NFL Europe
| Sport | American football |
|---|---|
| Founded | 1989[1] |
| Inaugural season | 1991 |
| Ceased | 2007 |
| Owner(s) | National Football League |
| No. of teams | 10 (1991–1992) 6 (1995–2007) |
| Countries | Canada (1991–1992) Germany (1991–2007) Netherlands (1995–2007) Spain (1991–2003) United Kingdom (1991–2004) United States (1991–1992) |
| Last champion(s) | Hamburg Sea Devils |
| Most titles | Frankfurt Galaxy, 4 |
The World League of American Football (shortened to WLAF or World League[2]), later renamed the NFL Europe League (NFL Europe for short) and then NFL Europa, was a professional American football league which operated between 1991 and 2007. It was backed by the National Football League (NFL), the largest league in the United States. Each season culminated with the World Bowl.
The World League of American Football was founded in 1989 to serve as a type of spring league. Seven of the ten teams were based in North America, and the other three in Europe. This format lasted for two seasons, with no league in 1993–94.
The WLAF returned in 1995 with six teams, all in Europe, and in 1998 the league was rebranded as the NFL Europe League[3] or NFL Europe, until 2006. For the league's last season, 2007, it officially changed its name to NFL Europa.
The league's squads were predominantly assigned by NFL teams, who wanted these younger, developmental players to get additional game experience and coaching.[3] The NFL assumed the expenses of players and coaches living in Europe.[3] The European six-team format was maintained for 12 seasons, from 1995 to 2007, but by 2007 five teams were based in Germany. Making a reported $30 million loss per season, with teams such as the London Monarchs going defunct, on 29 June 2007, the NFL announced the end of NFL Europa.[4]
Contents
1 History
1.1 World League of American Football (WLAF)
1.1.1 1991 season
1.1.2 1992 season
1.1.3 1995 comeback
1.1.4 1996 season
1.1.5 1997 season
1.2 NFL Europe
1.3 NFL Europa/Cessation of operations
2 Teams
3 Experimental rules
3.1 Uniforms
4 Television coverage
4.1 1991–92
4.2 1995–2007
5 Stadiums
5.1 Attendance
6 Presidents
7 Notes and references
8 See also
9 External links
History
A previous proposed league in the 1970s, the Intercontinental Football League, had contained many elements of the eventual all-European league.[5] West German entrepreneur Adalbert Wetzel and sports coach Bob Kap secured the release of several NFL players to the IFL for a planned 1975 season.[5] The IFL would have involved teams in Barcelona, Rome, West Berlin, Munich, Vienna and Istanbul, but was cancelled due to economic and political problems.[5]
World League of American Football (WLAF)

WLAF logo
The World League of American Football was formed in 1989, by a unanimous vote of NFL owners,[1] as a spring developmental league, the "brainchild" of commissioner Paul Tagliabue.[3] This came after the NFL had played popular American Bowls in London's Wembley Stadium and elsewhere since 1986. Of the 28 NFL teams, 26 paid $50,000 each in start-up costs for the WLAF.[6] Team payrolls and budgets were controlled by the WLAF office[6] but not all teams were owned by the league; in May 1992 it owned five (including Barcelona, London and Frankfurt) and part-owned three.[1]
The WLAF was set up as a professional American football league for North America and Europe: six teams from the United States, three European teams, and one Canadian team. In 1991 parties in Moscow and Japan expressed an interest in additional franchises.[7]
Teams were aligned in three divisions:
- North American West: Birmingham Fire, Sacramento Surge, San Antonio Riders
- North American East: Montreal Machine, New York/New Jersey Knights, Orlando Thunder, Raleigh–Durham Skyhawks (replaced by Ohio Glory in 1992)
- European: Barcelona Dragons, Frankfurt Galaxy, London Monarchs
The WLAF played two seasons in the spring of 1991 and 1992, with 10 teams playing a 10-game regular season with the World Bowl championship game. Rules unique to WLAF included assigning increasing point value to field goals based on distance, and a requirement that at least one player of non-US nationality participate in at least every other series of downs.
New ideas were successfully tested, like using the two-point conversion rule also on the professional field (which was already in use in the Canadian Football League) before adopting it in the NFL in 1994. Other minor tweaks in gameplay, such as a shorter kickoff tee, were also first used in the WLAF. Several technical innovations, such as helmet mounted cameras[8] and one-way radios, enabling coaches to tell plays directly to quarterbacks, were also developed.
