances:
Se eu for eleito presidente, mudarei a lei.- If I am elected president, I will change the law.
Quando fores mais velho, vais entender.- When you grow older, you will understand.
- The personal infinitive can inflect according to its subject in person and number. often shows who is expected to perform a certain action. É melhor voltares "It is better [for you] to go back," É melhor voltarmos "It is better [for us] to go back." Perhaps for that reason, infinitive clauses replace subjunctive clauses more often in Portuguese than in other Romance languages.
Writing system
| Portugal and non-1990 Agreement countries | Brazil and 1990 Agreement countries | translation |
|---|---|---|
| direcção | direção | direction |
| óptimo | ótimo | best, excellent, optimal |
Portuguese is written with 26 letters of the Latin script, making use of five diacritics to denote stress, vowel height, contraction, nasalization, and etymological assibilation (acute accent, circumflex, grave accent, tilde, and cedilla). The trema was also formerly used in Brazilian Portuguese, and can still be encountered in words derived from proper names in other languages, such as Anhangüera and mülleriano.[127][128] Accented characters and digraphs are not counted as separate letters for collation purposes.
Spelling reforms
See also
- Anglophone pronunciation of foreign languages (Portuguese section)
- Portuguese literature
- Portuguese Africans
- Angolan literature
- Brazilian literature
- European Portuguese
- Gallaecian language
- International Portuguese Language Institute
- List of countries where Portuguese is an official language
- List of international organisations which have Portuguese as an official language
- List of Portuguese-language poets
- Lusitanian language
- Mozambican Portuguese
- Portuguese in Asia and Oceania
- Portuguese poetry
- Portuñol
References
Citations
^ ab Portuguese at Ethnologue (21st ed., 2018)
^ Government of the Republic of Equatorial Guinea. "Acts continue to mark Portuguese Language and Portuguese Culture Day"..mw-parser-output cite.citationfont-style:inherit.mw-parser-output qquotes:"""""""'""'".mw-parser-output code.cs1-codecolor:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registrationcolor:#555.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration spanborder-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-errordisplay:none;font-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-errorfont-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-formatfont-size:95%.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-leftpadding-left:0.2em.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-rightpadding-right:0.2em
^ "El portugués uruguayo y las marcas de la oralidad en la poesía del escritor uruguayo Agustín R. Bisio" (PDF).
^ "Historia lingüística del Uruguay". www.historiadelaslenguasenuruguay.edu.uy.
^ Bruzzese, Mahira González; Ingold, Cecilia Rodriguez. "Algunas notas teórico metodológicas sobre la relación entre regiones y aprendizajes en Uruguay" (PDF). pp. 11–15.
^ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds. (2017). "Portuguese". Glottolog 3.0. Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
^ abc "Estados-membros da CPLP" (in Portuguese). 7 February 2017.
^ Michael Swan; Bernard Smith (2001). "Portuguese Speakers". Learner English: a Teacher's Guide to Interference and Other Problems. Cambridge University Press.
^ "The Origin and Formation of The Portuguese Language". Judeo-Lusitanica. Archived from the original on 10 May 2017. Retrieved 15 October 2016.
^ Bittencourt de Oliveira, João. "Breves considerações sobre o legado das línguas célticas". filologia.org.br.
^ "CIA World Factbook". Retrieved 12 June 2015.
^ https://africa-facts.org/top-10-most-spoken-languages-in-africa/
^ Benozzo, F. (2018): "Uma paisagem atlântica pré-histórica. Etnogénese e etno-filologia paleo-mesolítica das tradições galega e portuguesa", in proceedings of Jornadas das Letras Galego-Portugesas 2015–2017. Università de Bologna, DTS and Academia Galega da Língua Portuguesa. pp. 159–170
^ Galicia and North Portugal are the origin of European celticity, interview with Prof. Francesco Benozzo, 13/03/2016
^ Comparative Grammar of Latin 34 Archived 27 September 2007 at the Wayback Machine.
^ Ethnologic Map of Pre-Roman Iberia (circa 200 B.C.). Arkeotavira.com. Retrieved on 14 November 2011.
