Tropic of Capricorn
Coordinates: 23°26′12.5″S 0°0′0″W / 23.436806°S -0.00000°E / -23.436806; -0.00000 (Prime Meridian)

World map showing the Tropic of Capricorn

Monument marking the Tropic of Capricorn just north of Antofagasta, Chile

Sundial on the Tropic of Capricorn, Jujuy Province, Argentina

Sign marking the tropic in Maringá, Brazil

Tropic of Capricorn in 1794 Dunn Map of the World

Tropic of Capricorn on the Diamantina Developmental Road, Amaroo, Queensland, Australia

Longreach, Queensland, Australia
The Tropic of Capricorn (or the Southern Tropic) is the circle of latitude that contains the subsolar point on the December (or southern) solstice. It is thus the southernmost latitude where the Sun can be directly overhead. Its northern equivalent is the Tropic of Cancer.
The Tropic of Capricorn is one of the five major circles of latitude that mark maps of Earth. As of 30 March 2019, its latitude is 23°26′12.4″ (or 23.43679°)[1] south of the Equator, but it is very gradually moving northward, currently at the rate of 0.47 arcseconds, or 15 metres, per year.
Contents
1 Name
2 Geography and environment
2.1 Africa
2.2 Australia
2.3 South America
3 Around the world
4 Places located along the Tropic of Capricorn
5 List of countries entirely south of the Tropic of Capricorn
6 Length
7 Note
8 References
9 External links
10 See also
Name
When this line of latitude was named in the last centuries BC[citation needed], the Sun was in the constellation Capricornus (Latin for goat horn) at the December solstice, the time each year that the Sun reaches its zenith at this latitude. Due to the precession of the equinoxes, this is no longer the case; today the Sun is in Sagittarius at the December solstice. The word "tropic" itself comes from the Greek "trope (τροπή)", meaning to turn or change direction, referring to the fact that the Sun appears to "turn back" at the solstices.
Geography and environment
The Tropic of Capricorn is the dividing line between the Southern Temperate Zone to the south and the tropics to the north. The Northern Hemisphere equivalent of the Tropic of Capricorn is the Tropic of Cancer.
The Tropic of Capricorn's position is not fixed, but constantly changes because of a slight wobble in the Earth's longitudinal alignment relative to its orbit around the Sun. Earth's axial tilt varies over a 41,000 year period from 22.1 to 24.5 degrees and currently resides at about 23.4 degrees. This wobble means that the Tropic of Capricorn is currently drifting northward at a rate of almost half an arcsecond (0.468″) of latitude, or 15 metres, per year (it was at exactly 23° 27′S in 1917 and will be at 23° 26'S in 2045). See under circles of latitude for information.
There are approximately 13 hours, 35 minutes of daylight during the summer solstice. During the winter solstice, there are 10 hours, 41 minutes of daylight.
Africa
In southern Africa, where rainfall is reliable, farming is possible, though yields are low even with fertilisers.
Australia
In Australia, areas on the Tropic have some of the most variable rainfall in the world[2] and thus even the wetter areas cannot be generally farmed, since irrigation sources invariably dry up in drought years.[citation needed]
South America
In South America, whilst in the continental cratons soils are almost as old as in Australia and Southern Africa, the presence of the geologically young and evolving Andes means that this region is on the western side of the subtropical anticyclones and thus receives warm and humid air from the Atlantic Ocean. As a result, areas in Brazil adjacent to the Tropic are extremely important agricultural regions, producing large quantities of crops such as sugarcane, and the natural rainforest vegetation has been almost entirely cleared, except for a few remaining patches of Atlantic Forest. Further south in Argentina, the temperate grasslands of the Pampas region is one of the most productive agricultural regions in the world, producing of wheat, soybeans, maize, and beef, making the country one of the largest worldwide agricultural exporters, similar to the role played by the Prairies region in Canada.
West of the Andes, however, the Humboldt Current makes conditions extremely arid, creating the Atacama Desert, one of the driest in the world, so that no glaciers exist between Volcán Sajama at 18˚30'S and Cerro Tres Cruces at 27˚S.[3]Vegetation here is almost non-existent, though on the eastern slopes of the Andes rainfall is adequate for rainfed agriculture.
Around the world
Starting at the Prime Meridian and heading eastwards, the Tropic of Capricorn passes through 10 countries:
Co-ordinates Country, territory or sea Notes
23°26′S 0°0′E / 23.433°S 0.000°E / -23.433; 0.000 (Prime Meridian)Atlantic Ocean
23°26′S 14°27′E / 23.433°S 14.450°E / -23.433; 14.450 (Namibia) Namibia
Namibia
Erongo, Khomas, Hardap, Khomas (again), and Omaheke regions
23°26′S 20°0′E / 23.433°S 20.000°E / -23.433; 20.000 (Botswana) Botswana
Botswana
Kgalagadi, Kweneng and Central districts
23°26′S 27°18′E / 23.433°S 27.300°E / -23.433; 27.300 (South Africa) South Africa
South Africa
Limpopo Province
23°26′S 31°33′E / 23.433°S 31.550°E / -23.433; 31.550 (Mozambique) Mozambique
Mozambique
Gaza and Inhambane provinces
23°26′S 35°26′E / 23.433°S 35.433°E / -23.433; 35.433 (Indian Ocean)Indian Ocean
Mozambique Channel
23°26′S 43°45′E / 23.433°S 43.750°E / -23.433; 43.750 (Madagascar) Madagascar
Madagascar
Toliara and Fianarantsoa provinces
23°26′S 47°39′E / 23.433°S 47.650°E / -23.433; 47.650 (Indian Ocean)Indian Ocean
23°26′S 113°47′E / 23.433°S 113.783°E / -23.433; 113.783 (Australia) Australia
Australia
Western Australia, Northern Territory and Queensland
23°26′S 151°3′E / 23.433°S 151.050°E / -23.433; 151.050 (Coral Sea)
Coral SeaPassing just south of Cato Reef in  Australia's Coral Sea Islands Territory
Australia's Coral Sea Islands Territory
23°26′S 166°46′E / 23.433°S 166.767°E / -23.433; 166.767 (Pacific Ocean)Pacific Ocean Passing just north of the Minerva Reefs (  Tonga), and just south of Tubuai (
Tonga), and just south of Tubuai ( French Polynesia)
French Polynesia)
23°26′S 70°36′W / 23.433°S 70.600°W / -23.433; -70.600 (Chile) Chile
Chile
Antofagasta Region
23°26′S 67°07′W / 23.433°S 67.117°W / -23.433; -67.117 (Argentina) Argentina
Argentina
Jujuy, Salta, Jujuy (again), Salta (again) and Formosa provinces
23°26′S 61°23′W / 23.433°S 61.383°W / -23.433; -61.383 (Paraguay) Paraguay
Paraguay
Boquerón, Presidente Hayes, Concepción, San Pedro and Amambay departments
23°26′S 55°38′W / 23.433°S 55.633°W / -23.433; -55.633 (Brazil) Brazil
Brazil
Mato Grosso do Sul, Paraná, and São Paulo states
23°26′S 45°2′W / 23.433°S 45.033°W / -23.433; -45.033 (Atlantic Ocean)Atlantic Ocean
Places located along the Tropic of Capricorn
The following cities and landmarks are either located near the Tropic of Capricorn, or the tropic passes through them.
|
|
|

