Feedback
 |
| Complex systems |
|---|
Topics |
Emergence Emergence |
Self-organization Collective consciousness |
Collective behaviour Social dynamics Collective intelligence Swarm behaviour |
Networks Scale-free networks Social network analysis Adaptive networks |
Evolution and adaptation Artificial neural networks Evolutionary computation Evolvability |
Pattern formation Spatial fractals Reaction-diffusion systems Geomorphology |
Systems theory Homeostasis Operationalization Complexity measurement |
Nonlinear dynamics Time series analysis Ordinary differential equations Coupled map lattices |
Game theory Prisoner's dilemma Rational choice theory Evolutionary game theory |

Feedback exists between two parts when each affects the other.[1](p53)

A feedback loop where all outputs of a process are available as causal inputs to that process
Feedback occurs when outputs of a system are routed back as inputs as part of a chain of cause-and-effect that forms a circuit or loop.[2] The system can then be said to feed back into itself. The notion of cause-and-effect has to be handled carefully when applied to feedback systems:
.mw-parser-output .templatequoteoverflow:hidden;margin:1em 0;padding:0 40px.mw-parser-output .templatequote .templatequoteciteline-height:1.5em;text-align:left;padding-left:1.6em;margin-top:0
Simple causal reasoning about a feedback system is difficult because the first system influences the second and second system influences the first, leading to a circular argument. This makes reasoning based upon cause and effect tricky, and it is necessary to analyze the system as a whole.
— Karl Johan Åström and Richard M. Murray, Feedback Systems: An Introduction for Scientists and Engineers[3]
Contents
1 History
2 Types
2.1 Positive and negative feedback
2.1.1 Terminology
2.1.2 Limitations of negative and positive feedback
2.2 Other types of feedback
3 Applications
3.1 Dynamical systems
3.2 Biology
3.3 Climate science
3.4 Control theory
3.5 Mechanical engineering
3.6 Electronic engineering
3.6.1 Negative feedback
3.6.2 Positive feedback
3.6.3 Oscillator
3.6.4 Latches and flip-flops
3.7 Software
3.7.1 User interface design
3.8 Video feedback
3.9 Social sciences
3.9.1 Economics and finance
4 See also
5 References
6 Further reading
7 External links
History
Self-regulating mechanisms have existed since antiquity, and the idea of feedback had started to enter economic theory in Britain by the eighteenth century, but it wasn't at that time recognized as a universal abstraction and so didn't have a name.[4]
The verb phrase "to feed back", in the sense of returning to an earlier position in a mechanical process, was in use in the US by the 1860s,[5][6] and in 1909, Nobel laureate Karl Ferdinand Braun used the term "feed-back" as a noun to refer to (undesired) coupling between components of an electronic circuit.[7]
By the end of 1912, researchers using early electronic amplifiers (audions) had discovered that deliberately coupling part of the output signal back to the input circuit would boost the amplification (through regeneration), but would also cause the audion to howl or sing.[8] This action of feeding back of the signal from output to input gave rise to the use of the term "feedback" as a distinct word by 1920.[8]
Over the years there has been some dispute as to the best definition of feedback. According to Ashby (1956), mathematicians and theorists interested in the principles of feedback mechanisms prefer the definition of circularity of action, which keeps the theory simple and consistent. For those with more practical aims, feedback should be a deliberate effect via some more tangible connection.
[Practical experimenters] object to the mathematician's definition, pointing out that this would force them to say that feedback was present in the ordinary pendulum ... between its position and its momentum—a "feedback" that, from the practical point of view, is somewhat mystical. To this the mathematician retorts that if feedback is to be considered present only when there is an actual wire or nerve to represent it, then the theory becomes chaotic and riddled with irrelevancies.[1](p54)
Focusing on uses in management theory, Ramaprasad (1983) defines feedback generally as "...information about the gap between the actual level and the reference level of a system parameter" that is used to "alter the gap in some way." He emphasizes that the information by itself is not feedback unless translated into action.[9]
Types
Positive and negative feedback

Maintaining a desired system performance despite disturbance using negative feedback to reduce system error
There are two types of feedback: positive feedback and negative feedback.