The average game attendance for the first season was 25,361, and 24,216 in the second season.[9] The original WLAF was barely noticed in the United States, having a "minor-league or developmental image"[7] and low TV ratings.[6] In the non-U.S. cities of London, Barcelona, Frankfurt and Montreal, crowds surpassed early expectations.[7] The Monarchs' home attendance led the league,[10] and the 1991 World Bowl played at Wembley Stadium was attended by 61,108.[11]
In May 1991, the L.A. Times's Chris Dufresne said American fans were less likely than Europeans to "shell out hard-earned dollars for games featuring roster-cut leftovers" and suggested there was a post-USFL backlash in Orlando, Birmingham, and San Antonio.[12] The WLAF lost $7 million in 1991.[1]
The playoff format consisted of four teams: the three divisional champions, plus a wild card with the best overall non-division winning record. The two teams emerging from the WLAF semi-final playoffs met at the end of the season in the World Bowl. The first two World Bowl locations were predetermined before the season.
Operations of the WLAF were suspended after the 1992 season as the league lost money and the involved NFL owners were not willing to invest more. However, the NFL still needed another pro Football league to help their cause in the antitrust and free agency lawsuit with the National Football League Players' Association.

Wembley Stadium, the host stadium of World Bowl '91
1991 season
The three Europe-based teams dominated in 1991, with a combined 24–6 record, while no North American team managed better than 5–5. The London Monarchs won the World Bowl. The Raleigh-Durham Skyhawks lost all 10 games and ultimately their franchise, which was moved to Ohio for 1992.
Semifinals | World Bowl '91 | ||||||||
| 1 | 10 | ||||||||
| 4 | 3 | ||||||||
| 0 | |||||||||
21 | |||||||||
| 3 | 42 | ||||||||
| 2 | 26 | ||||||||

The site of World Bowl '92 was the Olympic Stadium (Montreal)
1992 season
The WLAF's second season was confirmed to go ahead on 23 October 1991, six months before it kicked off.[11][13]
In 1992, fortunes changed and none of the European teams had winning seasons. Despite this, the European fans remained loyal, but the NFL owners suspended the WLAF after the season.[14]Paul Tagliabue mentioned plans to bring it back with only European teams, possibly in 1994.[14][15] British sports writer Matt Tench cited "an ambivalence on the part of the NFL owners: they wanted a spring league but did not want to create a rival to the NFL. In the end they did not create enough of a rival."[15]
The Sacramento and San Antonio franchises left the WLAF, with their ownership groups attempting to secure franchises in the Canadian Football League in preparation for their U.S. expansion in 1993. The Sacramento Gold Miners would play in the CFL for three years, becoming the first American franchise in the league (and beginning a three-season sojurn in the U.S. for the CFL).
Semifinals | World Bowl '92 | ||||||||
| 1 | Birmingham Fire | 7 | |||||||
| 4 | Orlando Thunder | 45 | |||||||
Sacramento Surge | 21 | ||||||||
| Orlando Thunder | 17 | ||||||||
| 3 | Barcelona Dragons | 15 | |||||||
| 2 | Sacramento Surge | 17 | |||||||
1995 comeback
After 1992, the World League was suspended for two years. The spring developmental league had enough NFL support to continue, but without any North American teams. The new teams were announced in July 1994,[16] and the third WLAF season began in April 1995. The 1995 WLAF[2] was based entirely in Europe, and was reduced to six teams.[17] The three existing European teams (London, Barcelona and Frankfurt) were joined by three new teams in Amsterdam (the Admirals), Düsseldorf (Rhein Fire) and Edinburgh (Scottish Claymores).
In the wake of Fox's new contract to broadcast NFL games, Fox became a co-owner of the WLAF and a major financial contributor, in return for broadcasting rights.[18] The relaunched league was sponsored by Reebok, which also manufactured team uniforms and apparel.[19]
All six teams played in a single division. By playing each other twice (home and away), the WLAF's regular season lasted for 10 games, as it had in 1991–92. Under the new format, the World Bowl championship game was between the first-half league leader and end-of-season league leader (or runner-up, if the first-half champion also had the best overall record). The first-half champion also hosted the World Bowl. This selection process was abandoned after the 1997 World Bowl.