^ Domingos Maria da Silva, Os Búrios, Terras de Bouro, Câmara Municipal de Terras de Bouro, 2006. (in Portuguese)
^ Lay, Stephen (2015). "Sanctity and Social Alienation in Twelfth-Century Braga as Portrayed in the Vita Sancti Geraldi". Portuguese Studies. 31 (2): 153–168. doi:10.5699/portstudies.31.2.0153.
^ Jean-Pierre Juge (2001) Petit précis – Chronologie occitane – Histoire & civilisation, p. 25
^ Henry Edward Watts. Miguel de Cervantes: His Life & Works.
^ Shipley, Joseph T. (1946). Encyclopedia of Literature. Philosophical Library. p. 1188.
^ Poddar, Prem; Patke, Rajeev S.; Jensen, Lars (2008). "Introduction: The Myths and Realities of Portuguese (Post) Colonial Society". A historical companion to postcolonial literatures: continental Europe and its empires. Edinburgh University Press. p. 431. ISBN 978-0-7486-2394-5.
^ ab NOVAimagem.co.pt / Portugal em Linha (8 March 2006). "Museu da Língua Portuguesa aberto ao público no dia 20". Noticiaslusofonas.com. Retrieved 23 July 2012.
^ "Brazil: Fire engulfs Portuguese language museum in Sao Paulo, one killed". International Business Times. 22 December 2015.
^ Carvalho, Daniela de (1 February 2013). Migrants and Identity in Japan and Brazil: The Nikkeijin. ISBN 978-1-135-78765-3.
^ "Portuguese language in Brazil". Countrystudies.us. Retrieved 23 July 2012.
^ "Special Eurobarometer 243 "Europeans and their Languages"" (PDF). European Commission. 2006. p. 6. Retrieved 11 May 2011.
^ Angola: Language Situation (2005). Keith Brown, ed. Encyclopedia of Language and Linguistics (2 ed.). Elsevier. ISBN 0-08-044299-4.
^ Medeiros, Adelardo. Portuguese in Africa – Angola
^ A. D. Medeiros, Adelardo. "Portuguese in Africa – Mozambique". Retrieved 12 June 2015.
^ A. D. Medeiros, Adelardo. "Portuguese in Africa – Guinea-Bissau". Retrieved 12 June 2015.
^ 13,100 Portuguese nationals in 2010 according to Population par nationalité on the site of the "Département des Statistiques d'Andorre" Archived 20 May 2011 at the Wayback Machine.
^ "Bermuda". World InfoZone. Retrieved 21 April 2010.
^ "Population by mother tongue, by province and territory (2006 Census)". Statistics Canada. Archived from the original on 13 March 2012.
^ ~500,000 use it as their mother tongue in the 2012 estimate, see Répartition des étrangers par nationalité
^ "Japão: imigrantes brasileiros popularizam língua portuguesa" (in Portuguese). 2008.
^ "4.6% according to the 2001 census, see". Cia.gov. Retrieved 23 July 2012.
^ ab Carin Pretorius – Developed CEIT Development CC. "The Namibian".
^ "Paraguay Ethnologue".
^ "Languages of Macau".
^ Fibbi, Rosita (2010). "Les Portugais en Suisse" (PDF). Office fédéral des migrations. Retrieved 13 May 2011.
^ See "Languages of Venezuela".
^ Carvalho, Ana Maria (2010). "Portuguese in the USA". In Potowski, Kim. Language Diversity in the USA. Cambridge University Press. p. 346. ISBN 978-0-521-74533-8.
^ "Portuguese Language in Goa". Colaco.net. Archived from the original on 29 May 2001. Retrieved 21 April 2010.
^ "The Portuguese Experience: The Case of Goa, Daman and Diu". Rjmacau.com. Archived from the original on 26 August 2009. Retrieved 21 April 2010.
^ "1.500 pessoas estudam português em Goa". Revistamacau.com. 2 June 2014. Retrieved 10 July 2015.
^ Factoria Audiovisual S.R.L. (20 July 2010). "El portugués será el tercer idioma oficial de la República de Guinea Ecuatorial – Página Oficial del Gobierno de la República de Guinea Ecuatorial". Guineaecuatorialpress.com. Retrieved 23 July 2012.