As an example of negative feedback, the diagram might represent a cruise control system in a car, for example, that matches a target speed such as the speed limit. The controlled system is the car; its input includes the combined torque from the engine and from the changing slope of the road (the disturbance). The car's speed (status) is measured by a speedometer. The error signal is the departure of the speed as measured by the speedometer from the target speed (set point). This measured error is interpreted by the controller to adjust the accelerator, commanding the fuel flow to the engine (the effector). The resulting change in engine torque, the feedback, combines with the torque exerted by the changing road grade to reduce the error in speed, minimizing the road disturbance.
The terms "positive" and "negative" were first applied to feedback prior to WWII. The idea of positive feedback was already current in the 1920s with the introduction of the regenerative circuit.[10] Friis and Jensen (1924) described regeneration in a set of electronic amplifiers as a case where the "feed-back" action is positive in contrast to negative feed-back action, which they mention only in passing.[11]Harold Stephen Black's classic 1934 paper first details the use of negative feedback in electronic amplifiers. According to Black:
Positive feed-back increases the gain of the amplifier, negative feed-back reduces it.[12]
According to Mindell (2002) confusion in the terms arose shortly after this:
...Friis and Jensen had made the same distinction Black used between "positive feed-back" and "negative feed-back", based not on the sign of the feedback itself but rather on its effect on the amplifier's gain. In contrast, Nyquist and Bode, when they built on Black's work, referred to negative feedback as that with the sign reversed. Black had trouble convincing others of the utility of his invention in part because confusion existed over basic matters of definition.[10](p121)
Even prior to the terms being applied, James Clerk Maxwell had described several kinds of "component motions" associated with the centrifugal governors used in steam engines, distinguishing between those that lead to a continual increase in a disturbance or the amplitude of an oscillation, and those that lead to a decrease of the same.[13]
Terminology
The terms positive and negative feedback are defined in different ways within different disciplines.
- the altering of the gap between reference and actual values of a parameter, based on whether the gap is widening (positive) or narrowing (negative).[9]
- the valence of the action or effect that alters the gap, based on whether it has a happy (positive) or unhappy (negative) emotional connotation to the recipient or observer.[14]
The two definitions may cause confusion, such as when an incentive (reward) is used to boost poor performance (narrow a gap). Referring to definition 1, some authors use alternative terms, replacing positive/negative with self-reinforcing/self-correcting,[15]reinforcing/balancing,[16]discrepancy-enhancing/discrepancy-reducing[17] or regenerative/degenerative[18] respectively. And for definition 2, some authors advocate describing the action or effect as positive/negative reinforcement or punishment rather than feedback.[9][19]
Yet even within a single discipline an example of feedback can be called either positive or negative, depending on how values are measured or referenced.[20]
This confusion may arise because feedback can be used for either informational or motivational purposes, and often has both a qualitative and a quantitative component. As Connellan and Zemke (1993) put it:
Quantitative feedback tells us how much and how many. Qualitative feedback tells us how good, bad or indifferent.[21](p102)
Limitations of negative and positive feedback
While simple systems can sometimes be described as one or the other type, many systems with feedback loops cannot be so easily designated as simply positive or negative, and this is especially true when multiple loops are present.
When there are only two parts joined so that each affects the other, the properties of the feedback give important and useful information about the properties of the whole. But when the parts rise to even as few as four, if every one affects the other three, then twenty circuits can be traced through them; and knowing the properties of all the twenty circuits does not give complete information about the system.[1](p54)
Other types of feedback
In general, feedback systems can have many signals fed back and the feedback loop frequently contain mixtures of positive and negative feedback where positive and negative feedback can dominate at different frequencies or different points in the state space of a system.
The term bipolar feedback has been coined to refer to biological systems where positive and negative feedback systems can interact, the output of one affecting the input of another, and vice versa.[22]
Some systems with feedback can have very complex behaviors such as chaotic behaviors in non-linear systems, while others have much more predictable behaviors, such as those that are used to make and design digital systems.