In 1995, league attendances averaged less than 15,000.[20]
The London Monarchs left Wembley for reasons of cost, size and availability,[17][18] and the team's home games were played at Tottenham Hotspur F.C.'s White Hart Lane in the 1995 and 1996 seasons.[21] White Hart Lane's field was only 93 yards long – nowhere near enough to hold a full 120-yard field and endzones – so the WLAF had to grant an exemption from the usual rules.[22][23]
1996 season
The 1996 season was confirmed to go ahead before World Bowl '95, ten months before the 1996 kickoff.[20]
More than 100 players with World League experience played in the American NFL in 1996.[24][25] Meanwhile, the WLAF signed some players who had been more famous in other leagues and sports – in 1996 the London Monarchs signed former NFL star William Perry[26][27] and the Scottish Claymores' kicker was Scotland's national rugby union team captain, Gavin Hastings.[26][28]
1997 season
The London Monarchs moved to Stamford Bridge for the 1997 season.[29]
By the end of the 1997 season, there were growing concerns that WLAF markets, except Germany, were not living up to their potential. Average attendance for the Monarchs was around 10,000 in 1995–97.[30] Radical changes were made to the two British teams and venues for the upcoming 1998 season. Then, at a press conference in San Diego during Super Bowl XXXII weekend, the league announced it too would be changing: the league would be rebranded as NFL Europe.
NFL Europe

NFL Europe logo

Frankfurt's Michael Bishop passing against Scotland, 2001
Starting in 1998, the league was known as NFL Europe. Qualification for the World Bowl championship game also changed. The two teams with the best overall record after 10 games competed in the World Bowl, to be hosted at a pre-determined site. A team could no longer secure a World Bowl berth midway through the season. The change was largely attributed to the play of the eventual 1997 World Bowl champions, the Barcelona Dragons, who secured a World Bowl berth with a 4–1 first-half record and proceeded to rest players and play what some argued was low-intensity football in the second half, finishing with just a 5–5 record and third place overall in the league's standings.
The Scottish Claymores began to divide their schedule between Edinburgh and Glasgow's Hampden Park, having previously only played at Murrayfield. The London Monarchs became the England Monarchs,[31] playing home games in London, Birmingham and Bristol, and switching their colors from blue, gold and red to red, white and black.
In the late 1990s two future NFL star quarterbacks were active in the European league.[3]Kurt Warner played for the Amsterdam Admirals in 1998, with Jake Delhomme as his backup quarterback. Delhomme played at the Frankfurt Galaxy the following season in an unorthodox two-quarterback system with Pat Barnes, with the Galaxy winning the 1999 World Bowl.
The NFL Europe era was beset by instability, but NFL Europe president Oliver Luck was "well past being concerned with the short term"[30] and claimed attendances were less vital to revenues than before 1998.[30] However, with attendances slumping to an average of 5,944 the England Monarchs were shut down after the 1998 season, being replaced by the Berlin Thunder. In 2002, the Barcelona Dragons became an official section of FC Barcelona, adopting the name FC Barcelona Dragons. However, after only one year Barcelona dropped its sponsorship. With the team struggling financially and generating little fan support, the NFL was not interested in keeping the franchise alive, and replaced it with the Cologne Centurions for the 2004 season.

Barcelona Dragons played at FC Barcelona’s reserves mini stadium (pictured in 2003) for one full season before being dropped by the club due to lack of fan interest and financial difficulties
The Scottish Claymores, one of the three teams added to the league in 1995, were also discontinued in 2004, and replaced by the Hamburg Sea Devils, being established for the 2005 season. With this change, five of the six teams in the league's final incarnation were from Germany, with one from the Netherlands, leading some of the league's detractors to refer to it as 'NFL Deutschland' or 'NFL Germany';[32] even speculating that the Admirals were only still in Amsterdam because they were the champions of World Bowl XIII. German teams, unsurprisingly, won all 7 World Bowl Championships between 1998 and 2004.
In 2005 the total attendance at the thirty games was 568,935, and the average attendance of 18,965 was the highest since 1992. On the other hand, TV contracts were canceled as a result of teams moving out of the countries they were based upon, such as the NFLEL deal with satellite TV platform Digital+ in Spain after the demise of the Barcelona Dragons.
In 2006, the league's schedule opened and closed one month earlier than normal because of the 2006 FIFA World Cup, which was played at four of the five German stadiums that hosted NFL Europa teams. Only the LTU Arena in Düsseldorf was not chosen to host World Cup matches, and that stadium hosted the World Bowl that year.
NFL Europa/Cessation of operations

The league's final logo
| Wikinews has related news: NFL Europa ceases after 15 seasons |
On 11 September 2006, NFL Europe officially re-branded itself as NFL Europa to reflect the name of Europe in most European languages, including Dutch and German. "NFL Europe" continued to be used informally in the United States, including for the league's English-language website, nfleurope.com.