^ "Equatorial Guinea Adds Portuguese as the Country's Third Official Language". PR Newswire. Retrieved 7 February 2017.
^ Government of the Republic of Equatorial Guinea. "Equatorial Guinea, member of the Community of Portuguese Language Countries".
^ "Official languages of Mercosul as agreed in the Protocol of Ouro Preto". Actrav.itcilo.org. Retrieved 23 July 2012.
^ Statutes, Article 1"Official statute of the organization". Oei.es. Retrieved 23 July 2012.
^ Constitutive Treaty of the Union of South American Nations, Article 23 Tratado Constitutivo de la Unión de Naciones Suramericanas (PDF)
^ General Assembly of the OAS, Amendments to the Rules of Procedure of the General Assembly, 5 June 2000
^ abc Article 11, Protocol on Amendments to the Constitutive Act of the African Union "Protocol on the Amendments to the Constitutive Act of the African Union" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 December 2013. Retrieved 5 February 2016.
^ "Languages in Europe – Official EU Languages". EUROPA web portal. Archived from the original on 2 February 2009. Retrieved 12 October 2009.
^ "The World Factbook – Field Listing – Population – CIA". Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 2015-03-07.
^ "Uruguayan government makes Portuguese mandatory" (in Portuguese). 5 November 2007. Retrieved 13 July 2010.
^ "Portuguese language will be option in the official Venezuelan teachings" (in Portuguese). 24 May 2009. Archived from the original on 22 May 2011. Retrieved 13 July 2010.
^ "Zambia will adopt the Portuguese language in their Basic school" (in Portuguese). 26 May 2009. Archived from the original on 28 May 2009. Retrieved 13 July 2010.
^ abcd "Congo will start to teach Portuguese in schools" (in Portuguese). 4 June 2010. Archived from the original on 7 August 2010. Retrieved 13 July 2010.
^ "The World Factbook – Field Listing – Population – CIA". Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 2015-03-07.
^ "Portuguese language gaining popularity". Anglopress Edicões e Publicidade Lda. 5 May 2007. Retrieved 18 May 2011.
^ Leach, Michael (2007). "talking Portuguese; China and East Timor". Arena Magazine. Archived from the original on 5 November 2011. Retrieved 18 May 2011.
^ Viviane Maia dos Santos. "A Constituição de Corpora Orais Para a Análise das Formas de Tratamento" (PDF). Anais do IX Encontro do CELSUL Palhoça, SC, out. 2010 Universidade do Sul de Santa Catarina. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 10 August 2017.
^ Béliche Alves, Cibelle Corrêa (2012). "'Por onde tá "o tu"?' no português falado no Maranhão". Signum: Estudos da Linguagem. 15 (1): 13–31. Retrieved 10 August 2017.
^ Loremi Loregian-Penkal (2005). "Alternância tu/você em Santa Catarina: uma abordagem variacionista" (PDF). Departamento de Letras – Universidade Estadual do Centro Oeste (UNICENTRO). Retrieved 10 August 2017.
^ "Audio samples of the dialects of Portuguese". Instituto Camões. Retrieved 12 June 2015.
^ "Nheengatu and caipira dialect". Sosaci.org. Retrieved 23 July 2012.
^ (in Portuguese) Acoustic-phonetic characteristics of the Brazilian Portuguese's retroflex /r/: data from respondents in Pato Branco, Paraná. Irineu da Silva Ferraz. Pages 19–21
^ (in Portuguese) Syllable coda /r/ in the "capital" of the paulista hinterland: sociolinguistic analysis. Cândida Mara Britto LEITE. Page 111 (page 2 in the attached PDF)
^ (in Portuguese) Callou, Dinah. Leite, Yonne. Iniciação à Fonética e à Fonologia. Jorge Zahar Editora 2001, p. 24
^ (in Portuguese) To know a language is really about separating correct from awry? Language is a living organism that varies by context and goes far beyond a collection of rules and norms of how to speak and write Museu da Língua Portuguesa. Archived 22 December 2012 at the Wayback Machine.