Feedback is used extensively in digital systems. For example, binary counters and similar devices employ feedback where the current state and inputs are used to calculate a new state which is then fed back and clocked back into the device to update it.
Applications
Dynamical systems
By using feedback properties, the behavior of a system can be altered to meet the needs of an application; systems can be made stable, responsive or held constant. It is shown that dynamical systems with a feedback experience an adaptation to the edge of chaos.[23]
Biology
In biological systems such as organisms, ecosystems, or the biosphere, most parameters must stay under control within a narrow range around a certain optimal level under certain environmental conditions. The deviation of the optimal value of the controlled parameter can result from the changes in internal and external environments. A change of some of the environmental conditions may also require change of that range to change for the system to function. The value of the parameter to maintain is recorded by a reception system and conveyed to a regulation module via an information channel. An example of this is insulin oscillations.
Biological systems contain many types of regulatory circuits, both positive and negative. As in other contexts, positive and negative do not imply that the feedback causes good or bad effects. A negative feedback loop is one that tends to slow down a process, whereas the positive feedback loop tends to accelerate it. The mirror neurons are part of a social feedback system, when an observed action is "mirrored" by the brain—like a self-performed action.
Normal tissue integrity is preserved by feedback interactions between diverse cell types mediated by adhesion molecules and secreted molecules that act as mediators; failure of key feedback mechanisms in cancer disrupts tissue function.[24]
In an injured or infected tissue, inflammatory mediators elicit feedback responses in cells, which alter gene expression, and change the groups of molecules expressed and secreted, including molecules that induce diverse cells to cooperate and restore tissue structure and function. This type of feedback is important because it enables coordination of immune responses and recovery from infections and injuries. During cancer, key elements of this feedback fail. This disrupts tissue function and immunity.[25][26]
Mechanisms of feedback were first elucidated in bacteria, where a nutrient elicits changes in some of their metabolic functions.[27]
Feedback is also central to the operations of genes and gene regulatory networks. Repressor (see Lac repressor) and activator proteins are used to create genetic operons, which were identified by Francois Jacob and Jacques Monod in 1961 as feedback loops.[28] These feedback loops may be positive (as in the case of the coupling between a sugar molecule and the proteins that import sugar into a bacterial cell), or negative (as is often the case in metabolic consumption).
On a larger scale, feedback can have a stabilizing effect on animal populations even when profoundly affected by external changes, although time lags in feedback response can give rise to predator-prey cycles.[29]
In zymology, feedback serves as regulation of activity of an enzyme by its direct product(s) or downstream metabolite(s) in the metabolic pathway (see Allosteric regulation).
The hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis is largely controlled by positive and negative feedback, much of which is still unknown.
In psychology, the body receives a stimulus from the environment or internally that causes the release of hormones. Release of hormones then may cause more of those hormones to be released, causing a positive feedback loop. This cycle is also found in certain behaviour. For example, "shame loops" occur in people who blush easily. When they realize that they are blushing, they become even more embarrassed, which leads to further blushing, and so on.[30]
Climate science
The climate system is characterized by strong positive and negative feedback loops between processes that affect the state of the atmosphere, ocean, and land. A simple example is the ice-albedo positive feedback loop whereby melting snow exposes more dark ground (of lower albedo), which in turn absorbs heat and causes more snow to melt.
Control theory
Feedback is extensively used in control theory, using a variety of methods including state space (controls), full state feedback (also known as pole placement), and so forth. Note that in the context of control theory, "feedback" is traditionally assumed to specify "negative feedback".[31]
The most common general-purpose controller using a control-loop feedback mechanism is a proportional-integral-derivative (PID) controller. Heuristically, the terms of a PID controller can be interpreted as corresponding to time: the proportional term depends on the present error, the integral term on the accumulation of past errors, and the derivative term is a prediction of future error, based on current rate of change.[32]
Mechanical engineering
In ancient times, the float valve was used to regulate the flow of water in Greek and Roman water clocks; similar float valves are used to regulate fuel in a carburettor and also used to regulate tank water level in the flush toilet.