On 29 June 2007, NFL officials announced that the NFL Europa league would be disbanded effective immediately.[4][33] The announcement came less than a week after the Hamburg Sea Devils beat the Frankfurt Galaxy 37–28 in World Bowl XV in Frankfurt in front of a crowd of 48,125.
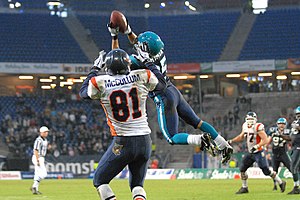
Hamburg Sea Devils's Brent Grimes intercepts against Amsterdam Admirals, May 12, 2007
NFL commissioner Roger Goodell thanked the fans for their support but said it was time to develop a new international strategy, terming the move to fold NFL Europa the "best business decision".[34] The league reportedly was losing about $30 million a season.[34]
ESPN.com's Len Pasquarelli wrote after the league's disbandment in 2007, "Recently, the European league became far less a laboratory for player development and more an exercise in amassing exemptions for NFL summer training camps. [...] there weren't many [NFL] team officials who adhered to the original intent anymore."[3]
Pasquarelli also named J. T. O'Sullivan as the best 2007 NFL Europa player, at a time when O'Sullivan was no better than third-choice quarterback at the Chicago Bears.[3] According to Pasquarelli, NFL Europe and NFL Europa "simply stopped producing players with even scant name recognition", and most coaches would prefer to develop their players themselves.[3]
NFL Europe/NFL Europa was credited with giving training to coaching interns and game officials, and as a useful testing ground for potential NFL rule changes.[3]
Various reasons were put forward for NFL Europe’s collapse and the game’s limited appeal outside North America, with John Williams, director of the Center for the Sociology of Sport at the University of Leicester, citing its “lack of flow”, with play, broken up for “tactical talks and time outs”, being deemed as “too contrived” among fans of more free flowing sports.[35]
The NFL announced plans for a "stronger international focus on regular-season games outside the United States".[36] The NFL International Series began in October 2007 at Wembley, London, and continues today. The Bills Toronto Series started in 2008, but ended in 2013. However, no mainland European country has hosted any NFL games for 20 years, since Germany hosted exhibition games from 1991 to 1994.
Since 2007, the most prominent intra-European competitions have been the BIG6 league, European Football League, EFAF Cup (2002–2013), and EFAF European Championship.
Teams
| North American teams | Active |
|---|---|
Birmingham Fire | 1991–92 |
Montreal Machine | 1991–92 |
New York/New Jersey Knights | 1991–92 |
Ohio Glory | 1992 |
Orlando Thunder | 1991–92 |
Raleigh–Durham Skyhawks | 1991 |
Sacramento Surge | 1991–92 |
San Antonio Riders | 1991–92 |
| European teams | Active |
|---|---|
Amsterdam Admirals | 1995–2007 |
Barcelona Dragons | 1991–2003 |
Berlin Thunder | 1999–2007 |
Cologne Centurions | 2004–2007 |
Frankfurt Galaxy | 1991–2007 |
Hamburg Sea Devils | 2005–2007 |
London/England Monarchs | 1991–1998 |
Rhein Fire | 1995–2007 |
Scottish Claymores | 1995–2004 |
All competing teams, 1991–92:

Skyhawks
All competing teams, 1995–2007:

The league existed in two forms – the 10-team transatlantic league in 1991 and 1992, then the six-team format in Europe only from 1995 to 2007.
The three European teams from 1991 to 1992, Frankfurt, Barcelona and London, were the only original teams to continue playing when the league was resurrected in 1995. By 2007, only the Frankfurt Galaxy remained of the original WLAF teams.
Experimental rules
In this era, NFL overtime was a single quarter of sudden death, with the first team to score being the winner. A regular-season game would end in a tie if no team scored in 15 minutes. (Postseason games lasted indefinitely until one team scored.)
In WLAF/NFL Europe, however, overtime period lasted for only 10 minutes, with a rule that each team must have the opportunity of possession at least once. Therefore, if the first team to possess the ball scored, the other would get a chance to either equalize or win the game. The winner was the team with the highest score after both teams had had possession. Sudden death applied if the score was even after each team had had one possession. If still tied after 10 minutes, the game ended as a tie. Only two games ever remained tied after overtime in WLAF/NFL Europe history: London Monarchs vs. Birmingham Fire in 1992, and Berlin Thunder at Hamburg Sea Devils in 2006. The score of both games was 17–17.[37]
Since 2010, the NFL has applied a similar set of overtime rules and several further tweaks were made in 2012.[38] Starting with the 2017 season, the 15-minute overtime period was shortened to 10 minutes after gaining approval from the NFL team owners.[39]
With association football (or soccer) being the traditionally popular sport in Europe and American football being a relative newcomer, the rules were changed slightly to encourage a greater element of kicking which was intended to make the game more enjoyable for soccer and rugby fans. The league did this by awarding four points to field goals of more than 50 yards, as opposed to three points in the NFL. This had the interesting side-effect that a touchdown and point-after lead (seven points) could be equaled by one regular field goal (three points) along with a long field goal (four points).