^ (in Portuguese) Linguistic prejudice and the surprising (academic and formal) unity of Brazilian Portuguese
^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 5 April 2014. Retrieved 19 April 2013.CS1 maint: Archived copy as title (link)
^ Viviane Maia dos Santos (2012). ""Tu vai para onde? ... Você vai para onde?": manifestações da segunda pessoa na fala carioca" (PDF). Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro. Retrieved 10 August 2017.
^ Maria do Socorro Silva de Aragão. "Aspectos Fonético-Fonológicos do Falar do Ceará: O Que Tem Surgido nos Inquéritos Experimentais do Atlas Lingüístico do Brasil – ALiB-Ce" (PDF). Universidade Federal do Ceará. Retrieved 10 August 2017.
^ Seung Hwa Lee (2006). "Sobre as vogais pré-tônicas no Português Brasileiro" (PDF). www.gel.org.br. Faculdade de Letras – Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais (UFMG). Retrieved 10 August 2017.
^ Maria do Socorro Silva de Aragão (2009). "OS ESTUDOS FONÉTICO-FONOLÓGICOS NOS ESTADOS DA PARAÍBA E DO CEARÁ (Volume 8, No. 1)" (PDF). Universidade Federal do Ceará (UFC), Universidade Federal de Pernambuco (UFPE), Projeto Atlas Linguístico do Brasil (ALiB). Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 October 2017. Retrieved 10 August 2017.
^ "Revisitando a palatalização no português brasileiro – Silva – Revista de Estudos da Linguagem". ufmg.br.
^ "Learn about Portuguese language". Sibila. Retrieved 27 November 2012.
^ Note: the speaker of this sound file is from Rio de Janeiro, and he is talking about his experience with nordestino and nortista accents.
^ por Caipira Zé Do Mér dia 17 de maio de 2011, 6 Comentários. "O MEC, o "português errado" e a linguistica... | ImprenÇa". Imprenca.com. Archived from the original on 19 April 2012. Retrieved 23 July 2012.
^ "Cartilha Do Mec Ensina Erro De Português". Saindo da Matrix. Retrieved 23 July 2012.
^ "Livro do MEC ensina o português errado ou apenas valoriza as formas linguísticas?". Jornal de Beltrão (in Portuguese). 26 May 2011. Retrieved 23 July 2012.
^ "Sotaque branco". Meia Maratona Internacional CAIXA de Brasília. Archived from the original on 17 May 2016. Retrieved 25 September 2012.
^ "O Que É? Amazônia". Associação de Defesa do Meio Ambiente Araucária (AMAR). Archived from the original on 22 December 2012. Retrieved 25 September 2012.
^ "Fala NORTE". Fala UNASP – Centro Universitário Adventista de São Paulo. Archived from the original on 22 December 2012. Retrieved 25 September 2012.
^ Giorgi, Alessandra; Pianesi, Fabio (1997). Tense and Aspect: From Semantics to Morphosyntax. ISBN 9780195091939.
^ "Rothari -Edictus" (PDF). Retrieved 12 June 2015.
^ https://dicionario.priberam.org/Canja
^ da Prista, Alexander (1979). Say It in Portuguese. Courier Dover Publications. p. vii. ISBN 9780486148069. Retrieved 12 June 2015.
^ Keller, Karen (2006). Portuguese for Dummies. p. 9. ISBN 9780470049730. Retrieved 12 June 2015.
^ Swan, Michael; Smith, Bernard (2001). Learner English. Cambridge University Press. p. 113. ISBN 9780521779395. Retrieved 12 June 2015.
^ Florentino, Manolo, and Machado, Cacilda. (in Portuguese) Essay about Portuguese immigration and the patterns of miscegenation in Brazil in the 19th and 20th centuries (PDF file)
^ (in Portuguese) Eduardo Fonseca, the Dutch Brazilians – Brazilians in the Netherlands
^ Renato Pinto Venâncio, "Presença portuguesa: de colonizadores a imigrantes" (Portuguese presence: from colonizers to immigrants), chap. 3 of Brasil: 500 anos de povoamento (IBGE). Relevant extract available at [1] Archived 24 February 2013 at the Wayback Machine.
^ Jensen, John B. (1989). "On the Mutual Intelligibility of Spanish and Portuguese". Hispania. 72 (4): 848–852. doi:10.2307/343562. JSTOR 343562.