The Dutch inventor Cornelius Drebbel (1572-1633) built thermostats (c1620) to control the temperature of chicken incubators and chemical furnaces. In 1745, the windmill was improved by blacksmith Edmund Lee, who added a fantail to keep the face of the windmill pointing into the wind. In 1787, Thomas Mead regulated the rotation speed of a windmill by using a centrifugal pendulum to adjust the distance between the bedstone and the runner stone (i.e., to adjust the load).
The use of the centrifugal governor by James Watt in 1788 to regulate the speed of his steam engine was one factor leading to the Industrial Revolution. Steam engines also use float valves and pressure release valves as mechanical regulation devices. A mathematical analysis of Watt's governor was done by James Clerk Maxwell in 1868.[13]
The Great Eastern was one of the largest steamships of its time and employed a steam powered rudder with feedback mechanism designed in 1866 by John McFarlane Gray. Joseph Farcot coined the word servo in 1873 to describe steam-powered steering systems. Hydraulic servos were later used to position guns. Elmer Ambrose Sperry of the Sperry Corporation designed the first autopilot in 1912. Nicolas Minorsky published a theoretical analysis of automatic ship steering in 1922 and described the PID controller.[33]
Internal combustion engines of the late 20th century employed mechanical feedback mechanisms such as the vacuum timing advance but mechanical feedback was replaced by electronic engine management systems once small, robust and powerful single-chip microcontrollers became affordable.
Electronic engineering

The simplest form of a feedback amplifier can be represented by the ideal block diagram made up of unilateral elements.[34]
The use of feedback is widespread in the design of electronic amplifiers, oscillators, and stateful logic circuit elements such as flip-flops and counters. Electronic feedback systems are also very commonly used to control mechanical, thermal and other physical processes.
If the signal is inverted on its way round the control loop, the system is said to have negative feedback;[35] otherwise, the feedback is said to be positive. Negative feedback is often deliberately introduced to increase the stability and accuracy of a system by correcting or reducing the influence of unwanted changes. This scheme can fail if the input changes faster than the system can respond to it. When this happens, the lag in arrival of the correcting signal can result in overcorrection, causing the output to oscillate or "hunt".[36] While often an unwanted consequence of system behaviour, this effect is used deliberately in electronic oscillators.
Harry Nyquist at Bell Labs derived the Nyquist stability criterion for determining the stability of feedback systems. An easier method, but less general, is to use Bode plots developed by Hendrik Bode to determine the gain margin and phase margin. Design to ensure stability often involves frequency compensation to control the location of the poles of the amplifier.
Electronic feedback loops are used to control the output of electronic devices, such as amplifiers. A feedback loop is created when all or some portion of the output is fed back to the input. A device is said to be operating open loop if no output feedback is being employed and closed loop if feedback is being used.[37]
When two or more amplifiers are cross-coupled using positive feedback, complex behaviors can be created. These multivibrators are widely used and include:
- astable circuits, which act as oscillators
- monostable circuits, which can be pushed into a state, and will return to the stable state after some time
- bistable circuits, which have two stable states that the circuit can be switched between
Negative feedback
A Negative feedback occurs when the fed-back output signal has a relative phase of 180° with respect to the input signal (upside down). This situation is sometimes referred to as being out of phase, but that term also is used to indicate other phase separations, as in "90° out of phase". Negative feedback can be used to correct output errors or to desensitize a system to unwanted fluctuations.[38] In feedback amplifiers, this correction is generally for waveform distortion reduction[citation needed] or to establish a specified gain level. A general expression for the gain of a negative feedback amplifier is the asymptotic gain model.
Positive feedback
Positive feedback occurs when the fed-back signal is in phase with the input signal. Under certain gain conditions, positive feedback reinforces the input signal to the point where the output of the device oscillates between its maximum and minimum possible states. Positive feedback may also introduce hysteresis into a circuit. This can cause the circuit to ignore small signals and respond only to large ones. It is sometimes used to eliminate noise from a digital signal. Under some circumstances, positive feedback may cause a device to latch, i.e., to reach a condition in which the output is locked to its maximum or minimum state. This fact is very widely used in digital electronics to make bistable circuits for volatile storage of information.