An NFL-style team entrance at a 2007 NFL Europe game
In the 1995 season, in every team's home games, at least seven "local" players had to be playing or on the bench (three locals in away games).[40] In the years before 2006, each team had to field at least one player of non-American extraction, called a "national" player, on every down of every other series. In 2006 the rule was changed to every series. In addition to European players a number of Mexican and Japanese players played as national players. Up until the 2004 season, kicked conversion attempts and short field goals were attempted by national players. Since there are few European players who have had the chance to compete at a level comparable to U.S. college football and the NFL, many, if not most, of the European players ended up as kickers.
Notable national players included Scott McCready, an English wide receiver who played some preseason games for the New England Patriots; the Claymores' wide receiver Scott Couper, who played a pre-season game for the Chicago Bears; Constantin Ritzmann, a German defensive end who had played for the University of Tennessee; and Rob Hart, an English rugby player who became a placekicker[41] and kicked barefoot. Lavar Ball who played for the London Monarchs who is now the owner and CEO of Big Baller Brand and the father of Lonzo Ball, LiAngelo Ball, and LaMelo Ball.
Running back Victor Ebubedike played for the Monarchs from 1991 to 1998, becoming the first Briton to score in the World League in 1991.[42] The Monarchs' first kicker was former Norwich City centre-half Phil Alexander. Ex-Tottenham Hotspur striker Clive Allen also kicked for the Monarchs,[43][44] while fellow footballers Jesús Angoy, Manfred Burgsmüller and Silvio Diliberto kicked for the Barcelona Dragons, Rhein Fire and Amsterdam Admirals respectively.[45]
Uniforms
The 1995 WLAF relaunch featured uniforms with a significantly different look from what is traditionally associated with American football. Instead of the standard large numbers centered on the front of the jersey, the team logos took precedence, with a smaller number over the right collarbone area.[46] The Monarchs reverted to the traditional look in 1997 and the rest of the league followed a year later.[citation needed] The 1998 uniform designs were "thought to appeal to european tastes".[30]
Television coverage
1991–92
USA Network carried most of the WLAF games on Saturday and Monday nights in the 1991 season and again on Saturday nights for the 1992 season. Diana Nyad served as the network's host for pregame and halftime. The network premiered the helmet cam to TV audiences.
ABC Sports broadcast some games in both seasons, mostly on Sunday afternoons. ABC showed the 1991 World Bowl, while USA carried the game in 1992.
The reported cost of the contracts varied – the L.A. Times said that ABC had paid $28m for two years, and USA $25m.[6] For the 1992 season the WLAF charged each network less for broadcasting rights; The New York Times reported that ABC's annual fee went down from $12m to $3m, and USA's from $14m to $10m.[1] The ABC coverage's average ratings fell from 1991 to 1992, from around 2.1 to 1.7, and USA's from 1.2 to 1.1.[1][6] Both networks asked the WLAF to expand into two major U.S. markets for 1993.[1]
1991 season coverage in Europe was mostly on satellite. Eurosport showed games on delay[10] and Super Channel showed the 1991 World Bowl.[10]Channel 4 showed half-hour highlights of Monarchs games on Saturday mornings.[10]The Philadelphia Inquirer's Larry Eichel wrote, "The only way a Monarchs fan could watch the team's first-round playoff game from the Meadowlands was to go to Wembley to see it on closed circuit."[10]
Coverage in Canada was led by RDS, a French-language broadcaster, which focused on Montreal Machine games.
1995–2007
Although the league no longer had any U.S. teams, American television coverage continued until the end. Fox Sports had become a co-owner of the league,[18][47] and from 1995 to 1998 the primary TV carrier was FX, which carried two games a week, on Saturday and Sunday. From 1995 to 2005, Fox showed the World Bowl and two or three regular season games annually. From 1999 to 2004, Fox Sports Net showed a "game of the week" on Saturday, with DirecTV viewers receiving additional live games on channels that normally carried NFL Sunday Ticket. In 2005, NFL Network began showing all regular season games, either live or on tape delay, and this continued until the league folded. NFL Network also showed the 2006 and 2007 title games.
