1991 Indian general election
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 545 seats in the Lok Sabha 273 seats were needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
  | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
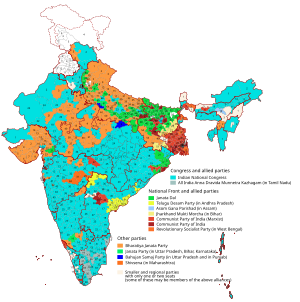
General elections were held in India in 1991 to elect the members of the 10th Lok Sabha. The result of the election was that no party could get a majority, so a minority government (Indian National Congress with the help of left parties) was formed, resulting in a stable government for the next 5 years, under the new Prime Minister P.V. Narasimha Rao.
Contents
1 Background
1.1 Mandal-Mandir Issue
1.2 Rajiv Gandhi Assassination
1.3 Jammu & Kashmir, Punjab
2 Results
3 Premiership
4 See also
5 References
Background
The 1991 Indian general election were held because the previous Lok Sabha had been dissolved just 16 months after government formation. The elections were held in a polarised environment and are also referred to as the 'Mandal-Mandir' elections after the two most important poll issues, the Mandal Commission fallout and the Ram Janmabhoomi-Babri Masjid issue.
Mandal-Mandir Issue
While the Mandal Commission report implemented by the VP Singh government gave 27 per cent reservation to the Other Backward Castes (OBCs) in government jobs, it led to widespread violence and protests across the country by the forward castes. Mandir represented the hallmark of this election, where there was a debate over the disputed Babri Masjid structure at Ayodhya, which the Bharatiya Janata Party was using as its major election manifesto.
The Mandir issue led to numerous riots in many parts of the country and the electorate was polarised on caste and religious lines. With the National Front falling apart, the Congress managed to make the most of the polarisation, by getting the most seats and forming a minority government.
Rajiv Gandhi Assassination
A day after the first round of polling took place on 20 May, former prime minister Rajiv Gandhi was assassinated while campaigning for Margatham Chandrasekar at Sriperembudur. The remaining election days were postponed until mid-June and voting finally took place on 12 and 15 June. Voting was the lowest ever in parliamentary elections with just 53 per cent of the electorate exercising their right to vote.
Since the assassination took place after first phase of polling in 211 of 534 constituencies and the balance constituencies went to polls after the assassination, the 1991 results varied greatly between phases. The congress party did poorly in the pre-assassination constituencies and swept the post-assassination constituencies. The end result was a minority Congress-led government led by P. V. Narasimha Rao, a politician who had announced his retirement from politics.
Jammu & Kashmir, Punjab
No elections were held in Jammu and Kashmir and Punjab, a total of 19 Lok Sabha seats.[2]
India |
|---|
 |
This article is part of a series on the politics and government of India |
Constitution and law
———————
|
Government of India
———————
———————
Judiciary:
|
Elections Election commission:
———————
National coalitions:
|
Federalism
———————
Legislatures:
———————
Urban bodies:
|
|
Results
Lok Sabha elections 1991 .mw-parser-output .noboldfont-weight:normal Electoral participation: 55,71%. No elections held in Jammu and Kashmir. In Punjab elections were held in 1992. | % | Won (total 545) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Janata Dal | JD | 11.77 | 69 |
Communist Party of India (Marxist) | CPI(M) | 6.14 | 35 |
Communist Party of India | CPI | 2.48 | 14 |
Indian Congress (Socialist) | IC(S) | 0.35 | 1 |
Indian National Congress | INC | 35.66 | 244 |
Bharatiya Janata Party | BJP | 20.04 | 120 |
Janata Dal (Secular) | JD | 0.0 | 0 |
Janata Party | JP | 3.34 | 5 |
Lok Dal | LD | 0.06 | 0 |
All India Anna Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam | AIADMK | 1.61 | 11 |
All India Forward Bloc | AIFB | 0.41 | 3 |
Asom Gana Parishad | AGP | 0.54 | 1 |
Bahujan Samaj Party | BSP | 1.8 | 3 |
Indian Union Muslim League | MUL | 0.3 | 2 |
Jammu & Kashmir Panthers Party | JPP | 0.0 | 0 |
Jharkhand Mukti Morcha | JMM | 0.53 | 6 |
Kerala Congress (Mani) | KC(M) | 0.14 | 1 |
Manipur Peoples Party | MPP | 0.06 | 1 |
Nagaland Peoples Council | NPC | 0.12 | 1 |
Revolutionary Socialist Party | RSP | 0.63 | 5 |
Shiv Sena | SS | 0.79 | 4 |
Sikkim Sangram Parishad | SSP | 0.04 | 1 |
Telugu Desam Party | TDP | 2.96 | 13 |
United Minorities Front, Assam | UMFA | 0.07 | 1 |
All India Majlis-e-Ittehadul Muslimen | AIMIM | 0.16 | 1 |
Autonomous State Demand Committee | ASDC | 0.5 | 1 |
Haryana Vikas Party | HVP | 0.12 | 1 |
Janata Dal (Gujarat) | JD(G) | 0.5 | 1 |
| Independents | - | 4.01 | 1 |
| Nominated Anglo-Indians | - | - | 2 |
Premiership
The 10th Lok Sabha constituted. Congress was in a position to form government. The persons, mentioned in media, as probable Prime Minister, were:[3]
Former Home, and Foreign minister P. V. Narasimha Rao.[3]
Chief Minister of Maharashtra Sharad Pawar.[3]
Former Chief Minister of Madhya Pradesh Arjun Singh.[3]
Former Finance, and Foreign minister N. D. Tiwari.[4]
Congress eventually formed the government under the Prime Ministership of P. V. Narasimha Rao. After Lal Bahadur Shastri, Rao was the second Congress Prime Minister from outside the Nehru-Gandhi family and the first Congress Prime Minister to head a minority government that completed full 5 year term.[5] He introduced Economic reforms in India.
See also
- Election Commission of India
- Indian general election, 1989
References
^ http://www.ipu.org/parline-e/reports/arc/2145_91.htm
^ "ONCE UPON A POLL: Tenth Lok Sabha Elections (1991)". The Indian Express. 2014-03-21. Retrieved 2018-04-07..mw-parser-output cite.citationfont-style:inherit.mw-parser-output .citation qquotes:"""""""'""'".mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registrationcolor:#555.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration spanborder-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output code.cs1-codecolor:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-errordisplay:none;font-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-errorfont-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-maintdisplay:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-formatfont-size:95%.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-leftpadding-left:0.2em.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-rightpadding-right:0.2em
^ abcd "Rao, Pawar in race for CPP-I leadership". The Indian Express. Madras. June 18, 1991. Retrieved 2016-03-12.
^ "A meeting of hearts". The Indian Express. Madras. June 15, 1991. Retrieved 2016-03-12.
^ "How Shukla saved Rao govt in 1992 - Times of India". The Times of India. Retrieved 19 April 2018.