The loud squeals that sometimes occurs in audio systems, PA systems, and rock music are known as audio feedback. If a microphone is in front of a loudspeaker that it is connected to, sound that the microphone picks up comes out of the speaker, and is picked up by the microphone and re-amplified. If the loop gain is sufficient, howling or squealing at the maximum power of the amplifier is possible.
Oscillator
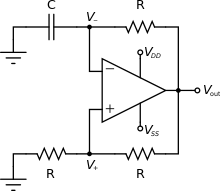
A popular op-amp relaxation oscillator.
An electronic oscillator is an electronic circuit that produces a periodic, oscillating electronic signal, often a sine wave or a square wave.[39][40] Oscillators convert direct current (DC) from a power supply to an alternating current signal. They are widely used in many electronic devices. Common examples of signals generated by oscillators include signals broadcast by radio and television transmitters, clock signals that regulate computers and quartz clocks, and the sounds produced by electronic beepers and video games.[39]
Oscillators are often characterized by the frequency of their output signal:
- A low-frequency oscillator (LFO) is an electronic oscillator that generates a frequency below ≈20 Hz. This term is typically used in the field of audio synthesizers, to distinguish it from an audio frequency oscillator.
- An audio oscillator produces frequencies in the audio range, about 16 Hz to 20 kHz.[40]
- An RF oscillator produces signals in the radio frequency (RF) range of about 100 kHz to 100 GHz.[40]
Oscillators designed to produce a high-power AC output from a DC supply are usually called inverters.
There are two main types of electronic oscillator: the linear or harmonic oscillator and the nonlinear or relaxation oscillator.[40][41]
Latches and flip-flops

An SR latch, constructed from a pair of cross-coupled NOR gates.
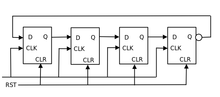
A 4-bit ring counter using D-type flip flops
A latch or a flip-flop is a circuit that has two stable states and can be used to store state information. They typically constructed using feedback that crosses over between two arms of the circuit, to provide the circuit with a state. The circuit can be made to change state by signals applied to one or more control inputs and will have one or two outputs. It is the basic storage element in sequential logic. Latches and flip-flops are fundamental building blocks of digital electronics systems used in computers, communications, and many other types of systems.
Latches and flip-flops are used as data storage elements. Such data storage can be used for storage of state, and such a circuit is described as sequential logic. When used in a finite-state machine, the output and next state depend not only on its current input, but also on its current state (and hence, previous inputs). It can also be used for counting of pulses, and for synchronizing variably-timed input signals to some reference timing signal.
Flip-flops can be either simple (transparent or opaque) or clocked (synchronous or edge-triggered). Although the term flip-flop has historically referred generically to both simple and clocked circuits, in modern usage it is common to reserve the term flip-flop exclusively for discussing clocked circuits; the simple ones are commonly called latches.[42][43]
Using this terminology, a latch is level-sensitive, whereas a flip-flop is edge-sensitive. That is, when a latch is enabled it becomes transparent, while a flip flop's output only changes on a single type (positive going or negative going) of clock edge.
Software
Feedback loops provide generic mechanisms for controlling the running, maintenance, and evolution of software and computing systems.[44] Feedback-loops are important models in the engineering of adaptive software, as they define the behaviour of the interactions among the control elements over the adaptation process, to guarantee system properties at run-time. Feedback loops and foundations of control theory have been successfully applied to computing systems.[45] In particular, they have been applied to the development of products such as IBM's Universal Database server and IBM Tivoli. From a software perspective, the autonomic (MAPE, monitor analyze plan execute) loop proposed by researchers of IBM is another valuable contribution to the application of feedback loops to the control of dynamic properties and the design and evolution of autonomic software systems.[46][47]
User interface design
Feedback is also a useful design principle for designing user interfaces.