The revived WLAF's UK coverage was mainly on Sky Sports, with coverage also on Channel 4,[20][47]STV,[20][47] and Carlton.[20] Eight European continental broadcasters also showed coverage,[47] including Germany's Vox and DSF.[20]
Announcers who called NFL Europe games over the years included Curt Menefee, Nick Halling, Ari Wolfe, Troy Aikman, Daryl "Moose" Johnston, Michael Reghi, and Brentson Buckner.
EuroPass, an offshoot of FieldPass, broadcast Internet video of games, free of charge, in the league's later years.
Stadiums
North America (1991–1992)
| Team | Stadium, city | Years used | Capacity |
|---|---|---|---|
Birmingham Fire | Legion Field, Birmingham, Alabama | 1991–1992 | 83,091 |
Montreal Machine | Olympic Stadium, Montreal, Quebec | 1991–1992 | 65,255 |
New York/New Jersey Knights | Giants Stadium, East Rutherford, New Jersey | 1991–1992 | 76,891 |
Ohio Glory | Ohio Stadium, Columbus, Ohio | 1992 | 91,470 |
Orlando Thunder | Citrus Bowl, Orlando, Florida | 1991–1992 | 65,438 |
Raleigh–Durham Skyhawks | Carter–Finley Stadium, Raleigh, North Carolina | 1991 | 47,000 |
Sacramento Surge | Charles C. Hughes Stadium, Sacramento, California | 1991 | 20,311 |
Hornet Stadium, Sacramento | 1992 | 26,000 | |
San Antonio Riders | Alamo Stadium, San Antonio, Texas | 1991 | 23,000 |
Bobcat Stadium, San Marcos, Texas | 1992 | 16,000 approx. |
Europe (1991–1992, 1995–2007)
| Team | Stadium, city | Years used | Capacity |
|---|---|---|---|
Amsterdam Admirals | Olympisch Stadion, Amsterdam, Netherlands | 1995–1996 2000 (one game) 2007 (one game) | 31,600 |
De Meer Stadion, Amsterdam | 1995 (two games) | 19,000 | |
Amsterdam ArenA, Amsterdam | 1997–2007 | 51,859 | |
Barcelona Dragons | Estadi Olímpic Lluís Companys, Barcelona, Spain | 1991–1992, 1995–2002 | 56,000 |
Mini Estadi, Barcelona | 2002 (one game) 2003 | 15,276 | |
Berlin Thunder | F. L. Jahn Sportpark, Berlin, Germany | 1999–2002 2006 (one game) | 19,500 |
Olympiastadion, Berlin | 2003–2007 | 76,000 | |
Cologne Centurions | RheinEnergieStadion, Cologne, Germany | 2004–2007 | 50,374 |
Frankfurt Galaxy | Waldstadion/Commerzbank-Arena, Frankfurt, Germany | 1991–1992, 1995–2007 | 52,000 |
Hamburg Sea Devils | AOL Arena, Hamburg, Germany | 2005–2007 | 55,989 |
London/England Monarchs | Wembley Stadium, London, England | 1991–1992 | 80,000 |
White Hart Lane, London | 1995–1996 | 36,240 | |
Stamford Bridge, London | 1996 (one game) 1997 | 42,449 | |
Crystal Palace National Sports Centre, London | 1998 | 15,500 | |
Alexander Stadium, Birmingham, England | 1998 (one game) | 7,600 | |
Ashton Gate, Bristol, England | 1998 (one game) | 21,500 | |
Rhein Fire | Rheinstadion, Düsseldorf, Germany | 1995–2002 | 55,900 |
Arena AufSchalke, Gelsenkirchen, Germany | 2003–2004 | 61,524 | |
LTU Arena, Düsseldorf | 2005–2007 | 51,500 | |
Scottish Claymores | Murrayfield Stadium, Edinburgh, Scotland | 1995–1998 1999–2000 (part-time) 2002 (one game) | 67,500 |
Hampden Park, Glasgow, Scotland | 1998 (one game) 1999–2000 (part-time) 2001–2004 | 52,500 |
Attendance
| Year | Games | Total | Average |
|---|---|---|---|
WLAF[9] | |||
| 1991 | 50 | 1,268,066 | 25,361 |
| 1992 | 50 | 1,210,817 | 24,216 |
| 1993 | – | – | – |
| 1994 | – | – | – |
| 1995 | 30 | 436,853 | 14,562 |
| 1996 | 30 | 516,171 | 17,206 |
| 1997 | 30 | 546,433 | 18,214 |
NFL Europe[9] | |||
| 1998 | 30 | 499,034 | 16,634 |
| 1999 | 30 | 544,844 | 18,161 |
| 2000 | 30 | 540,438 | 18,015 |
| 2001 | 30 | 557,038 | 18,568 |
| 2002 | 30 | 541,546 | 18,052 |
| 2003 | 30 | 494,448 | 16,482 |
| 2004 | 30 | 477,741 | 15,925 |