Atsimo-Andrefana Region, Madagascar
The Tropic of Capricorn marked in Jujuy Province in northern Argentina
Monument marking the Tropic of Capricorn as it passes through Botswana

A sign marking the Tropic of Capricorn as it passes through Namibia
Roadway plaque marking the Tropic of Capricorn in the city of Santana do Parnaíba, Brazil, at the correct latitude for year 1917.
Marker for the tropic in Maringá, Paraná, Brazil, July 2012

Roadside monument marking Tropic of Capricorn in Rockhampton, Queensland, Australia, 28 January 2005

Monument marking Tropic of Capricorn in Rockhampton, Queensland, Australia, 1970

Road sign marking Tropic of Capricorn in Western Australia, Australia, 26 August 2008

Monument marking the Tropic of Capricorn just north of Alice Springs, Northern Territory, Australia
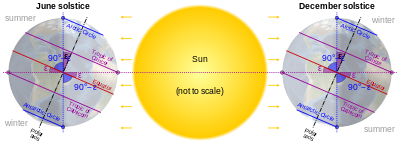
Relationship between Earth's axial tilt (ε) to the tropical and polar circles
List of countries entirely south of the Tropic of Capricorn
As the major portion of earth's land is located in the Northern Hemisphere there are only four countries entirely south of the Tropic of Capricorn (there are 74 countries entirely north of the Tropic of Cancer):
- Lesotho
New Zealand[a]
Eswatini (formerly Swaziland)- Uruguay
Length
Length of the Tropic on 11 June 2015, at 23°26′14″S is 36,788 kilometres (22,859 mi).[4]
Note
^ The Cook islands, Tokelau and Niue, which are part of the Realm of New Zealand lie above the Tropic of Capricorn.
References
^ obliquity of the ecliptic (Eps Mean)
^ Geographical Patterning of Interannual Rainfall Variability in the Tropics and Near Tropics
^ Exposure dating of Late Glacial and pre-LGM moraines in the Cordon de Doña Rosa, Northern/Central Chile (~31°S)
^ RhumbSolve online rhumb line calculator.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Tropic of Capricorn. |
| Look up tropic of capricorn in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
- Temporal Epoch Calculations
Useful constants" See: Obliquity of the ecliptic- Montana State University: Milankovitch Cycles & Glaciation
See also
Circle of latitude- Arctic Circle
- Tropic of Cancer
- Equator
- 23rd parallel south
- 24th parallel south
- Antarctic Circle
- Axial tilt
- Milankovitch cycles
- Capricornus