Video feedback
Video feedback is the video equivalent of acoustic feedback. It involves a loop between a video camera input and a video output, e.g., a television screen or monitor. Aiming the camera at the display produces a complex video image based on the feedback.[48]
Social sciences
Economics and finance
The stock market is an example of a system prone to oscillatory "hunting", governed by positive and negative feedback resulting from cognitive and emotional factors among market participants. For example:
- When stocks are rising (a bull market), the belief that further rises are probable gives investors an incentive to buy (positive feedback—reinforcing the rise, see also stock market bubble and momentum investing); but the increased price of the shares, and the knowledge that there must be a peak after which the market falls, ends up deterring buyers (negative feedback—stabilizing the rise).
- Once the market begins to fall regularly (a bear market), some investors may expect further losing days and refrain from buying (positive feedback—reinforcing the fall), but others may buy because stocks become more and more of a bargain (negative feedback—stabilizing the fall, see also contrarian investing).
George Soros used the word reflexivity, to describe feedback in the financial markets and developed an investment theory based on this principle.
The conventional economic equilibrium model of supply and demand supports only ideal linear negative feedback and was heavily criticized by Paul Ormerod in his book The Death of Economics, which, in turn, was criticized by traditional economists. This book was part of a change of perspective as economists started to recognise that chaos theory applied to nonlinear feedback systems including financial markets.
See also
- Audio feedback
Black box (see "experiment model")- Cybernetics
- Feed forward
- Interaction
- Low-key feedback
- Optical feedback
- Perverse incentive
- Recursion
- Resonance
- Stability criterion
- Strange loop
- Tactile
- Unintended consequence
References
^ abc
W. Ross Ashby (1957). An introduction to cybernetics (PDF). Chapman & Hall..mw-parser-output cite.citationfont-style:inherit.mw-parser-output .citation qquotes:"""""""'""'".mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registrationcolor:#555.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration spanborder-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output code.cs1-codecolor:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-errordisplay:none;font-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-errorfont-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-maintdisplay:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-formatfont-size:95%.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-leftpadding-left:0.2em.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-rightpadding-right:0.2em
^ Andrew Ford (2010). "Chapter 9: Information feedback and causal loop diagrams". Modeling the Environment. Island Press. pp. 99 ff. ISBN 9781610914253.This chapter describes causal loop diagrams to portray the information feedback at work in a system. The word causal refers to cause-and-effect relationships. The wordloop refers to a closed chain of cause and effect that creates the feedback.
^ Karl Johan Åström; Richard M. Murray (2010). "§1.1: What is feedback?". Feedback Systems: An Introduction for Scientists and Engineers. Princeton University Press. p. 1. ISBN 9781400828739. Online version found here.
^
Otto Mayr (1989). Authority, liberty, & automatic machinery in early modern Europe. Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 978-0-8018-3939-9.
^
"Heretofore ... it has been necessary to reverse the motion of the rollers, thus causing the material to travel or feed back, ..."
HH Cole, "Improvement in Fluting-Machines", US Patent 55,469 (1866) accessed 23 Mar 2012.
^
"When the journal or spindle is cut ... and the carriage is about to feed back by a change of the sectional nut or burr upon the screw-shafts, the operator seizes the handle..." JM Jay, "Improvement in Machines for Making the Spindles of Wagon-Axles", US Patent 47,769 (1865) accessed 23 Mar 2012.
^ "...as far as possible the circuit has no feed-back into the system being investigated."
[1]
Karl Ferdinand Braun, "Electrical oscillations and wireless telegraphy", Nobel Lecture, 11 December 1909. Retrieved 19 Mar 2012.
^ ab Stuart Bennett (1979). A history of control engineering, 1800–1930. Stevenage; New York: Peregrinus for the Institution of Electrical Engineers. ISBN 978-0-906048-07-8.
[2]
^ abc Ramaprasad, Arkalgud (1983). "On the definition of feedback". Behavioral Science. 28: 4–13. doi:10.1002/bs.3830280103.
^ ab
David A. Mindell (2002). Between Human and Machine : Feedback, Control, and Computing before Cybernetics. Baltimore, MD, US: Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 9780801868955.
^
Friis, H.T., and A.G.Jensen. "High Frequency Amplifiers" Bell System Technical Journal 3 (April 1924):181–205.