| 2005 | 30 | 568,935 | 18,965 |
| 2006 | 30 | 529,988 | 17,666 |
NFL Europa[9] | |||
| 2007 | 30 | 600,600 | 20,020 |
| 490 | 9,332,952 | 19,047 | |
| Team | Year 2005 | Year 2006 | Year 2007 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Frankfurt Galaxy | 29,377 | 28,118 | 33,043 |
| Rhein Fire | 22,532 | 22,020 | 24,473 |
| Hamburg Sea Devils | 17,920 | 15,082 | 20,874 |
| Berlin Thunder | 16,848 | 13,819 | 15,710 |
| Cologne Centurions | 14,238 | 13,538 | 14,352 |
| Amsterdam Admirals | 12,877 | 13,421 | 11,668 |
| Average | 18,966 | 17,666 | 20,020 |
Presidents
Tex Schramm 18 April 1989 – 10 October 1990
Mike Lynn 10 October 1990 – 30 July 1991- Joe Bailey (COO) 1992
- Marc Lory 12 September 1994 – 1995
Oliver Luck 13 July 1995 – 1999- Bill Peterson 8 November 1999 – 2000
- Jim Connelly 27 March 2001 – 2007
Notes and references
^ abcdefg SMITH, TIMOTHY W. (7 May 1992). "World League vs. N.F.L., In a Board Room, That Is". The New York Times. Retrieved 27 May 2014..mw-parser-output cite.citationfont-style:inherit.mw-parser-output qquotes:"""""""'""'".mw-parser-output code.cs1-codecolor:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registrationcolor:#555.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration spanborder-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-errordisplay:none;font-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-errorfont-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-formatfont-size:95%.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-leftpadding-left:0.2em.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-rightpadding-right:0.2em
^ ab The abbreviation "World League" was often used in field signs/ads/merchandise/books in 1991 and 1992, but "World League of American Football" was often used on TV and posters in 1995, 1996 and 1997
^ abcdefghi Pasquarelli, Len (29 June 2007). "NFL Europa failed to produce players, profits". ESPN.com. Retrieved 24 May 2014.
^ ab "NFL Europa to cease operations". NFL.com. 29 June 2007. Archived from the original on 3 July 2007. Retrieved 29 June 2007.
^ abc Mark L. Ford and Massimo Foglio. "THE FIRST "NFL EUROPE"" (PDF). THE COFFIN CORNER: Vol. 27, No. 6 (2005). Pro Football Researchers. Retrieved 24 May 2014.
^ abcde Dufresne, Chris (21 May 1991). "Europe Takes to WLAF, but Will It Catch On Here?". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved 26 May 2014.
^ abc Stellino, Vito (7 April 1991). "WLAF attendance surpassing early hopes in Europe and Canada". Baltimore Sun. Retrieved 26 May 2014.
^ "Chicago Bears install helmet cameras to study quarterback play at rookie camp". Sports Illustrated. 2013-05-11. Retrieved 2013-05-11.The World League of American Football used similar cameras as part of its game broadcasts in the 1990s
^ abcd "League History". WLAF. Retrieved 26 May 2014.
^ abcde Eichel, Larry (8 June 1991). "In Europe, WLAF's Game Was More Than Football". The Philadelphia Inquirer. Retrieved 26 May 2014.
^ ab "WLAF History: 1991". WLAF. Retrieved 26 May 2014.
^ Dufresne, Chris (21 May 1991). "Europe Takes to WLAF, but Will It Catch On Here? [Page 2]". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved 26 May 2014.
^ Greene, Jerry (5 June 1992). "Bailey: World League 'Will Be Back'". Retrieved 27 May 2014.
^ ab "NFL owners disband World League". The Independent. 18 September 1992. Retrieved 26 May 2014.
^ ab Tench, Matt (19 September 1992). "End of the World League (1992)". The Independent. Retrieved 27 May 2014.
^ "Sporting Digest: American Football". The Independent. 22 July 1994. Retrieved 29 May 2014.