^ Penny, Ralph (2000). Variation and Change in Spanish. Cambridge University Press. p. 14. ISBN 978-0-521-78045-2.
^ Dalby, Andrew (1998). Dictionary of Languages: The Definitive Reference to More Than 400 Languages. Columbia University Press. p. 501. ISBN 978-0-231-11568-1.
^ Ginsburgh, Victor; Weber, Shlomo (2011). How Many Languages Do We Need?: The Economics of Linguistic Diversity. Princeton University Press. p. 90. ISBN 978-0-691-13689-9.
^ ab Lipski, John M (2006). Face, Timothy L; Klee, Carol A, eds. "Too close for comfort? the genesis of 'portuñol/portunhol'" (PDF). Selected Proceedings of the 8th Hispanic Linguistics Symposium: 1–22. Retrieved 21 June 2015.
^ ab "A Fala Galego-Portuguesa da Baixa-Limia e Castro Laboreiro" (PDF). Retrieved 2018-10-05.
^ Grupo El Correo Gallego. "O galego deixa de ser unha das linguas "en perigo" para a Unesco". Galicia Hoxe – Noticias en galego a diario. Retrieved 30 May 2015.
^ "Galician". Ethnologue. Retrieved 21 April 2010.
^ "Jerónimo Cantador de Argote e a Dialectologia Portuguesa (continuação)". Lusografias. Retrieved 30 May 2015.
^ Silva, António de Morais (1823). Diccionario da lingua portugueza. Retrieved 30 May 2015.
^ "D.Dinis: o Rei a Língua e o Reino" (PDF). Retrieved 12 June 2015.
^ Camus, Yves. "Jesuits' Journeys in Chinese Studies" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 September 2015. Retrieved 12 June 2015.
^ Dicionário Português–Chinês : Pu Han ci dian: Portuguese–Chinese dictionary, by Michele Ruggieri, Matteo Ricci; edited by John W. Witek. Published 2001, Biblioteca Nacional.
ISBN 972-565-298-3. Partial preview available on Google Books
^ ab "Multilingual Multiscript Plant Name Database: Sorting Citrus Names". University of Melbourne <http://www.search.unimelb.edu.au>. Retrieved 11 December 2012.
^ Ostergren, Robert C. & Le Bosse, Mathias (2011). The Europeans, Second Edition: A Geography of People, Culture, and Environment. Guilford Press. p. 129. ISBN 978-1-60918-140-6.
^ Handbook of the International Phonetic Association pp. 126–130
^ Cruz-Ferreira (1995:91)
^ Barbosa & Albano (2004:228–229)
^ Sobre os Ditongos do Português Europeu Archived 29 November 2015 at the Wayback Machine.. Carvalho, Joana. Faculdade de Letras da Universidade do Porto. Page 20 (page 10 of PDF file). Citation: A conclusão será que nos encontramos em presença de dois segmentos fonológicos /kʷ/ e /ɡʷ/, respetivamente, com uma articulação vocálica. Bisol (2005:122), tal como Freitas (1997), afirma que não estamos em presença de um ataque ramificado. Neste caso, a glide, juntamente com a vogal que a sucede, forma um ditongo no nível pós-lexical.
Esta conclusão implica um aumento do número de segmentos no inventário segmental fonológico do português.
^ ab Bisol (2005:122). Citation: A proposta é que a sequencia consoante velar + glide posterior seja indicada no léxico como uma unidade monofonemática /kʷ/ e /ɡʷ/. O glide que, nete caso, situa-se no ataque não-ramificado, forma com a vogal seguinte um ditongo crescente em nível pós lexical. Ditongos crescentes somente se formam neste nível. Em resumo, a consoante velar e o glide posterior, quando seguidos de a/o, formam uma só unidade fonológica, ou seja, um segmento consonantal com articulação secundária vocálica, em outros termos, um segmento complexo.