^
H.S. Black, "Stabilized feed-back amplifiers", Electrical Engineering, vol. 53, pp. 114–120, January 1934.
^ ab
Maxwell, James Clerk (1868). "On Governors" (PDF). Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. 16: 270–283. doi:10.1098/rspl.1867.0055.
^ Herold, David M., and Martin M. Greller. "Research Notes. FEEDBACK THE DEFINITION OF A CONSTRUCT." Academy of management Journal 20.1 (1977): 142-147.
^
Peter M. Senge (1990). The Fifth Discipline: The Art and Practice of the Learning Organization. New York: Doubleday. p. 424. ISBN 978-0-385-26094-7.
^
John D. Sterman, Business Dynamics: Systems Thinking and Modeling for a Complex World, McGraw Hill/Irwin, 2000.
ISBN 978-0-07-238915-9
^
Charles S. Carver, Michael F. Scheier: On the Self-Regulation of Behavior Cambridge University Press, 2001
^
Hermann A Haus and Richard B. Adler, Circuit Theory of Linear Noisy Networks, MIT Press, 1959
^
BF Skinner, The Experimental Analysis of Behavior, American Scientist, Vol. 45, No. 4 (SEPTEMBER 1957), pp. 343-371
^
"However, after scrutinizing the statistical properties of the structural equations, the members of the committee assured themselves that it is possible to have a significant positive feedback loop when using standardized scores, and a negative loop when using real scores."
Ralph L. Levine, Hiram E. Fitzgerald. Analysis of dynamic psychological systems: methods and applications,
ISBN 978-0306437465 (1992) page 123
^ Thomas K. Connellan and Ron Zemke, "Sustaining Knock Your Socks Off Service" AMACOM, 1 July 1993.
ISBN 0-8144-7824-7
^
Alta Smit; Arturo O'Byrne (2011). "Bipolar feedback". Introduction to Bioregulatory Medicine. Thieme. p. 6. ISBN 9783131469717.
^ Wotherspoon, T.; Hubler, A. (2009). "Adaptation to the edge of chaos with random-wavelet feedback". J. Phys. Chem. A. 113 (1): 19–22. Bibcode:2009JPCA..113...19W. doi:10.1021/jp804420g. PMID 19072712.
^ Vlahopoulos, SA; Cen, O; Hengen, N; Agan, J; Moschovi, M; Critselis, E; Adamaki, M; Bacopoulou, F; Copland, JA; Boldogh, I; Karin, M; Chrousos, GP (20 June 2015). "Dynamic aberrant NF-κB spurs tumorigenesis: A new model encompassing the microenvironment". Cytokine & Growth Factor Reviews. 26 (4): 389–403. doi:10.1016/j.cytogfr.2015.06.001. PMC 4526340. PMID 26119834.
^ Vlahopoulos, SA (August 2017). "Aberrant control of NF-κB in cancer permits transcriptional and phenotypic plasticity, to curtail dependence on host tissue: molecular mode". Cancer Biology & Medicine. 14 (3): 254–270. doi:10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2017.0029. PMC 5570602. PMID 28884042.
^ Korneev, KV; Atretkhany, KN; Drutskaya, MS; Grivennikov, SI; Kuprash, DV; Nedospasov, SA (January 2017). "TLR-signaling and proinflammatory cytokines as drivers of tumorigenesis". Cytokine. 89: 127–135. doi:10.1016/j.cyto.2016.01.021. PMID 26854213.
^ Sanwal, BD (March 1970). "Allosteric controls of amphilbolic pathways in bacteria". Bacteriol. Rev. 34 (1): 20–39. PMC 378347. PMID 4315011.
^ Jacob, F; Monod, J (June 1961). "Genetic regulatory mechanisms in the synthesis of proteins". J Mol Biol. 3 (3): 318–356. doi:10.1016/S0022-2836(61)80072-7. PMID 13718526.
^
CS Holling. "Resilience and stability of ecological systems". Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics 4:1-23. 1973
^ Scheff, Thomas (2009-09-02). "The Emotional/Relational World". Psychology Today. Retrieved 2013-07-10.
^
"There is a tradition in control theory that one deals with a negative feedback loop in which a negative sign is included in the feedback loop..."