^ ab Elliott, Keith (26 March 1993). "Plan for smaller World League". The Independent. Retrieved 27 May 2014.
^ abc O'Hagan, Simon (26 March 1995). "Monarchs seek to rule the world". The Independent. Retrieved 27 May 2014.
^ Carter, Meg (15 January 1995). "Media: Sports sponsors play for a bigger stake in the game". The Independent. Retrieved 29 May 2014.
^ abcdef Halling, Nick (19 June 1995). "WLAF to build on a fitting finale". The Independent. Retrieved 29 May 2014.
^ "Monarchs to play at Spurs". 24 August 1994. Retrieved 27 May 2014.
^ Cassidy, Alex (2015). American Football's Forgotten Kings: The Rise and Fall of the London Monarchs. Pitch Publishing. p. 191. ISBN 1785311085. Retrieved 26 August 2016.
^ Rushin, Steve (September 25, 2013). "Up next for the NFL in UK ... How about the London Fletchers?". Sports Illustrated. Retrieved 26 August 2016.
^ "WORLD CLASS: OTHER WORLD LEAGUERS MAKING A LIVING IN THE NFL". The Independent. 4 November 1996. Retrieved 29 May 2014.
^ Halling, Nick (24 June 1997). "World League set fair for future". The Independent. Retrieved 27 May 2014.
^ ab "World League's big chance". The Independent. 11 April 1996. Retrieved 27 May 2014.
^ Tench, Matt (11 April 1996). "What's in The Fridge?". The Independent. Retrieved 29 May 2014.
^ Halling, Nick (10 April 1996). "Hastings ready for his big kick-off". The Independent. Retrieved 28 May 2014.
^ "London Monarchs to play World League matches at Stamford Bridge". The Independent. 13 December 1996. Retrieved 27 May 2014.
^ abcd Halling, Nick (3 April 1998). "Monarchs look to wider market as World League adopts new identity". The Independent. Retrieved 26 May 2014.
^ "Sporting Digest: American football (Monarchs name change)". The Independent. 8 October 1997. Retrieved 28 May 2014.
^ Referred to as "NFL Germany" in Der Spiegel: “Kirmes, Hot Dogs und Eiertanz”. 02.04.2004.
^ "NFL Europa closes" (Press release). National Football League. 3 August 2007. Retrieved 26 July 2012.
^ ab Starcevic, Nesha (29 June 2007). "NFL Europa Folds After 16 Years". Washington Post. Retrieved 25 May 2014.
^ "America Is Exporting a Rotten Product to Great Britain". Time. October 24, 2013.
^ Associated Press. "NFL folds Europe league, to focus on regular-season games abroad". ESPN. Retrieved 25 August 2014.
^ Europass: Unusual tie is Thunder's gain NFL.com. Accessed 29 June 2007.
^ "NFL overtime rules". NFL.com. National Football League. Retrieved 23 June 2015.
^ [1]
^ O'Hagan, Simon (21 May 1995). "Monarchs in a grid-locked state". The Independent. Retrieved 27 May 2014.
^ McGROARTY, FRANK (18 April 1999). "Our Brave Hart". Sunday Mirror. Retrieved 28 May 2014.
^ Halling, Nick (17 April 1995). "Ebubedike excels for the Monarchs". The Independent. Retrieved 28 May 2014.
^ "Allen tackles gridiron goal". The Independent. 7 February 1997. Retrieved 28 May 2014.
^ Halling, Nick (12 May 1997). "Allen puts Monarchs back on target". The Independent. Retrieved 28 May 2014.
^ Bandini, Paolo (5 August 2009). "Which football team has the most sponsors' logos on their kit?". theguardian.com. Guardian Media Group. Retrieved 26 September 2013.
^ World League of American Football/National Football League Europe Uniforms
^ abcd Halling, Nick (13 April 1996). "Three-pronged attack in quest for credibility". The Independent. Retrieved 28 May 2014.
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to NFL Europe. |
- NFL International Series
- World Bowl
- European Football League
- Eurobowl
- German Bowl
- List of leagues of American football
- Sports league attendances
- Super Bowl
External links
- Historical site index for WLAF and NFL Europe/Europa
- WLAF and NFL Europe/Europa history at The Football Database
- MacGille's World League of American Football website: http://www.worldleagueofamericanfootball.com
- Natures Images Photography – Photos of the Frankfurt Galaxy home games: http://www.frankfurt-galaxy.eu
- Lee's Autograph Hall of Fame – Photos of a San Antonio Riders home game with team history: http://lee.n8d.com/?p=1336