^ Rodrigues (2012:39–40)
^ Bisol (2005:123)
^ Thomas (1974:8)
^ Perini, Mário Alberto (2002), Modern Portuguese (A Reference Grammar), New Haven: Yale University Press, ISBN 978-0-300-09155-7
^ Mateus & d'Andrade (2000:5–6, 11)
^ Grønnum (2005:157)
^ Barbosa & Albano (2004:228)
^ Cruz-Ferreira (1995:92)
^ Mateus & d'Andrade (2000:11)
^ Squartini, Mario (1998). Verbal Periphrases in Romance: Aspect, Actionality, and Grammaticalization. Berlin: Mouton de Gruyter. ISBN 3-11-016160-5. OCLC 39007172.
^ "Most Recent Changes to the Portuguese Language".
^ "Guia do Acordo Ortográfico" (PDF) (in Portuguese). Moderna. Archived from the original (PDF) on 1 June 2010.
Sources
História da Lingua Portuguesa Instituto Camões
A Língua Portuguesa in Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Norte, Brazil
Carta de dotação e fundação da Igreja de S. Miguel de Lardosa, a.D. 882 (o mais antigo documento latino-português original conhecido) [2]
- Literature
Poesia e Prosa Medievais, by Maria Ema Tarracha Ferreira, Ulisseia 1998, 3rd ed.,
ISBN 978-972-568-124-4.
Bases Temáticas—Língua, Literatura e Cultura Portuguesa in Instituto Camões
Portuguese literature in The Catholic Encyclopedia
- Phonology, orthography and grammar
Barbosa, Plínio A.; Albano, Eleonora C. (2004). "Brazilian Portuguese". Journal of the International Phonetic Association. 34 (2): 227–232. doi:10.1017/S0025100304001756.- Bergström, Magnus & Reis, Neves Prontuário Ortográfico Editorial Notícias, 2004.
Bisol, Leda (2005), Introdução a estudos de fonologia do português brasileiro (in Portuguese), Porto Alegre – Rio Grande do Sul: EDIPUCRS, ISBN 978-85-7430-529-5
Cruz-Ferreira, Madalena (1995). "European Portuguese". Journal of the International Phonetic Association. 25 (2): 90–94. doi:10.1017/S0025100300005223.
Grønnum, Nina (2005), Fonetik og fonologi, Almen og Dansk (3rd ed.), Copenhagen: Akademisk Forlag, ISBN 978-87-500-3865-8
Mateus, Maria Helena; d'Andrade, Ernesto (2000), The Phonology of Portuguese, Oxford University Press, ISBN 978-0-19-823581-1
Rodrigues, Marisandra Costa (2012), Encontros Vocálicos Finais em Português: Descrição e Análise Otimalista (PDF) (thesis), Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro
Thomas, Earl W. (1974), A Grammar of Spoken Brazilian Portuguese, Nashville, TN: Vanderbilt University Press, ISBN 978-0-8265-1197-3- A pronúncia do português europeu—European Portuguese Pronunciation
- Dialects of Portuguese at the Instituto Camões
- Audio samples of the dialects of Portugal
- Audio samples of the dialects from outside Europe
- Portuguese Grammar
- Reference dictionaries
Antônio Houaiss (2000), Dicionário Houaiss da Língua Portuguesa (228,500 entries).
Aurélio Buarque de Holanda Ferreira, Novo Dicionário da Língua Portuguesa (1809pp)- English–Portuguese–Chinese Dictionary (Freeware for Windows/Linux/Mac)
- Linguistic studies
- Cook, Manuela. Portuguese Pronouns and Other Forms of Address, from the Past into the Future – Structural, Semantic and Pragmatic Reflections, Ellipsis, vol. 11, APSA, www.portuguese-apsa.com/ellipsis, 2013
Cook, Manuela (1997). "Uma Teoria de Interpretação das Formas de Tratamento na Língua Portuguesa". Hispania. 80 (3): 451–464. doi:10.2307/345821. JSTOR 345821.- Cook, Manuela. On the Portuguese Forms of Address: From Vossa Mercê to Você, Portuguese Studies Review 3.2, Durham: University of New Hampshire, 1995
- Lindley Cintra, Luís F. Nova Proposta de Classificação dos Dialectos Galego- Portugueses (PDF) Boletim de Filologia, Lisboa, Centro de Estudos Filológicos, 1971.
External links
Portuguese edition of Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia |
Portuguese language at Curlie