A.I.Mees, "Dynamics of Feedback Systems", New York: J. Wiley, c1981.
ISBN 0-471-27822-X. p69
^ Araki, M., PID Control (PDF)
^ Minorsky, Nicolas (1922). "Directional stability of automatically steered bodies". J. Amer. Soc of Naval Engineers. 34 (2): 280–309. doi:10.1111/j.1559-3584.1922.tb04958.x.
^
Wai-Kai Chen (2005). "Chapter 13: General feedback theory". Circuit Analysis and Feedback Amplifier Theory. CRC Press. p. 13–1. ISBN 9781420037272.[In a practical amplifier] the forward path may not be strictly unilateral, the feedback path is usually bilateral, and the input and output coupling networks are often complicated.
^
Santiram Kal (2009). Basic Electronics: Devices, Circuits and IT Fundamentals. PHI Learning Pvt. Ltd. p. 191. ISBN 9788120319523.If the feedback signal reduces the input signal, i.e. it is out of phase with the input [signal], it is called negative feedback.
^ With mechanical devices, hunting can be severe enough to destroy the device.
^ P. Horowitz & W. Hill, The Art of Electronics, Cambridge University Press (1980), Chapter 3, relating to operational amplifiers.
^
For an analysis of desensitization in the system pictured, see S.K Bhattacharya (2011). "§5.3.1 Effect of feedback on parameter variations". Linear Control Systems. Pearson Education India. pp. 134–135. ISBN 9788131759523.The parameters of a system ... may vary... The primary advantage of using feedback in control systems is to reduce the system's sensitivity to parameter variations.
^ ab Snelgrove, Martin (2011). "Oscillator". McGraw-Hill Encyclopedia of Science and Technology, 10th Ed., Science Access online service. McGraw-Hill. Retrieved 1 March 2012.
^ abcd Chattopadhyay, D. (2006). Electronics (fundamentals And Applications). New Age International. pp. 224–225. ISBN 978-81-224-1780-7.
^ Garg, Rakesh Kumar; Ashish Dixit; Pavan Yadav (2008). Basic Electronics. Firewall Media. p. 280. ISBN 978-8131803028.
^
Volnei A. Pedroni (2008). Digital electronics and design with VHDL. Morgan Kaufmann. p. 329. ISBN 978-0-12-374270-4.
^ Latches and Flip Flops (EE 42/100 Lecture 24 from Berkeley) "...Sometimes the terms flip-flop and latch are used interchangeably..."
^
H. Giese; Y. Brun; J. D. M. Serugendo; C. Gacek; H. Kienle; H. Müller; M. Pezzè; M. Shaw (2009). "Engineering self-adaptive and self-managing systems". Springer-Verlag.
^
J. L. Hellerstein; Y. Diao; S. Parekh; D. M. Tilbury (2004). Feedback Control of Computing Systems. John Wiley & Sons.
^
J. O. Kephart; D. M. Chess (2003). "The vision of autonomic computing".
^
H. A. Müller; H. M. Kienle & U. Stege (2009). "Autonomic computing: Now you see it, now you don't—design and evolution of autonomic software systems".
^ Hofstadter, Douglas (2007). I Am a Strange loop. New York: Basic Books. p. 67. ISBN 978-0-465-03079-8.
Further reading
- Katie Salen and Eric Zimmerman. Rules of Play. MIT Press. 2004.
ISBN 0-262-24045-9. Chapter 18: Games as Cybernetic Systems.
Korotayev A., Malkov A., Khaltourina D. Introduction to Social Macrodynamics: Secular Cycles and Millennial Trends. Moscow: URSS, 2006.
ISBN 5-484-00559-0- Dijk, E., Cremer, D.D., Mulder, L.B., and Stouten, J. "How Do We React to Feedback in Social Dilemmas?" In Biel, Eek, Garling & Gustafsson, (eds.), New Issues and Paradigms in Research on Social Dilemmas, New York: Springer, 2008.
External links
| Look up feedback in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
 Media related to Feedback at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Feedback at Wikimedia Commons
